
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
State the reagent/solvent necessary for the reaction below
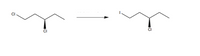
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a chemical reaction involving two organic molecules. On the left side, there is a chlorinated alkane structure with a chlorine (Cl) atom bonded at each end. On the right side, the leftmost chlorine atom is replaced by an iodine (I) atom, while the rest of the molecular structure remains unchanged. The reaction arrow indicates the transformation from the starting material to the product.
### Diagram Explanation:
- **Left Structure (Reactant):**
- The molecule consists of a chain of carbon atoms (four in total).
- A chlorine (Cl) atom is bonded to the first carbon.
- Another chlorine (Cl) atom is bonded to the third carbon, depicted with a solid wedge indicating a specific stereochemistry.
- **Right Structure (Product):**
- The structure is similar to the reactant but with an iodine (I) atom replacing the chlorine (Cl) atom at the first carbon position.
- The chlorine (Cl) atom bonded to the third carbon retains its position and stereochemistry (solid wedge).
This diagram illustrates a halogen exchange reaction, where the substitution of a chlorine atom with an iodine atom occurs.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Just answer to question 18 pleasearrow_forwardWhich of the following can complete the reaction below? O Br2/FeBr3 O NBS/(PhCO2)2 O H2SO4 in boling water O H₂, Pt, Ethanol at 130 atm. ?arrow_forwardGive each product in the series of reactions shown below CH;CI HNO3 A Sn В HCI OH. NANO2, HCI, CUCN E F AICI3 H2SO4 0°Carrow_forward
- The following equilibrium equation has a K. = 24.0 at 200°C. If 0.0085 M of cis- stilbene and 0.24 M trans-stilbene are initially introduced, what is the equilibrium concentration of trans-stilbene? Hint: Determine Q first. Write answer to four significant figures. H. hv H. trans-stibene cis-stilbenearrow_forwardQuestion attachedarrow_forwardComplete the following synthesis writing each step for the synthesis of the product showing all reactants and conditionsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY