
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
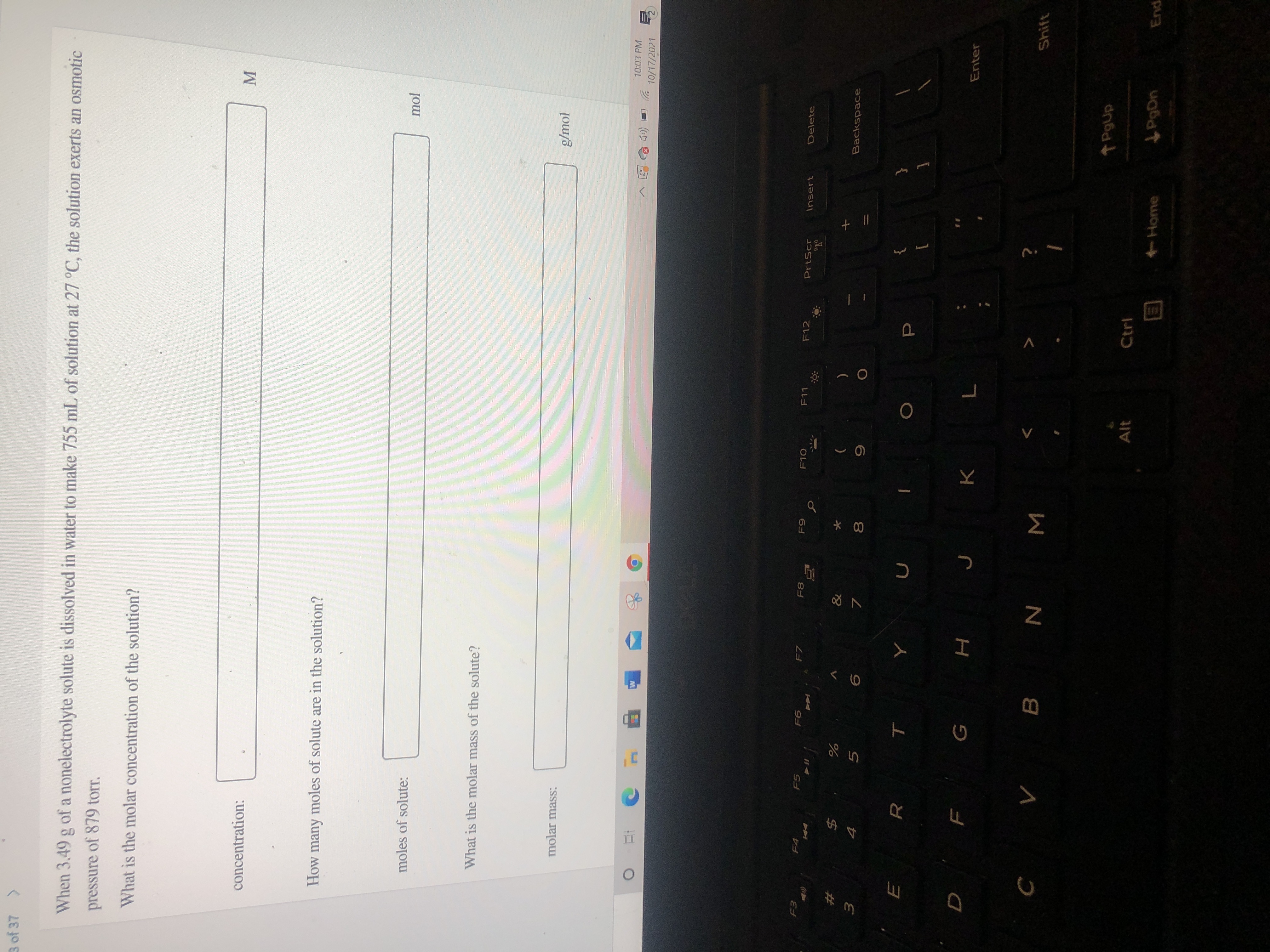
Transcribed Image Text:**Osmotic Pressure and Molar Concentration Calculation**
When 3.49 g of a nonelectrolyte solute is dissolved in water to make 755 mL of solution at 27 °C, the solution exerts an osmotic pressure of 879 torr.
**Questions:**
1. **What is the molar concentration of the solution?**
- **Concentration:** ___________ M
2. **How many moles of solute are in the solution?**
- **Moles of solute:** ___________ mol
3. **What is the molar mass of the solute?**
- **Molar mass:** ___________ g/mol
**Instructions:**
- Use the ideal gas law equation for osmotic pressure: \(\Pi = iMRT\), where:
- \(\Pi\) = osmotic pressure (in atms, convert torr to atm)
- \(i\) = van't Hoff factor (for nonelectrolytes, \(i = 1\))
- \(M\) = molarity (moles/L)
- \(R\) = ideal gas constant (\(0.0821 \, \text{L atm/mol K}\))
- \(T\) = temperature in Kelvin
- Convert the temperature from Celsius to Kelvin.
- Calculate the molar concentration from the given osmotic pressure.
- Calculate the number of moles of solute using the molarity and volume.
- Determine the molar mass using the mass of the solute and the number of moles calculated.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given :-
Mass of non-electrolyte solute = 3.48 g
Volume of solution = 755 mL
Temperature = 27°C
Osmotic pressure = 879 torr
To be calculated :-
- Molar concentration of solution
- Number of moles of solute
- Molar mass of solute
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When 3.61 g of a nonelectrolyte solute is dissolved in water to make 375 mL of solution at 29 °C, the solution exerts an osmotic pressure of 821 torr. What is the molar concentration of the solution? concentration: How many moles of solute are in the solution? moles of solute: What is the molar mass of the solute? molar mass: M mol g/molarrow_forwardCalculate the molality of a solution formed by adding 2.60 g NHCl to 19.1 g of water. molality: m NH₂Clarrow_forwardA student dissolves 6.7 g of biphenyl (C12H10) in 425. mL of a solvent with a density of 1.05 g/mL. The student notices that the volume of the solvent does not change when the biphenyl dissolves in it. Calculate the molarity and molality of the student's solution. Round both of your answers to 2 significant digits. molarity Ox10 olo Ar molality 미arrow_forward
- please help with the following questiongarrow_forwardAn aqueous solution containing 9.15 g of a certain non-electrolyte has a volume of 590 mL. The solution's osmotic pressure at 25 °C was found to be 1.75 torr. Calculate the molar mass of the compound. 2.17×10-1 g/mol 2.17×102 g/mol 1.38×104 g/mol 1.65×105 g/mol 1.67×107 g/molarrow_forwardWhat is the mole fraction of solute in a 3.79 ?3.79 m aqueous solution?arrow_forward
- What is the mole fraction of solute in a 3.12 m aqueous solution? Xsolute = x10 TOOLSarrow_forwardWhen 2.60 g of a nonelectrolyte solute is dissolved in water to make 275 mL of solution at 29 °C, the solution exerts an osmotic pressure of 915 torr. What is the molar concentration of the solution? concentration: How many moles of solute are in the solution? mol moles of solute: What is the molar mass of the solute? molar mass: g/molarrow_forwardWhat is the mole fraction of solute in a 3.69 m aqueous solution? Xsolute = x10 TOOLSarrow_forward
- An aqueous solution of a compound used in antifreeze has an osmotic pressure of 0.589 atm at 20.0°C. It is prepared by dissolving 1.14 g of the compound in enough water to make 0.750 L of solution. What is the molar mass of the antifreeze compound? O 62.1 g/mol O 124 g/mol O 82.8 g/mol O 54.4 g/mol O 4.23 g/molarrow_forwardexplain step by steparrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of a solution of NaCl (molar mass is 58.44 g/mol) that is prepared by dissolving 3.25 g of NaCl in water and diluting to a final volume of 50.0mL?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY