
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Compare your measurement to the generally accepted value of g (from a textbook or other source). Does the accepted value fall within the range of your values? If so, your experiment agrees with the accepted value. If not, describe why it does not. Make sure to calculate the percent error for the experiment.
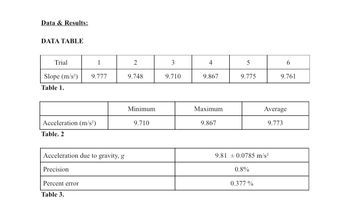
Transcribed Image Text:Data & Results:
DATA TABLE
Trial
Slope (m/s²)
Table 1.
Acceleration (m/s²)
Table. 2
1
9.777
Acceleration due to gravity, g
Precision
Percent error
Table 3.
2
9.748
Minimum
9.710
3
9.710
4
9.867
Maximum.
9.867
5
9.775
9.81 0.0785 m/s²
0.8%
0.377 %
6
9.761
Average
9.773
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- surface, denoted by “g”. In this imaginary experiment, you have measured g three times. The values you obtain are: g1 = 10.2 meters per second squared (m/s2) g2 = 10.4 m/s2 g3 = 10.0 m/s2 To find the Average Value of g, denoted by gav, simple add up the experimental values and divide by the number of experimental values you have: g1 + g2 + g3 10.2 + 10.4 + 10 gav = __________ = ____________ = 10.2 m/s2 . 3 3 Percent Error (PE) To find the Percent Error (PE), you compare the average experimental value to the standard or handbook value of the physical quantity you are measuring. The Standard Value of gravitational acceleration at Earth’s surface , gst, is 9.8 m/s2. Mathematically, PE is defined as: (Average - Standard)…arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between accuracy and precision? Explain 2. Calculate the volume and percent error/uncertainty in the volume of a rectangular sample block of length 13.51 ±0.05 cm, width 6.23 ±0.02 cm, and thickness of 1.76±0.02 cm. 3. Calculate the mass density and uncertainty in the mass density of the sample block. Mass of the block is 289± 1gr. 1.arrow_forwardA marathon runner completes a 42.188-km course in 2 h, 35 min, and 39 s. There is an uncertainty of 28 m in the distance traveled and an uncertainty of 1 s in the elapsed time. (Give all answers to the appropriate number of significant figures. Note that uncertainties should be reported to one significant figure and percent uncertainties should be reported to two significant figures.) (a) Calculate the percent uncertainty in the distance. _________% (b) Calculate the percent uncertainty in the elapsed time. __________%arrow_forward
- A series of four measurements of g are made in the physics lab. The results of these measurements in ms2/ are: 9.63, 9.58, 9.71, 9.68. The average of these four measurements is the experimental value of g and the accepted value is 9.80 ms2/. What is the percent error of these measurements?arrow_forwardTwo metal bars are welded together to shape a more extended bar. The length of the primary bar is L₁ = = 0.97 ± 0.02 m And the length of the secondary bar is L2₂ 1.13 0.01 m. = Figure out the length of the bar (including uncertainty). Show your steps.arrow_forwardProblem 2. 1-3arrow_forward
- A hot tub with a surface area of 28 ft2 is filled with water to a depth of 29 in . Hint: volume is calculated as area × height (A × h). A) What is the volume of water in the tub, in liters? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. B) How many kilojoules are needed to heat the water from 59∘F to 103 ∘F? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. C) If the hot-tub heater provides 5900 kJ/min, how long, in hours, will it take to heat the water in the hot tub from 59∘F to 103∘F? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardI need help with a University Physics 1 (significant figures) - The problem is described in the image below:arrow_forwardy1 = sin(pi(x) - 2(pi)(t))......y2 = sin(pi(x)/2 + 2(pi)(t))arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON