
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
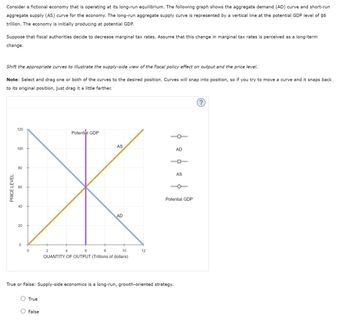
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a fictional economy that is operating at its long-run equilibrium. The following graph shows the aggregate demand (AD) curve and short-run
aggregate supply (AS) curve for the economy. The long-run aggregate supply curve is represented by a vertical line at the potential GDP level of $6
trillion. The economy is initially producing at potential GDP.
Suppose that fiscal authorities decide to decrease marginal tax rates. Assume that this change in marginal tax rates is perceived as a long-term
change.
Shift the appropriate curves to illustrate the supply-side view of the fiscal policy effect on output and the price level.
Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back
to its original position, just drag it a little farther.
120
Potential GDP
AS
100
PRICE LEVEL
60
80
60
40
40
20
20
0
0
2
4
6
8
AD
10
12
QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Trillions of dollars)
AD
1
AS
Potential GDP
True or False: Supply-side economics is a long-run, growth-oriented strategy.
True
False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the government engages in expansionary fiscal policy by increasing government spending. Show the initial impact by properly shifting the aggregate demand curve (AD), the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS), or the long-run aggregate supply curve on the graph below. Aggregate price level (P) LRAS SRAS * AD Aggregate output (Q)arrow_forwardThe policies of the federal government influence the outcomes of the various activities in that economy. When government policies change or unplanned events occur, the resulting economic events or activity will usually change. Listed below is a policy or event that affect the performance of the economy: The level of investment decreases because of a lack of confidence in the economy. for the question above, describe what would be the likely outcome in the economy. Use the appropriate tools of analysis, such as aggregate demand and aggregate supply where appropriate, to justify and explain your answer.arrow_forward• Assuming that there is no government spending or trade, an economy's GDP is the sum of domestic consumption C and investment I, ie. Y = C+ I • Assume that I is unaffected by GDP • Assume the consumption function is C = co + cY • In any equilibrium aggregate demand, AD must be equal to Y, GDP. Given this model, which of the following statements is correct? This question is worth 2 marks! Select one or more: a. The aggregate demand equation is given by AD = co + CY + I b. c, is equal to autonomous consumption c. if c, is a number between 0 and 1, and I+co >0 then the aggregate demand equation is a straight line that must intersect the 45 degree line at some point. d. In a demand-driven economy the AD curve is a vertical line e. In a demand-driven economy demand is equal to supply in equilibrium f. In a supply-driven economy demand is equal to supply in equilibrium g. In a demand-driven economy, supply creates its own demand h. If the economy above is a demand-driven economy, then the…arrow_forward
- We know the following about a closed economy: • Taxes: T = 20 . Government spending: G = 20 • Consumption: C = 10 + 0.6(Y - T) where Y denotes the GDP. We also know that investment is constant but we ignore its value. One day, the government initiates a Keynesian stimulus to support the economy. It increases spending to 40. To avoid a big increase in public debt, it also increases taxes to 30. What is the variation of GDP? Select one: a. It increases by 30 b. It increases by 35. c. It increases by 40 d. It increases by 50arrow_forwardSuppose the economy begins at full employment. Label this starting point as point "1." Then, suppose that a long strike by coal miners reduces the coal supply and increases the price of coal. Show the effects on your graph and label the new equilibrium point "2." Lastly, suppose our government wants the economy to return to full-employment as quickly as possible. Should the government intervene? If so, show the impact of successful fiscal policy on your graph. Label this new equilibrium point "3."arrow_forwardOn the following graph, AD1 represents the initial aggregate demand curve in a hypothetical economy, and AS represents the initial aggregate supply curve. The economy's full-employment output is $12 trillion. On the following graph, use the grey point (star symbol) to mark the equilibrium. (Note: You will not be graded on any adjustments made to the graph.) PRICE LEVEL (CPI) AS 106 105 104 103 63 102 101 100 99 98 AD AD 吕 1 97 96 Full Employment 96 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) AD 2 Equilibrium The initial short-run equilibrium level of real GDP is $ trillion, and the initial short-run equilibrium price level is Suppose the government, seeking full employment, borrows money and increases its expenditures by the amount it believes necessary to close thearrow_forward
- Assume the Canadian economy is currently at equilibrium. a. Using a correctly labeled aggregate demand and supply graph, show Full employment output (yf) Current price level (PL1) b. World War III breaks out and Canada has to get involved. The Prime Minister chooses to increase the military budget by 40%. On your graph from part A, show what will happen in the economy, labeling the new equilibrium as Q2, PL2. c. Using a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market, show how the Prime Minister’s decision will affect the economy.arrow_forwardConsider the following income/expenditure diagram in the simple Keynesian model. If taxes, T, were increased, then Group of answer choices A) The Y = C+S+T line would shift to the right, and equilibrium Y would increase. B) the C+I+G line would shift downward, and equilibrium Y would decrease. C) The Y = C+S+T line would shift to the left, and equilibrium Y would decrease. D) neither of the lines would shift, and equilibrium Y would stay the same. E) the C+I+G line would shift upward, and equilibrium Y would increase.arrow_forwardThe levels of real disposable income and aggregate expenditures for an economy are given in the following table. -- Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot the expenditures line for this economy on the following graph. Line segments will automatically connect the points. The black line represents the 45-degree line, where aggregate expenditures equal real GDP. Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate equilibrium real GDP. - - In the previous graph, if the economy produces at an output level that is higher than equilibrium GDP, then the economy is in because aggregate expenditures are real GDP, and unplanned inventory investment is Read GDP (Y) Aggregate Expenditures (AE) (Trillions of dollars per year) (Trillions of dollars per year) 0 1 1 1.75 2 2.5 3 3.25 4 4 5 4.75 6 5.5 7 6.25 8 7 Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot the expenditures line for this economy on the following graph. Line segments will automatically connect the points. The black line represents the…arrow_forward
- In an effort to increase output in the short run due to the poor economy, government officials have decided to cut taxes. They are considering two possible temporary tax cuts of equal size in terms of lost revenue. The first would reduce the taxes on people with incomes above $100,000 per year. The second would cut taxes on people with incomes below $60,000 for one year. Which change would have a greater impact on aggregate spending (i.e shift the aggregate demand curve further to the right)? Why?arrow_forwardUsing the Aggregate Supply -Aggregate Demand model describe both the short run and the long run effects of a reduction in corporation tax for an economy currently producing at their potential GDP level.arrow_forwardOn the following graph, AD1 represents the initial aggregate demand curve in a hypothetical economy, and AS represents the initial aggregate supply curve. The economy's full-employment output is $12 billion. On the following graph, use the grey point (star symbol) to mark the equilibrium. (Note: You will not be graded on any adjustments made to the graph.) PRICE LEVEL (CPI) 106 105 104 103 102 H AS 1ŏ1 101 ADA 100 AD 3 99 AD 2 98 AD1 97 Full Employment 96 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 REAL GDP (Billions of dollars) Equilibrium (?)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education