
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
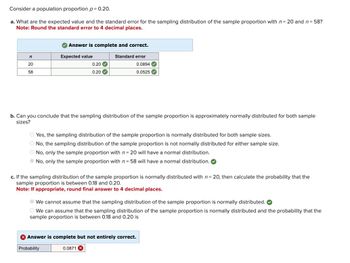
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a population proportion p = 0.20.
a. What are the expected value and the standard error for the sampling distribution of the sample proportion with n = 20 and n = 58?
Note: Round the standard error to 4 decimal places.
Answer is complete and correct.
n
Expected value
Standard error
20
58
0.20
0.20
0.0894
0.0525
b. Can you conclude that the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is approximately normally distributed for both sample
sizes?
Yes, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is normally distributed for both sample sizes.
No, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is not normally distributed for either sample size.
No, only the sample proportion with n = 20 will have a normal distribution.
No, only the sample proportion with n = 58 will have a normal distribution.
c. If the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is normally distributed with n = 20, then calculate the probability that the
sample proportion is between 0.18 and 0.20.
Note: If appropriate, round final answer to 4 decimal places.
We cannot assume that the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is normally distributed.
We can assume that the sampling distribution of the sample proportion is normally distributed and the probability that the
sample proportion is between 0.18 and 0.20 is
Answer is complete but not entirely correct.
Probability
0.0871
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I need typing clear full answers pls i will give 5 upvotesarrow_forwardThe variances of stocks A and B are 1 percentage square and 4 percentage square, respectively. If the covariance between the two stocks is 0.6 percentage square, what is the correlation? Dontarrow_forwardWhat is the mean of a binomial distribution in which the number of trials n = 100 and the probability of success p = 0.5? 550.0 500.0 0.500 50.00 100.0arrow_forward
- q8- When visualising the distribution of a variable using a histogram, if only the right tail has outliers, the data distribution is: a. Right-skewed b. Normal c. Left-skewed d. Uniformarrow_forwardFind the mean, variance, and standard deviation of the binomial distribution with the given values of n and p. n= 124, p = 0.56arrow_forwardThe average time of students spend on reading per day is __________. a sample random variable a fixed variable a continuous random variable a discrete random variablearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education