
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Answer ASAP would be appreciated
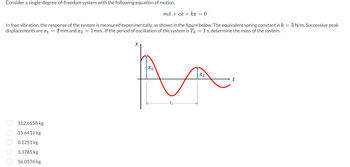
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a single-degree-of-freedom system with the following equation of motion.
In free vibration, the response of the system is measured experimentally, as shown in the figure below. The equivalent spring constant is k = 5 N/m. Successive peak
displacements are *₁ 2 mm and 2 = 1 mm. If the period of oscillation of the system is Ta = 1 s, determine the mass of the system.
=
0 0 0 0 0
112.6158 kg
15.6411 kg
0.1251 kg
3.3785 kg
56.0576 kg
mx + cx + kx = 0
X
X1
x2
A
Td
t
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- We have a rectangular piece. We wish to manufacture a parallel slot along thepiece in a vertical milling machine and 50 cm from the edge. The width of the slot is 40 mm. TheDepth of the slot is 25 mm. For this, several rough cutting steps and aFine cut with a depth of 0.20 mm. The depth for each of the steps ofrough cut is limited to 1.75 mmAditional information:What is the number of blades used for the rough cutting steps?What is the number of blades used for the fine cutting step?arrow_forward04 05 a Explain the reasons for the following: 1- The pure aluminum and the copper are generally rated as easy to machine 2- In ultrasonic machining, the stress produced by the impact of abrasive particles on the workpiece surface is high. 3- In rolling process, the coefficient of friction must be sufficient. 4- Difference in solidification between casting and welding processes. 5- Why is it desirable to use energy sources for welding that have high heat densities? 6- Why there might be a change in the density of a forged product as compared to that of the cast blank. D. A cylindrical workpart with D=2.5 in and h=2.5 in is upset forged in an open die to a height = 1.5 in. Coefficient of friction at the die -work interface = 0.10 The work material has a flow curve defined by: K= 40,000 lb/in' and n-0.15. Determine the instantaneous force in the operation (a) just as the yield point is reached (yield at strain = 0.002), (b) at height = 2.3 in. (c) h= 1.9 in, and (d) h = 1.5 in. a List…arrow_forwardI asked for problems 6 and 7 to be answered, but I did not get a properly structured answered as the example shows on problem number 1. Here is the link to the questions I already had answered, could you please rewrite the answer so its properly answered as the example shows (Problem 1)? https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/it-vivch-print-reading-for-industry-228-class-date-name-review-activity-112-for-each-local-note-or-c/cadc3f7b-2c2f-4471-842b-5a84bf505857arrow_forward
- 1. Define manufacturing processes, design engineer, industrial engineer and materials engineer? 2. Name and explain a protess to make cylinder shaft? 3. Discus at least three factors which will effect tool life? 4. Define finishing and roughing process? 5. Explain the negative effect of heat generated from machining process? 6. One limitation of sand casting is bad surface finish. Yes or No? Why? 7. What is permeability in casting process? 8. What are the major defects in casting process? 9. Which type of casting process should be use for high melting point casting, such as cast iron and why? 10. Casting problem A certain mold has a sprue whose length is 20 cm and the cross-sectional area at the base of the sprue is 2.5 cm?. The sprue feeds a horizontal runner leading into a mold cavity whose volume is 1560 cm³. Determine: (a) velocity of the molten metal at the base of the sprue, (b) volume rate of flow, and (c) time to fill the mold (in second). mfg m1 Spring 2020 999.pptxarrow_forward23. Mastery Objective 23: Perform shearing on triangles and parallelograms, and explain what measurements are preserved or change. (a) Shear the following triangle. Explain what measurements change and what stays the same, justifying your claims. D. (b) Shear the following parallelogram. Explain what measurements change and what stays the same, justifying your claims.arrow_forwardCan you please explain how to find the velocity using the methods described? And also why it's done that way? This is from Introduction to robotics mecahnics and controls. Please help ;( !arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY