
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
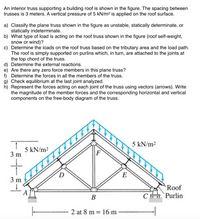
Transcribed Image Text:An interior truss supporting a building roof is shown in the figure. The spacing between
trusses is 3 meters. A vertical pressure of 5 kN/m² is applied on the roof surface.
a) Classify the plane truss shown in the figure as unstable, statically determinate, or
statically indeterminate.
b) What type of load is acting on the roof truss shown in the figure (roof self-weight,
snow or wind)?
c) Determine the loads on the roof truss based on the tributary area and the load path.
The roof is simply supported on purlins which, in turn, are attached to the joints at
the top chord of the truss.
d) Determine the external reactions.
e) Are there any zero force members in this plane truss?
f) Determine the forces in all the members of the truss.
g) Check equilibrium at the last joint analyzed.
h) Represent the forces acting on each joint of the truss using vectors (arrows). Write
the magnitude of the member forces and the corresponding horizontal and vertical
components on the free-body diagram of the truss.
5 kN/m²
5 kN/m2
3 m
E
Roof
A
B
C Purlin
2 at 8 m = 16 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The portion of the truss shown represents the upper part of a power transmission line tower. For the given loading, determine the force in each of the members located above members HJ. State whether 2. each member is in tension or compression. Ans: AB = DF = 2.29 kN T; AC = EF = 2.29 kN C; BD = 2.21 kN T; BC = DE = 0.60 kN C; BE = EH = 0; CE = 2.21 kN C; CH = EJ = 1.20 kN C %3Darrow_forwardPresent through calculations and figures an analysis of the truss system. Indicate, whether the members are in compression or tension and the force in each member.arrow_forwardHello, I need help with Q.1 (parts a b & c) Thank you,arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning