
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
solubility in water (1=most soluble, 3=least soluble)
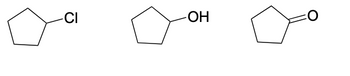
Transcribed Image Text:### Cyclopentane Derivatives: Structural Representation
The image represents the structural formulas of three cyclopentane derivatives. Each structure showcases a different functional group attached to the cyclopentane ring. Understanding these derivatives and their structures is fundamental in organic chemistry, as each functional group imparts unique chemical properties to the molecule.
1. **Chlorocyclopentane**
- **Structure Description:** The first molecule features a chlorocyclopentane structure. It consists of a cyclopentane ring (five-carbon ring) with a chlorine (Cl) atom attached to one of the carbon atoms in the ring.
- **Chemical Representation:**
```
Cl
|
/ \
| |
\ /
/______\
```
2. **Cyclopentanol**
- **Structure Description:** The second molecule shows cyclopentanol. It has a cyclopentane ring with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to one of the carbon atoms. This structure is typical of an alcohol functional group.
- **Chemical Representation:**
```
OH
|
/ \
| |
\ /
/______\
```
3. **Cyclopentanone**
- **Structure Description:** The third molecule represents cyclopentanone. It has a cyclopentane ring with a ketone functional group (=O), where the oxygen is double-bonded to one of the carbon atoms in the ring.
- **Chemical Representation:**
```
O
||
/ \
| |
\ /
/______\
```
### Functional Groups and Their Properties
- **Chlorine (Cl):** Chlorine is a halogen and, when attached to an organic molecule, it can significantly alter the reactivity and physical properties, making the compound more susceptible to nucleophilic substitution reactions.
- **Hydroxyl (OH):** The hydroxyl group characterizes alcohols. This functional group is polar and can form hydrogen bonds, impacting both the solubility in water and the boiling points.
- **Ketone (=O):** The carbonyl group (C=O) in ketones is highly polar, influencing the molecule's reactivity, particularly in nucleophilic addition reactions. Ketones also cannot hydrogen bond with themselves, but they can with other molecules that can donate hydrogen bonds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pick the compound that is most soluble in water (lone pairs are not indicated): HH Compound 1: H H H H Compound 2: H-C-C-C-C-H нон Compound 3: H-C-C-C-H Compound 1 Compound 2 Compound 3arrow_forwardAn impure sample of 250 mg of adipic acid was recrystallized from 2.0 mL of boiling water. The solution was cooled to room temperature slowly and further cooled in an ice bath. What is the maximum amount of recoverable adipic acid at 0 oC? Solubility of adipic acid at 0 oC is 0.3 g/ 100 mL Group of answer choices 6 mg 249 mg 244 mg 250 mgarrow_forwardWhat is the solubility of NY in pure water (where the concentration of MX = 0)? Question 12 options: 0.000938 mg/L 0.00114 mg/L 0.000881 mg/Larrow_forward
- Is the following molecule soluble in water or benzene? H3C A) Water B) Benzene N CH3 CH3 +arrow_forwardSubstance Formula Acetone. lodine Biphenyl C₂H₂O 1₂ C₁₂H₁0 Structure (show all bonds, Aen, label P/NP) Predicted Polarity Solubility Experimentál Solubility Polarityarrow_forwardWhich of the following will have the greatest solubility in water? Which will have greatest solubility in ethyl acetate (an organic solvent)? HO зас Select one: NH₂ منشود III CH₂ a. I in water and IV in ethyl acetate H₂C H₂C HO HO HO OH HO II IV NHarrow_forward
- Which of the following will increase the solubility of a solid solute, such as KCI, in water? stirring the mixture using smaller particles increasing the temperature of the solvent decreasing the temperature of the solventarrow_forwardHow many of the following are substantially soluble in hexane? Cl2 LiCl NH4SO4 C8H18 H2O KBr 2 3 4 5 6arrow_forwardWhich of the following organic molecules will most likely be soluble in water? 1 HO O НО ОН Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY