
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
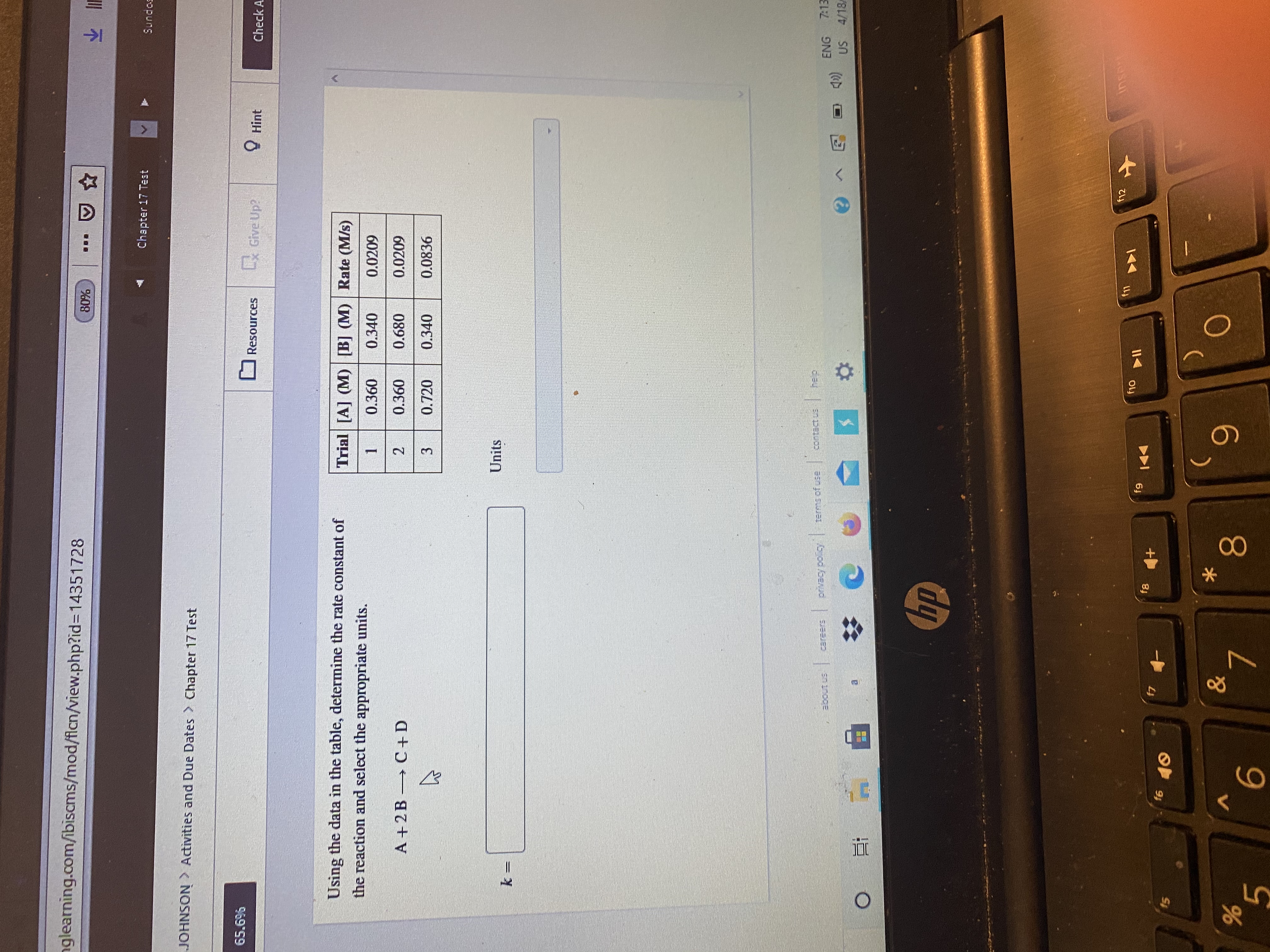
Using the data in the table, determine the rate constant of the reaction and select the appropriate unit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the rate law for the reaction A + B - C+D given the following experiment data. Trial [A]o 1 0.25 0.75 0.50 0.75 4.arrow_forwardThe half-life of a pesticide determines its persistence in the environment. A common pesticide degrades in a first-order process with a half-life of 6 days. What fraction (in decimal notation) of the pesticide remains in the environment after 20 days? Enter to 4 decimal places.arrow_forwardWrite true if the statement is true, otherwise change the underlined word to make the statement true. 1. Metal A has a higher specific heat than metal B. If the two metals are independently applied with equal heat, it is expected that metal A will have a higher change in temperature. 2. The units for the rate constant of an over-all 1st order reaction is s', when the reaction time is measured in seconds. 3. If K is much greater than 1 (that is, K>>1), the equilibrium will favor the formation of reactants. 4. In the iron-thiocyanate system, increasing the pH would produce a dark orange solution. 5. For a weak acid HA, the equilibrium concentration of H3O* is equal to [HA]i. 6. The buffer region is the pH range where a buffer effectively neutralizes added acids and bases, while maintaining a relatively constant pH. A buffer can be expressed by the Henderson-Hasselbaich equation. 7. 8. Diluting a concentrated weak base, results to an increase in pH. 9. The plot of absorbance versus…arrow_forward
- 2. Imagine you run a reaction whose free energy of activation (AG*) is 18 kcal/mol. If it were a first order reaction, its’ half life (the time for half the starting material to go away) or half the product to form (assuming a 100% yield) would by In2/k where k is the rate constant. How long will it take for the reaction to be done if you run the reaction in an ice-salt bath at room temperature (20 °C) if the rate constant were 1 x 104/sec?arrow_forwardA student runs a kinetics experiment and finds that the reaction order with respect to fictional reagent X is second order. What happens to the initial rate of the reaction if they run a trial where the concentration of X is doubled.arrow_forwarda)What is the average reaction rate between 0. and 1500. s? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. b)What is the average reaction rate between 500. and 1200. s ?Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. c)What is the instantaneous rate of the reaction at t=800.s? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- The rate of a certain reaction was studied at various temperatures. The table shows temperature (?) and rate constant (?) data collected during the experiments. Plot the data to answer the questions. What is the value of the activation energy, ?a , for this reaction? What is the value of the pre‑exponential factor (sometimes called the frequency factor), ? , for this reaction? Temperature (K) k (s^-1) 400 0.0000173 580 7.43arrow_forwardProblem 2 Consider the following reaction between nitrogen dioxide gas and carbon monoxide gas 21 + 2H* + H2O2 → I2 + 2H20 (g) The experimentally determined rate law for this reaction is Rate = k [I"] [H2Oz]. The following mechanism has been proposed I + H2O2 → HOI + OH" HOI + I → OH" + I2 (g) Slow Fast H* + OH" → H2O Fastarrow_forwardFor reactions that follow either first order or second order rate laws, the slope of the linear fit can be used to determine none of these the final concentration of products the rate law constant the initial concentration of the reactantsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY