
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Question**: The following chemical transformations involve multistep mechanisms. Please write a reasonable mechanism for each transformation and label each elementary step.
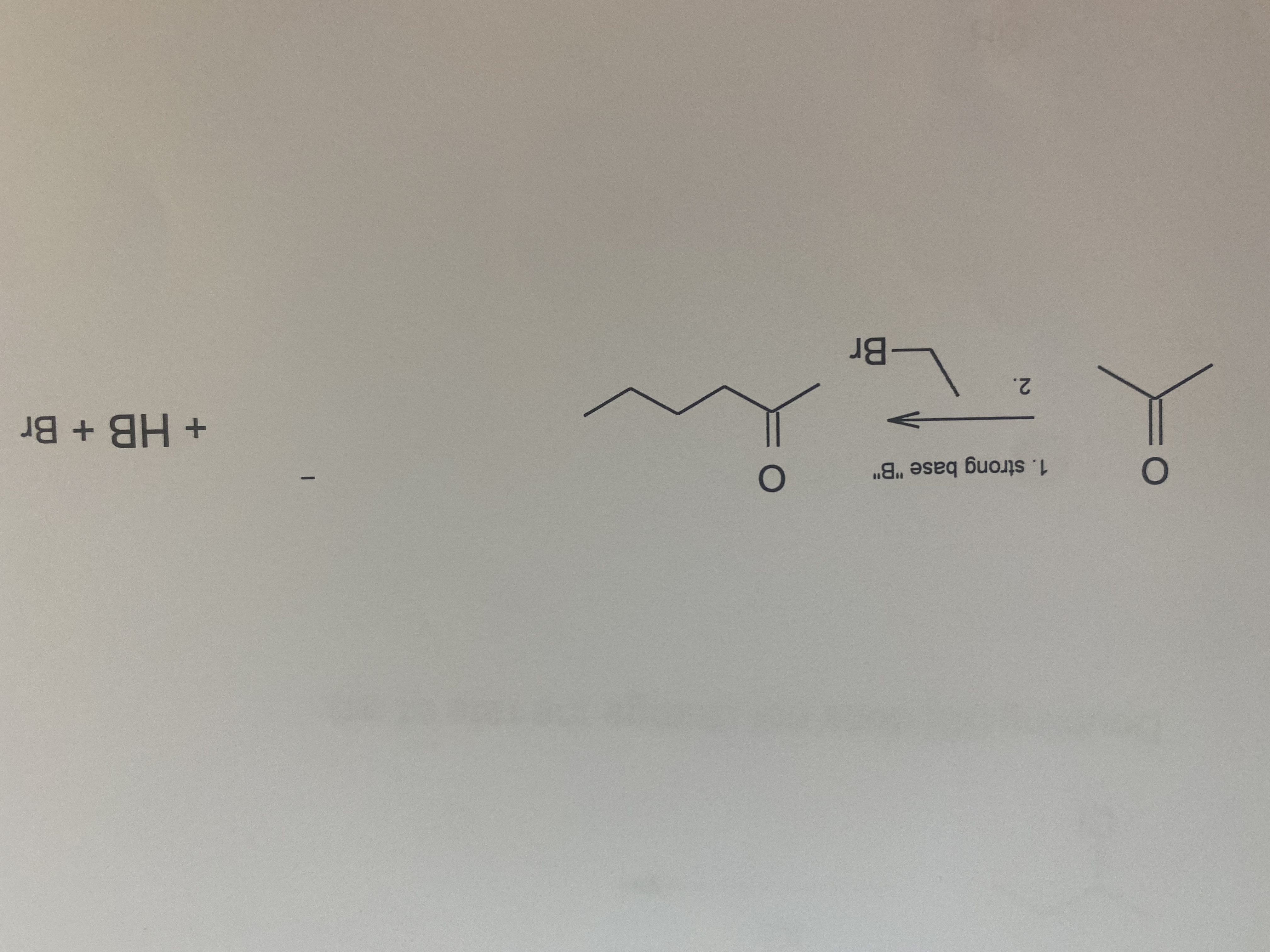
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription of Reaction Mechanism**
**Chemical Reaction:**
Starting Material:
- 2-butanone (C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>8</sub>O)
Reagents:
- 1. Strong base "B"
- 2. Bromoethane (C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>5</sub>Br)
Product:
- 4-heptanone (C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>14</sub>O)
Byproducts:
- HB
- Br<sup>-</sup>
**Mechanism Explanation:**
1. **Deprotonation Step:**
- The strong base "B" abstracts a hydrogen ion from the methyl group at position 2 of butanone, generating an enolate ion.
2. **Alkylation Step:**
- The enolate ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon in bromoethane, leading to the substitution and formation of a new C-C bond. This produces 4-heptanone as the main product while generating hydrogen bromide (HB) and bromide ion (Br<sup>-</sup>) as byproducts.
This reaction illustrates a typical alkylation of enolates using a strong base to form ketones from smaller ketones and alkyl halides.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each of the following reactions, indicate how the rate of disappearance of each reactant is related to the rate of appearance for each product. 2 H2O2 ---→ 2 H2O + O2 CO + 2 H2 ----> CH3OH B2H6 + 3 O2 ----> B2O3 + 3 H2Oarrow_forwardPayalbenarrow_forwardRecall the reaction in lecture slides #42 and #43: 2 NO2Cl(g) --> 2 NO2(g) + Cl2(g). The proposed mechanism from that example is below. (1) NO2Cl(g) --> NO2(g) + Cl(g)(2) NO2Cl(g) + Cl(g) --> NO2(g) + Cl2(g) If step (1) is the rate-determining step for the reaction, what is the reaction rate law? Group of answer choices rate = k [NO2Cl] rate = k [NO2Cl]2 rate = k [NO2Cl][Cl] rate = k [NO2Cl]2 [NO2]2 [Cl2] There is not enough information provided to predict the rate law.arrow_forward
- Parts A - D.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction. From the given choices of intermediates, choose the 5 related to this reaction and put them in order to describe the complete mechanism (all the steps involved) for this reaction.arrow_forwardWS-2.10: Draw the mechanism and list the elementary steps for reaction. H₂O TfOH Uarrow_forward
- for the reaction 2Fe2 + + H2O2 = 2Fe3 + + 2OH- the rate of formation of Fe3 + ions is given by the kinetic equation V = k [Fe2 +] [H2O2] .Propose a mechanism for the reaction and show the order for each elementary reaction.arrow_forwardThe following initial rate data are for the reaction of tertiary butyl bromide with hydroxide ion at 55 °C: (CH3)3CB + OH → (CH3)3COH + Br Experiment [(CH3)3CB1],, M [OH], M Initial Rate, Ms-1 1 0.890 1.50x10-3 1.50x10-3 3.01x10-3 3.01x10-3 0.118 0.118 2 1.78 0.890 1.78 3 0.237 4 0.237 Complete the rate law for this reaction in the box below. Use the form k[A]j™[B]" , where '1' is understood for m or n and concentrations taken to the zero power do not appear. Don't enter 1 for m or n Rate = From these data, the rate constant isarrow_forward0 State what rate law you would expect from this mechanism (Rate = k[Acetone]"[H*]"[[₂]') • Compare the expected rate law from the mechanism to the rate law you got from the Method of Initial rates and the Method of Isolation. If they are different, suggest 1-2 valid, specific, experimental reasons why they might be different. (fast, equilibrium) CH3 ソース H3C ག་ CH3 + H* = H3C H3C H. + H (slow) CH3 H3C CH2 + ↳2 Т + HIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY