
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Chlorine gas can be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of hydrochloric acid with manganese (IV) oxide.
4 HCl(aq) + MnO₂ (s) → MnCl₂ (aq) + 2 H₂O(l) + Cl₂ (g)
A sample of 42.5 g MnO₂ is added to a solution containing 50.9 g HCl.
What is the limiting reactant?
O MnO₂
HC1
What is the theoretical yield of Cl₂?
theoretical yield:
If the yield of the reaction is 84.1%, what is the actual yield of chlorine?
actual yield:
g Cl₂
g Cl₂
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
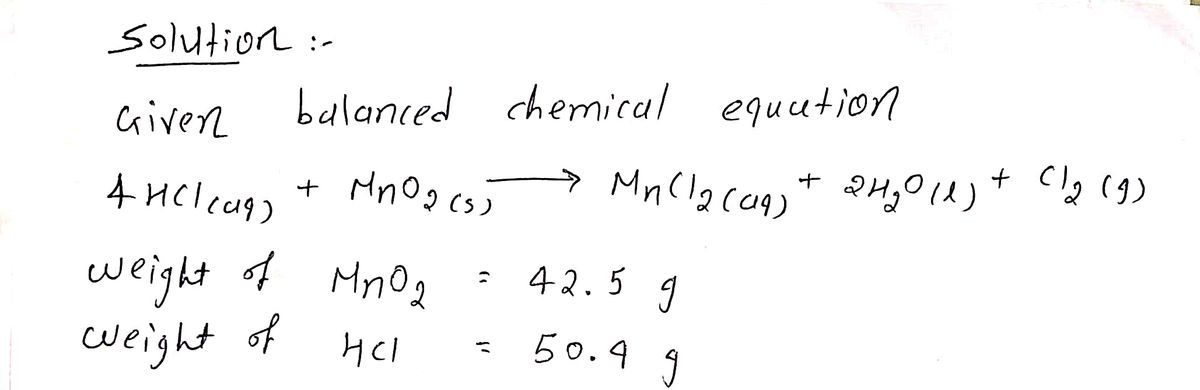
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sodium bicarbonate can be used to neutralize stomach acid, HCl(aq) and costs approximately 50 cents per pound at a grocery store. Your stomach acid is approximately 0.100M HCl. NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) --> NaCl(aq) +CO2(g) + H2O(l) From the balanced molecular equation , how many milligrams of sodium bicarbonate (Molar mass = 84.01 g/mol) can neutralize 125. mL of a 0.100M hydrochloric acid solution ?arrow_forwardWhat mass of precipitate (in g) is formed when 80.0 mL of 0.500 M AlCl₃ reacts with excess AgNO₃ in the following chemical reaction? AlCl₃(aq) + 3 AgNO₃(aq) → 3 AgCl(s) + Al(NO₃)₃(aq)arrow_forwardConsider the following balanced equation:2 H3PO4 (aq) + 3 CaCO3 (aq) → 3 Ca(PO4)2 (aq) + 3 H2O (l) + 3 CO2 (g)A commercial rust remover contains 7.30 mol/L of phosphoric acid, H3PO4.Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate scale inside a coffee maker that can be dissolved(reacts completely) by reacting with 45.0 mL of the phosphoric acid solution.arrow_forward
- The balanced chemical equation is P₄(s) + 6 Cl₂(g) → 4 PCl₃(g). What is the mass in grams of phosphorus trichloride that can be formed from 226.0 grams of chlorine gas based on the balanced chemical equation?arrow_forwardIn the reaction of silver nitrate with sodium chloride, how many grams of silver chloride will be produced from 100. g of silver nitrate when it is mixed with an excess of sodium chloride? The equation for the reaction is below. AgNO 3( aq) + NaCl( aq) → AgCl( s) + NaNO 3( aq)arrow_forwardTable salt (NaCl) is a product of the reaction between HCI and NaOH as seen below. How many grams of NaCl are formed from reaction of 0.467 mol of NaOH? NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) →→ NaCl(aq) + H₂O O 27.3g O 18.7 g O 0.467 g O 8.42 garrow_forward
- How many moles of precipitate are formed when 25.0 mL of 1.00 M FeCl₃ reacts with 28.0 mL of 1.50 M AgNO₃ in the following chemical reaction? FeCl₃ (aq) + 3 AgNO₃ (aq) → 3 AgCl (s) + Fe(NO₃)₃ (aq)arrow_forwardWhat mass of precipitate (in g) is formed when 45.5 mL of 0.300 M Na₃PO₄ reacts with 64.0 mL of 0.200 M Cr(NO₃)₃ in the following chemical reaction? Na₃PO₄(aq) + Cr(NO₃)₃(aq) → CrPO₄(s) + 3 NaNO₃(aq)arrow_forwardA 1.40 g sample of H2X reacts completely with 30.0 mL of 0.400 M NaOH according to reaction: H2X(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → 2H2O(l) + 2NaX(aq) What is the molar mass of H2X?arrow_forward
- What mass of precipitate (in g) is formed when 77.9 mL of 0.500 M FeCl₃ reacts with excess AgNO₃ in the following chemical reaction? FeCl₃(aq) + 3 AgNO₃(aq) → 3 AgCl(s) + Fe(NO₃)₃(aq)arrow_forwardSuppose 0.0350 g Mg is reacted with 10.00 mL of 6 M HCI to produce aqueous magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. Mg(s) + 2HC1(aq) → MgCl2(aq) +H2(g) What is the limiting reactant in this reaction? Select one: Magnesium metal Hydrochloric acid Magnesium chloride Hydrogen gasarrow_forwardWhat mass of precipitate (in g) is formed when 45.5 mL of 0.300 M Na₃PO₄ reacts with 58.5 mL of 0.200 M CrCl₃ in the following chemical reaction? Na₃PO₄(aq) + CrCl₃(aq) → CrPO₄(s) + 3 NaCl(aq)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY