
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The following information is available about the company:
a. All sales during the year were on account.
b. There was no change in the number of shares of common stock outstanding during the year.
c. The interest expense on the income statement relates to the bonds payable; the amount of
bonds outstanding did not change during the year.
d. Selected balances at the beginning of the current year were:
$ 140,000
$ 260,000
$1,160,000
Accounts receivable
Inventory
Total assets
e. Selected financial ratios computed from the statements below for the current year are:
Earnings per share
Debt-to-equity ratio
Accounts receivable turnover
$ 2.64
0.850
16.0
2.40
Current ratio
10%
5.0
Return on total assets
Times interest earned ratio
Acid-test ratio
1.17
Inventory turnover
8.0
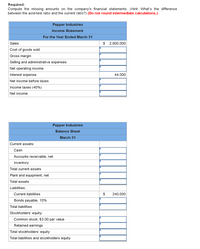
Transcribed Image Text:Required:
Compute the missing amounts on the company's financial statements. (Hint: What's the difference
between the acid-test ratio and the current ratio?) (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
Pepper Industries
Income Statement
For the Year Ended March 31
Sales
$ 2,900,000
Cost of goods sold
Gross margin
Selling and administrative expenses
Net operating income
Interest expense
44,000
Net income before taxes
Income taxes (40%)
Net income
Pepper Industries
Balance Sheet
March 31
Current assets:
Cash
Accounts receivable, net
Inventory
Total current assets
Plant and equipment, net
Total assets
Liabilities:
Current liabilities
$
240,000
Bonds payable, 10%
Total liabilities
Stockholders' equity:
Common stock, $3.00 par valu
Retained earnings
Total stockholders' equity
Total liabilities and stockholders equity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Under the allowance method of uncollectible accounts, the entry to write off a customer’s account affects the accounting equation by: decreasing an asset and decreasing stockholders’ equity (expense) increasing an asset and decreasing an asset increasing a liability and decreasing a liability decreasing a liability and increasing stockholders’ equity (revenue)arrow_forward5.) For each definition, list the “ratio category (or grouping)” that is described by filling in the blanks from (a) to (f) and provide one example for each category or grouping. a) Determines a company’s ability to pay off short term obligations or debts as they come due. ________________________ b) Relates company’s internal performance to the external judgment of the marketplace in terms of what it is worth. ________________________ c) Identifies percentage of earnings paid out to shareholders and what is reinvested for internal growth. ________________________ d) Speed at which company turns over its inventory, receivables and long-term assets. ________________________ e) How a company is financed between debt [lenders] and equity [owners]. ________________________ f) Measures return on sales, assets and total capital. ________________________arrow_forwardWhich of the following is the incorrect effect of counterbalancing errors?a. None of the statements is incorrect. b. The statement of financial position at the end of the first period is incorrect. c. The income statements for three successive periods are incorrect. d. The statements of financial position at the end of the second period is correct.arrow_forward
- at the bottom. Had there been a loss for the In reviewing the income statement of a profitable company, one can see that it begins with at the top and ends with year, the final result would have been a What exactly does the word balance mean in the title of the balance sheet? Why do we balance the two halves? (Select all the answers that apply.) A. The balance sheet balances the firm's assets against its financing, which can be either debt or equity. B. The total value of all of the firm's assets should equal the sum of its short- and long-term debt plus stockholder's equity. C. In order for the balance sheet to balance, stockholder's equity must exclude preferred stock, common stock at par value, paid in capital in excess of par on common stock and retained earnings from previous profitable years in which some of the earnings were held back and not paid out as dividends. D. When the balance sheet does not balance, the difference must be reported as an "off-balance sheet" account for…arrow_forwardThe current ratio is useful in determining a company’s ability to pay obligations when they become due. ____________. True or false?arrow_forwardPrepare an answer sheet with the column headings shown here. For each of the following transactions or adjustments, indicate the effect of the transaction or adjustment on the appropriate balance sheet category and on net income by entering for each account affected the account name and amount and indicating whether it is an addition (+) or a subtraction (-). Transaction a has been done as an illustration. Net income is not affected by every transaction. In some cases only one column may be affected because all of the specific accounts affected by the transaction are included in that category. a. Accrued interest revenue of $30 on a note receivable. b. Determined that the Allowance for Bad Debts account balance should be increased by $2,050. c. Recognized bank service charges of $22 for the month. d. Received $29 cash for interest accrued in a prior month. e. Purchased 3 units of a new item of inventory on account at a cost of $31 each. Perpetual inventory is maintained. f. Purchased…arrow_forward
- Indicate if the following transaction from Torte Baking Company increases or decreases assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expense, and net income. The pattern of the + and - must adhere to the balance sheet equation. Show the impact of revenue and expense on both net income and equity. If there is a + and - within one category (e.g., assets for transaction 2), then list the accounts that go up and down. Transaction (26) Recognize tax expense that will be paid later. Assets ["", "", ""] Liabilities ["", "", ""] Equity ["", "", ""] Revenue ["", "", ""] Expense ["", "", ""] Net Income ["", "", ""]arrow_forwardPlease help with the following question, need accurate and full answer. What is the effect on liabilities, stockholder’s equity, revenues and net income if a company does not make an unearned revenue adjusting entry? Explain with suitable examplesarrow_forwardWhat of the following is an incorrect statement? a) The final step in the accounting cycle is to close the temporary accounts. TESTER D Ob) A primary goal of accrual accounting is to appropriately match expenses with revenues. d) All of the statements are correct. c) Conservatism guides accountants to select the alternative that produces the highest amount of net income.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education