Question
In the circuit shown in Fig, switch S1 has been closed a long time while switch S2 has been left open. Then S2 is closed at the same instant when S1 is opened. Just after S2 is closed, the current through the resistor is 12.0 A and its rate of decrease is di/dt = -36.0 A/s. How long does it take the current to decrease to 6.00 A, one-half its initial value?
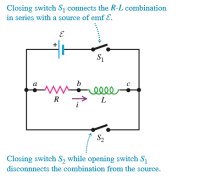
Transcribed Image Text:Closing switch S, connects the R-L combination
in series with a source of emf E.
S1
a
elle
R
S2
Closing switch S, while opening switch S1
disconnnects the combination from the source.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider the circuit shown in the figure, where &₁ = 20.7 V, ₂ = 11.3 V, and R = 13.00. (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations-including answers submitted in WebAssign.) &₁ &₂ ww R 28.0 Ω www → 12.0 Ω W ww →½2₂2 Is ℗ (a) What is the current (in A) in each resistor? 1₁ = A ¹₂ = X Apply Kirchhoff's junction and loop rules to the circuit to find three separate equations in terms of the unknown currents, and solve your system for I1, I2, and/or 13. A 13 = A (b) What is the power (in W) delivered to each resistor? P₁ = W P₂ = W P3 (c) What is the total power (in W) supplied by both batteries? Warrow_forwardIn the circuit shown below, the capacitor is initially charged with +36 μC on the upper plate and –36 μC on the lower plate, it has a capacitance of C=2μF, and Switch A is open. Switch A is then closed. a) Find the current I1 immediately after Switch A is closed. b)Find the amount of time it takes the current to be reduced by a factor of 1/e. That is, after how much time is the current I1 37% of its initial value?arrow_forwardIn the figure, & = 134 V, R₁ = 8.500, R₂ = 17.602, R3 = 26.4 02, and L = 2.14 H. Immediately after switch S is closed, what are (a) i₁ and (b) i2? (Let currents in the indicated directions have positive values and currents in the opposite directions have negative values.) A long time later, what are (c) i₁ and (d) i₂? The switch is then reopened. Just then, what are (e) i and (f) i2? A long time later, what are (g) i₁ and (h) i₂? (a) Number (b) Number i (c) Number (d) Number i (e) Number i =8 Units Units Units Units S Units R₁ i₂ {R₂ > > W R₁ > elearrow_forward
- In the circuit of the figure ℰ = 3.30 kV, C = 6.60 μF, R1 = R2 = R3 = 0.740 MΩ. With C completely uncharged, switch S is suddenly closed (at t = 0). At t = 0, what are (a) current i1 in resistor 1, (b) current i2 in resistor 2, and (c) current i3 in resistor 3? At t = ∞ (that is, after many time constants), what are (d)i1, (e)i2, and (f)i3? What is the potential difference V2 across resistor 2 at (g)t = 0 and (h)t = ∞? Answer parts d, e, and f pleasearrow_forwardIn the SI system of units, one coulomb (1 C) is defined to be the charge that passes a point every second when a constant (electric) current of one ampere, also called one amp, (1 A) flows past that point. Thus, one coulomb equals one ampere second (1 C = 1A-s). If Q is the charge and / is the constant (or average) current past a point in a time t, Q=It. An average current of 2.0 A flows through all parts of a wire for 5.0 minutes. How much charge passes by any point in the wire in that time? 10.0 C О В. 120.0 С 600.0 C O D.2.0 C Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers. Save All Answers Save and Sub P Type here to search 23arrow_forwardIn the accompanying figure, the rails, connecting end pieces, and rod all have a resistance per unit length of 40/cm. The rod moves to the left at v = 3 m/s. If B = 0.65 T everywhere in the region, what is the current in the circuit (a) when a = 8 cm? (b) when a = 4.5 cm? Description of Image B Hint a. When a = 8 cm, a counterclockwise mA flows in the circuit. b. When a = = 4.5 cm, 5.48 o current of 9.75 4.0 cm X = 5.48 mA flows in the circuit. X = 9.75arrow_forward
- Problem 5: A current of I- 2.6 A passes through the circuit shown, where R- 65 3R 5R V) 2R 6R 2R 7R 5R 10R Otheexpertta.com Part (a) In terms of R, I, and numeric values, write an expression for the voltage of the · source, V. Part (b) What is the voltage, V in volts? tan( sin() cotanO a acos cosh0t cosO asin() acotan 4 5 6 sinh() cotanhO *1 23 0 tanh0c O Degrees O Radians CLEAR BACKSPACEarrow_forwardIn the figure R₁ = 9.42 kQ, R₂ = 15.7 kQ, C = 0.439 µF, and the ideal battery has emf & = 18.0 V. First, the switch is closed a long time so that the steady state is reached. Then the switch is opened at time t = 0. What is the current in resistor 2 at t = 4.10 ms? Number Units R₁ R₂ Carrow_forwardIn the circuit of the figure ℰ = 3.30 kV, C = 6.60 μF, R1 = R2 = R3 = 0.740 MΩ. With C completely uncharged, switch S is suddenly closed (at t = 0). At t = 0, what are (a) current i1 in resistor 1, (b) current i2 in resistor 2, and (c) current i3 in resistor 3? At t = ∞ (that is, after many time constants), what are (d)i1, (e)i2, and (f)i3? What is the potential difference V2 across resistor 2 at (g)t = 0 and (h)t = ∞? Answer parts a, b, and c pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios