
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
At 20 °C, the vapor pressures of several alcohols are given in this table. Explain these vapor pressures in terms of types and extents of IMFs for these alcohols:
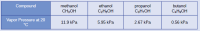
Transcribed Image Text:Compound
methanol
ethanol
propanol
C3H;OH
butanol
CH3OH
C2H5OH
C4H9OH
Vapor Pressure at 20
°C
11.9 kPa
5.95 kPa
2.67 kPa
0.56 kPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The solubility of Oz in water is approximately 0.00380 g L- of water when the temperature is 25.0°C and the partial pressure of gaseous oxygen is 760 torr. The oxygen gas above the water is replaced by air at the same temperature and pressure, in which the mole fraction of oxygen is 0.210. What will the solubility of oxygen in water be under these new conditions? 0.606 g L-1 B 1.33 x 10-3g L-1 1.05 x 10-6 g L-1 1.01 g L-1 E) 7.98 x 104 g L-1arrow_forwardThe normal boiling point of a certain liquid X is 104.30 °C, but when 102. g of iron(III) nitrate (Fe (NO,) are dissolved in 500. g of X the solution boils at 105.2 °C instead. Use this information to calculate the molal boiling point elevation constant K, of X. Round your answer to 1 significant digit. dl. °C.kg K, = 0 molarrow_forwardLiquids that readily evaporate are classified as volatile liquids. Such liquids have measurable vapor pressures at or near room temperature. If the vapor pressure of two or more liquids are compared at the same temperature, the more volatile liquid will have the higher vapor pressure. The vapor pressure of acetone is 24.6 kPa (read: kiloPascals) at 293 K. Is acetone more or less volatile than the organic liquid used in this activity? Explain or demonstrate.arrow_forward
- The average osmotic pressure of blood is 7.7 atm at 25 °C. What molarity of glucose 1C6H12O62 will be isotonic with blood?arrow_forwardA student was instructed to determine the molecular weight of an unknown white powder. He remembered that one way to do this is by exploiting the colligative properties of solution. After a simple conductivity test, he found that an aqueous solution of the sample is not conductive. He dissolved 22.87 grams of the unknown sample in 0.500 kg of water. He found that the boiling point of the resulting solution was 100.13 °C under normal atmospheric conditions. Given: K, of water is 0.512 °C/m a. Calculate the molality of the resulting solution. b. How many moles of the sample did he dissolve to perform the experiment? c. What is the molecular weight of the unknown sample?arrow_forward5 . If 40.2g NaCl are mixed into water and the total mass is 389g, what is the CHANGE in boiling if Kb= 0.52C/M (molal)? Assume NaCl does not dissociate in solution.arrow_forward
- A soln is made of 2 volatile components: toluene and benzene. At 60 degrees Celsius, the vapor pressure of benzene (C6H6) is 396mmHg and the vapor pressure of toluene (C7H8) is 1.40*102mmHg. The soln has 0.25 moles benzene and 0.50 moles toluene. Calculate the total pressure of the soln.arrow_forwardCompound XY is an ionic compound that dissociates as it dissolves in water. The lattice energy of XY is -594.4 kJ mol1. The hydration energy of its ions is -626.2 kJ mol-1. Write the thermochemical equations for the two steps in the formation of a solution of XY in water. Draw an enthalpy diagram for the formation of this solution. What is the net AH for the formation of a solution of XY? i kJ mol-1arrow_forward15 g of an unknown molecular substance was dissolved in 450 g of water. The resulting solution freezes at – 0.34 °C. What is the molar mass of the substance? (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1)arrow_forward
- A solution of ethanol (CH,CH,OH) and water that is 90.% ethanol by mass is boiling at 81.9 °C. The vapor is collected and cooled until it condenses to form a new solution. Calculate the percent by mass of ethanol in the new solution. Here's some data you may need: normal vapor pressure density boiling point at 81.9 °C g 0.79 mL ethanol 78. °C 865. torr 100. °C 1.00 mL 389. torr water Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced students: you may assume the solution and vapor above it are ideal. ?arrow_forwardbmitted The boiling point of water is 100.00 °C at 1 atmosphere. A student dissolves 12.10 grams of chromium(II) bromide, CrBr₂ (211.8 g/mol), in 241.5 grams of water. Use the table of boiling and freezing point constants to answer the questions below. Solvent Water Ethanol Chloroform Benzene Formula H₂O CH3CH₂OH CHCI 3 C6H6 Diethyl ether CH3CH₂CH₂CH3 The molality of the solution is The boiling point of the solution is Submit Answer Retry Entire Group Kb (°C/m) Kf (°C/m) 0.512 1.86 1.22 1.99 3.67 2.53 2.02 m. °C. 5.12 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forwardPart A What is the value of A-G for the reaction MCI, 6 H₂O(s) MCL, (s) + 6 H₂O(g) - when the pressure of water vapour is 28.7 mbar? Express your answer as an integer with the appropriate units. A.G= Value μA Submit Request Answer Part B A.G' = What is the value of A,C? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μA Units Value Units ? Submit Previous Answers Request Answer Un input for part B ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remainingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY