
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 14, Question 6
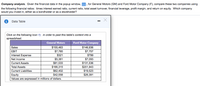
Transcribed Image Text:### Company Analysis
Given the financial data displayed in the popup window, compare General Motors (GM) and Ford Motor Company (F) using specific financial ratios: times interest earned ratio, current ratio, total asset turnover, financial leverage, profit margin, and return on equity. Decide which company you would invest in, either as a bondholder or as a stockholder.
#### Data Table
| | General Motors | Ford Motor Company |
|----------------------|----------------|--------------------|
| **Sales** | $155,463 | $146,936 |
| **EBIT** | $7,785 | $7,757 |
| **Interest Expense** | $321 | $799 |
| **Net Income** | $5,381 | $7,093 |
| **Current Assets** | $81,533 | $131,536 |
| **Total Assets** | $166,315 | $201,943 |
| **Current Liabilities** | $62,402 | $19,523 |
| **Equity** | $42,558 | $26,391 |
*Values are expressed in millions of dollars.*
### Analysis Steps
1. **Times Interest Earned Ratio**:
- Calculate by dividing EBIT by Interest Expense.
- GM: \( \frac{7,785}{321} \)
- Ford: \( \frac{7,757}{799} \)
2. **Current Ratio**:
- Determine by dividing Current Assets by Current Liabilities.
- GM: \( \frac{81,533}{62,402} \)
- Ford: \( \frac{131,536}{19,523} \)
3. **Total Asset Turnover**:
- Evaluate by dividing Sales by Total Assets.
- GM: \( \frac{155,463}{166,315} \)
- Ford: \( \frac{146,936}{201,943} \)
4. **Financial Leverage**:
- Assess by dividing Total Assets by Equity.
- GM: \( \frac{166,315}{42,558} \)
- Ford: \( \frac{201,943}{26,391} \)
5. **Profit Margin**:
- Calculate by dividing Net Income by Sales.
- GM: \( \frac{5,381
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 18 pts Multiple Functions 88 MULTIPLE CHOICE Question 2 ◄ Listen When f(x)=-3x-6 and g(x) = x²-x-6, what is ? A B C f 54 g = 3 fg = -3 x-3x=3 f 51 g = -2x+2; x=1arrow_forwardC B A Question 2 Listen What is tane for the given triangle? 13 53 12 25 55 13 12 13 earrow_forwardZina Manufacturing Company started and completed Job 501 in December with the following Job Cost Sheet and transferred it to the warehouse. Direct Materials Date Dec 17 Dec 30 Total Direct Labor Amount Date Amount $2,000 Dec 20 $4,000 8,000 Dec 30 3,800 Total Job Cost Sheet - Job No. 501 Total Cost The journal entry to record the transaction is A) WIP Inventory FG Inventory B) Cost of Goods Sold WIP Inventory C) FG Inventory WIP Inventory D) FG Inventory WIP Inventory Debit Credit 35,800 17,800 17,800 Manufacturing Overhead Date Amount Dec 24 $10,000 Dec 30 8,000 Total 35,800 35,800 17,800 17,800 35,800arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education