
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
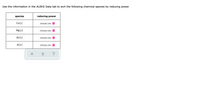
Transcribed Image Text:Use the information in the ALEKS Data tab to sort the following chemical species by reducing power.
species
reducing power
Ca (s)
choose one
Mg (s)
choose one
Zn (s)
choose one
Al (s)
choose one
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each of the following reactions, identify whether the reactants or the products would have more potential energy. + C(s) + 2H₂O(g) + 90.1 kJ → 2CO2(g) + 2H₂(9) CO(g) + H₂O(g) - 2CO₂(g) + 2H₂(g) + 41.2 kJ C₂H₂OH(I) + 30₂(9) - 2C0₂(g) + 3H₂O(g) C3H8(9) + 6H₂O(g) → 3CO₂(g) + 10H₂(g) Use the following to answer the next 3 questions. The smelting of iron occurs in a blast furnace, as represented by the following overall equation. Step I 3Fe2O3(s) + CO(g) - CO₂(g) + 2Fe3O4(s) A+H° = -47.2 kJ Step II Fe₂O4(s) + CO(g) - CO₂(g) + 3FeO(s) A,H+19.4 kJ Step III FeO(s) + CO(g) - CO₂(g) + Fe(s) AH = -11.0 kJ The molar enthalpy of reaction for Fe₂O3(s) in the reaction represented by Step I is Record your 3-digit answer. Include sign; do not include units. Potential Energy (kJ) AH-514.1 kJ Reactants ACH° +374.1 kJ Which steps in the above process can be represented by the following potential energy diagram? Select one: O Step II only O Steps I and III O Steps I, II and III O None of the above…arrow_forwardq4arrow_forwardLabel each reactant and product in the given chemical reaction. R F V CH4 96 5 G Search or type URL T + 20₂ G B tv 6 Y H Answer Bank product MacBook Pro N 9 U J CO₂ reactant 00 M 1 K ģ 69 + I O 2H₂0 L O command P Λ' : ; I option { [ ? = 1 O I } 1 delearrow_forward
- 1. Which of the following conditions describe the two step reaction energy profile below? (choose all that apply) Ea PE - ΔΕ Reaction Coordinate The first step is the rate determining step The first step is exothermic The second step is the rate determining step The second step is exothermic The overall reaction is endothermicarrow_forwardFor which reaction below would you expect to have the largest orientation factor (p)?(a) N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g)(b) O3(g) + O(g) → 2 O2(g)(c) CH3OH(l) + HCl(g) → CH3Cl(l) + H2O(l)(d) 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g)arrow_forwardGood hand written explanation Asap thanks Consider the reaction: AC (g) + 2 B (g) ↔ AB2 (g) + C (g) ΔH = -224.5 kJ The system is sitting at equilibrium. Describe what will happen when each of the following stresses are applied. The reaction will shift to the right.The reaction will shift to the left.The reaction will not be affected by this. B is selectively removed from the reaction vessel. The reaction will shift to the right.The reaction will shift to the left.The reaction will not be affected by this. Additional C is added to the reaction vessel. The reaction will shift to the right.The reaction will shift to the left.The reaction will not be affected by this. The temperature of the reaction vessle was raised.arrow_forward
- Choose the LEAST favorable reaction. If images/letters are not displaying correctly, try maximizing your screen. E+ E+ E* LE HO, `OH HO, `OH E REACTION A REACTION B REACTION C O REACTIONA O REACTION B O REACTION C O ALL ARE EQUALLY FAVORABLE CANNOT BE DETEREMINED FROM THE INFORMATION PROVIDEDarrow_forwardWhat is AG rxn for the following reaction? 3NO2(g) + H₂O() → 2HNO3() + NO(g) Substance AGf (kJ/mol) H₂O(1) HNO3(1) NO(g) NO2(g) -237.2 -79.9 86.7 51.8arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY