
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
CLAIM and REASONING
Template:
The ramp will need to be ___________meters high.
The law of conservation of energy states that __________________
If the skater could reach a speed of 12 m/s they had ____________J of energy. This means that they have _____________J of potential energy at the top of the hill.
Based on calculations, the height of the ramp would need to be ___________meters high to reach this speed.
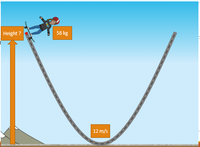
Transcribed Image Text:Height ?
58 kg
12 m/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A car engine produces a constant power of P = 341 hp. The car and motor have a combined mass of m = 1830 kg. 1.) The car starts from rest, after t=5 seconds, what is the cars speed, you may assume no energy is required to spin the tires. 2.) Assume a dragster of mass m=1000kg can accelerate to cover 450 m and accelerate in 7.2 s from a dead stop, how much horsepower is the engine producing, assuming acceleration is constant?arrow_forwardQuestion 8 Questions #8-9 start with the same description. A 1,100 kg horse is walking at 2.0 m/s. What type of energy is being described? Your answer: O chemical O elastic O gravitational O kineticarrow_forward⦁ Envision yourself doing a jumping jack. Imagine you assume a standing X position, with your arms above your shoulders in a wide V and legs apart in an inverted V. When you hold that position, you are demonstrating ______ energy. When you do the jumping jack from the previous position you are converting that energy into _____ energy. ,arrow_forward
- Person A and Person B are both using the same amount of work to lift something. Person A takes half as much time to do it. Using the formula for power, explain which person has the most Power and why.arrow_forwardA musket ball, 0.2 kilograms, is shot with the speed of 313 meters per second into a metal can holding some clay. The musket ball penetrates 0.134 meters into the clay before coming to a stop. What is the kinetic energy of the musket ball before it hits the clay? How much work does the clay do in stopping the musket ball, question mark? What forces the clay exert in stopping the musket ball?arrow_forwardAnswer both or NONE question 1 - For exercise, an athlete lifts a barbell that weighs 400 N from the ground to a height of 2.20 m at a constant speed in a time of 1.60 s. What is the metabolic power, in kW (kiloWatts)? Your answer needs to have 2 significant figure, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement. Question 2 - The metabolic power for typing is 150 W for Lili, not a lot as you know probably. How long does it take to burn off the energy in a slice of apple pie, which energy content is 1680 kJ (400 food calorie), in minutes? (Try to stay active, working/studying in front of a computer is not the best exercise you can do for your body.)arrow_forward
- Please use energy conservation ONLY to answer the following question!arrow_forwardA student uses a wheelchair to get around campus, which she travels to on a public bus. She boards the bus using a motorized lift attached near the bus door. The electric lift motor uses 1.4 kilojoules of energy to raise the student and wheelchair from the sidewalk to the level of the bus interior, a total displacement of 0.75 meters. If the mass of the wheelchair is 20 kilograms and the mass of the student and her belongings is 60 kilograms, what is the efficiency of the motor(Estimate g as 10 m/s2.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON