
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
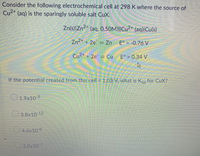
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following electrochemical cell at 298 K where the source of
Cu2+ (aq) is the sparingly soluble salt CuX.
Zn(s)|Zn²* (aq, 0.50M)||Cu²+ (aq)|Cu(s)
Zn2* + 2e = Zn E° = -0.76 V
Cu2+ + 2e = Cu
E° = 0.34 V
If the potential created from this cell = 1.03 V, what is Ksp for CuX?
O 1.9x10-9
3.8x10 12
4.6x10 6
2.0x10 7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Calculate the cell potential for the following reaction that takes place in an electrochemical cell at 25°C. Mg(s) ∣ Mg2+(aq, 1.74 M) || Cu2+(aq, 0.0053 M) ∣ Cu(s)arrow_forwardWhat is the cell potential of the following electrochemical cell? (Report your answer to 2 significant figures.) Co(s) | Co²+ (aq, 0.31 M || Co²+ (aq, 0.035 M) | Co(s) Co²+/Co(s) = -0.28 V Eºred 1 2 4 7 +/- 5 8 v 3 6 9 0 X с x 100arrow_forwardIf you said it was possible to calculate the cell voltage, do so and enter your answer here. Round your Ov answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- For the galvanic (voltaic) cell Fe(s) + Mn²⁺(aq) ⟶ Fe²⁺(aq) + Mn(s) (E° = 0.77 V at 25 °C), what is [Fe²⁺] if [Mn²⁺] = 0.030 M and E = 0.78 V? Assume T is 298 Karrow_forwardWrite the half-reactions as they occur at each electrode and the net cell reaction for this electrochemical cell containing indium and cadmium. In(s)||In3+(aq)‖‖Cd2+(aq)||Cd(s)In(s)|In3+(aq)‖Cd2+(aq)|Cd(s) anode: cathode: net cell reaction:arrow_forwardFor the cell: Zn(s) + 2H† (aq) →→ Zn2+(aq) + H2 (g) If [Zn2+] = 1 M, PH2 = 1 atm, and E = 0.123 V what is pH?arrow_forward
- Consider a galvanic electrochemical cell constructed using Cr/Cr³⁺ and Zn/Zn²⁺ at 25 °C. The following half-reactions are provided for each metal: Cr³⁺(aq) + 3 e⁻ → Cr(s) E°red = -0.744 V Zn²⁺(aq) + 2 e⁻ → Zn(s) E°red = -0.763 V Given that the standard cell potential is 0.019 V and the overall equation is 2 Cr³⁺ (aq) + 3 Zn (s) → 2 Cr (s) + 3 Zn²⁺ (aq), what is the cell potential for this cell at 25 °C when [Zn²⁺] = 0.0323 M and [Cr³⁺] = 0.1736 M?arrow_forwardA galvanic cell consists of a Ni/Ni²+ half-cell and a Co/Co²+ half-cell with initial concentrations: [Ni²+] = 0.80M and [Co²+] = 0.20 M at 298.15 K. half-reaction Eº (V) Ni²+ (aq) +2e→Ni(s) -0.25 Co²+ (aq) +2e→Co(s) -0.28arrow_forwardConsider the following voltaic cellat 25°C: Al(s) | Al3*(0.20 M, aq) || Al3+(0.75 M, aq) | Al(s) If the standard reduction potential for the Al3+(aq) /Al(s) redox couple is -1.66 V, what is the overall cell reaction and the cell potential of the voltaic cell shown above? (Reference the cell as written above.) The overall cell reaction is Al3+(0.75 M, aq) AIS*(0.20 M, ag) and E°cell = +0.0113 V. There is no overall cell reaction and E°cell = 0.00 V. The overall cell reaction is Al3+(0.20 M, aq) Als*(0.75 M, aq) and E°cell = +0.0113 V. The overall cell reaction is Al3+(0.20 M, aq) →A13+(0.75 M, ag) and E°cell| = -0.0113 V. The overall cell reaction is Al3*(0.75 M, aq) →AI3*(0.20 M, aq) and E°cell = -0.0113 V. None of thesearrow_forward
- A chemist designs a galvanic cell that uses these two half-reactions: half-reaction standard reduction potential 2+ Zn (aq)+2e - Zn(s) :-0.763 V (red |Cro (aq)+4 H2O(1)+3e Cr(OH)3(s)+5OH (aq) :-0.13 V = - (red Answer the following questions about this cell. Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that happens at the cathode. x10 Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that happens at the anode. Write a balanced equation for the overall reaction that powers the cell. Be sure the reaction is spontaneous as written.arrow_forwardWhich of the following reactions occurs at the anode of an electrochemical cell composed of Zn│Zn2+(aq) and Fe│Fe2+(aq) half-cells? Their reduction potentials are as follows: Zn2+ + 2e– --> Zn; Eo = -0.763 V Fe2+ + 2e– --> Fe; Eo = -0.447 V (A) Zn2+ + 2e– --> Cr; (B) Zn --> Zn2+ + 2e–; (C) Fe --> Fe2+ + 2e–; (D) Fe2+ + 2e– --> Fe;arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY