
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
(see problem attached)
Compute the pearson
The correlation is:
Medium and negative
Large and negative
Large and positive
Medium and positive
The alternative hypothesis in words for a two-tailed test is:
The correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series is significant
The correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series is not significant
The correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series is less than zero
The correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series is greater than zero
The null hypothesis in symbols for a two-tailed test is
H0: ρ = 0
H0: ρ ≠ 0
H0: r = 0
H0: r ≠ 0
If we use a two-tailed test with α = .01, the critical r values are:
±0.833
±0.874
±0.754
±0.669
Your decision is:
Reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is a significant correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series
Fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is a significant correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series
Reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is no significant correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series
Fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is no significant correlation between the scores on the 7-minute screen test and the scores on the cognitive series
Report the results in APA:
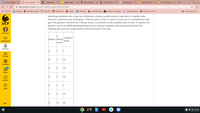
Transcribed Image Text:**Identifying Individuals at Risk for Alzheimer's: A Comparative Study**
Identifying individuals with a high risk of Alzheimer's disease usually involves a long series of cognitive tests. However, researchers have developed a 7-Minute Screen, which is a quick and easy way to accomplish the same goal. The question is whether the 7-Minute Screen is as effective as the complete series of tests. To address this question, Ijuin et al. (2008) administered both tests to a group of patients and compared the results. The following data represent results similar to those obtained in the study.
| Patient | 7-Minute Screen | Cognitive Series |
|---------|-----------------|------------------|
| A | 3 | 7 |
| B | 7 | 15 |
| C | 4 | 14 |
| D | 5 | 13 |
| E | 7 | 9 |
| F | 5 | 15 |
| G | 11 | 25 |
**Explanation of the Table:**
- **Patient**: Represents each participant in the study, labeled from A to G.
- **7-Minute Screen**: The scores obtained from the quick 7-Minute screening test.
- **Cognitive Series**: The scores obtained from the complete series of cognitive tests.
The table compares the scores from the two testing methods, illustrating how results from the 7-Minute Screen align with those from a more comprehensive test series.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following conclusions might be a conclusion that a researcher would make if he/she had just rejected the null hypothesis? there is a correlation in the population all brands are equally preferred in the population The treated population scores the same as the general population There is no difference between the population with the drug and the population without the drugarrow_forwardQuestion is on image and values of 12.2 are on the image with handwritingarrow_forwardA professor at the University of New Hampshire was interested in evaluating the effect of the unemployment rate on the incarceration rate. Using data from 50 states and the District of Columbia (n = 51), the researcher computed the Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the two variables. The results are presented below. Correlations Incarceration Unemployment Incarceration Pearson Correlation 1 .209 Sig. (2-tailed) .142 N 51 51 Unemployment Pearson Correlation .209 1 Sig. (2-tailed) .142 N 51 51 Using an alpha level of 0.05 and the four steps of the hypothesis testing process, test the research hypotheses that unemployment increases incarceration. Step 3 Step 4 Based on your decision to step 4 what type of error might you be making?arrow_forward
- You are a researcher interested in crime and crime rates. You’ve collected a sample of data from the county level for your state. You hypothesize that the rate of violent crimes will be higher in counties with bigger populations. Based on the below Pearson correlation results, is your hypothesis supported or rejected?arrow_forward2arrow_forwardCan someone help me out with these questions.arrow_forward
- What is the relationship between the amount of time statistics students study per week and their final exam scores? The results of the survey are shown below. Time 6 0 14 0 3 2 14 5 Score 64 66 91 65 59 60 86 71 Find the correlation coefficient: r=r= Round to 2 decimal places. The null and alternative hypotheses for correlation are:`H0: ` == 0`Ha:` ≠≠ 0 The p-value is: (Round to four decimal places) Use a level of significance of α=0.05α=0.05 to state the conclusion of the hypothesis test in the context of the study.arrow_forwardYou conduct a Pearson Product-Moment correlation test to see if two variables are related to each other. Even though the test is significant, you suspect that there actually isn't a real relationship between X and Y, and that they only seem to be related because of their relationship to another variable Z. This is called: bi-directionality the third-variable problem reverse-causality a causal effectarrow_forwardWhat’s the answer to these questions?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman