
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
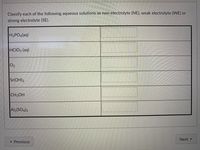
Transcribed Image Text:Classify each of the following aqueous solutions as non-electrolyte (NE), weak electrolyte (WE) or
strong electrolyte (SE).
H3PO4(aq)
HCIO3 (aq)
02
Sr(OH)2
CH;OH
Al2(SO4)3
Next►
« Previous
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Fe2+ (aq), Ca2+ (aq) , and Ba2+ (aq) are in a solution together what would you add to the water to get each separated?arrow_forwardConsider the following precipitation reaction: 2Na3PO4(aq) + 3CuCl2 (aq) → Cu3 (PO4)2 (s) + 6NaCl(aq) A Part A What volume of 0.156 M Na3PO4 solution is necessary to completely react with 92.8 mL of 0.103 M CuCl₂?arrow_forward150.00 grams of Iron (III) sulfate is dissolved in enough water to prepare 200.0 ml of solution. What is the concentration of Iron (III) sulfate in the solution above in moles per liter? What is the concentration of Fe^+3 ions in the solution above in moles per liter? What is the concentration of SO4^-2 ions in the solution above in moles per liter? How many milliliters of the solution above are required to supply 0.125 moles of Iron (III) sulfate?arrow_forward
- In Part A of this experiment, you will be standardizing a solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) against a sample of oxalic acid dihydrate (H2C2O4⋅2H2O, 126 g/mol). Calculate the number of grams of H2C2O4⋅2H2O required to completely neutralize 25.0 mL of 0.120M NaOH.arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following molecular reaction. Write the ionic and net ionic reactions. ___ BaCl2 (aq) + ___ Na2SO4 (aq) =arrow_forwardHow many grams of nitric acid, HNO₃, are required to neutralize (completely react with) 4.30 g of Ca(OH)₂ according to the acid-base reaction: 2 HNO₃(aq) +Ca(OH)₂(aq)→2 H₂O(l)+Ca(NO₃)₂(aq)arrow_forward
- Which of the following reactions are redox reactions? i) 2 C6H6 (l) + 15 O2 (g) -> 12 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) ii) Pb(NO3) 2 (aq) + 2 KCl (aq) --> PbCl2 (s) + 2 KNO3(aq) iii) 3 Mg (s) + 2 FeCl3 (aq) --> 3 MgCl2 (aq) + 2 Fe (s)arrow_forward4. Complete and balance the following Double Displacement reaction. Identify the cation and the anion in each of the reactants and the products. (write cation or anion underneath each species) Naz (COз) (ag) + Sr Cl2 (aq) → 5. Identify as strong /weak acid or base and salt. Predict if soluble or insoluble in water. Give the correct chemical name. Acid, Base, Salt Soluble or Insoluble Chemical Name a) MgCl2 b) Ca(CОз) c) Naz(SO3). d) NH4(NO3). e) Pb(OH)2 f) Cu3(PO4)2 g) HCI h) H2SO4 6. In the reaction below: Pb° (s) 2 Ag +1 -> Pb *(aq) + 2 Ag° (s) a) Which species is oxidized and which is reduced? b) Which species is the oxidizing agent and which is the reducing agent? 7. Calculate the formula weight of each below: Must show work. Round atomic weight off periodic table to two decimal places. a) KCI d) Na(SO3)2 b) Na3PO4 e) Al2(SO4)3 c) Fe(OH)2 f) (NH4)2CO3arrow_forwardUsing your knowledge of and bases, write balanced equations for the following acid-base reactions and indicate which reactant is the acid and which is the base. Write the molecular, ionic, and net ionic equations. HNO3 (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) → H2SO4 (aq) + KOH (aq) → CH3COOH (aq) + NaOH (aq) →arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solutionarrow_forwardhow do i balance Na(s)+HCl(aq) NACl(aq)+H2(g)arrow_forwardListen Which equation below correctly describes the formation of a solution of calcium chloride in water? A) CaCl2(s) + H₂O (1)→ Ca2+ (aq) + Cl₂ (aq) B) CaCl2(s) + H₂0 (1)→ Ca²+(aq) +2Cl¯(aq) OC) OD) CaCl2(s) + H₂O (1) CaCl₂(aq) CaCl2(s) + H₂O (1)→ CaCl2(s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY