
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![**Combustion Analysis of an Organic Compound**
A 7.478 gram sample of an organic compound containing carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) is analyzed through combustion analysis. The process produces 19.34 grams of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and 3.959 grams of water (H₂O).
In a separate experiment, the molar mass is determined to be 136.2 g/mol. Use this information to determine the empirical formula and the molecular formula of the organic compound.
**Enter the elements in the order C, H, O:**
- Empirical formula = [____]
- Molecular formula = [____]
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram depicted is a combustion analysis apparatus. It includes:
- **Furnace:** The main unit where the sample is heated.
- **Sample (labelled):** The organic compound under analysis.
- **H₂O Absorber:** A unit that captures the water produced during combustion.
- **CO₂ Absorber:** A unit that captures the carbon dioxide produced during combustion.
These components work together to analyze the combustion of an organic compound, allowing for the measurement of CO₂ and H₂O produced, which are critical for determining the composition of the compound.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/144ac4d4-58bf-4a39-b1bc-5bb4c77f8379/3ef005d8-ced5-4554-82d7-144ba86adfb1/amxkix.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Combustion Analysis of an Organic Compound**
A 7.478 gram sample of an organic compound containing carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) is analyzed through combustion analysis. The process produces 19.34 grams of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and 3.959 grams of water (H₂O).
In a separate experiment, the molar mass is determined to be 136.2 g/mol. Use this information to determine the empirical formula and the molecular formula of the organic compound.
**Enter the elements in the order C, H, O:**
- Empirical formula = [____]
- Molecular formula = [____]
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram depicted is a combustion analysis apparatus. It includes:
- **Furnace:** The main unit where the sample is heated.
- **Sample (labelled):** The organic compound under analysis.
- **H₂O Absorber:** A unit that captures the water produced during combustion.
- **CO₂ Absorber:** A unit that captures the carbon dioxide produced during combustion.
These components work together to analyze the combustion of an organic compound, allowing for the measurement of CO₂ and H₂O produced, which are critical for determining the composition of the compound.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
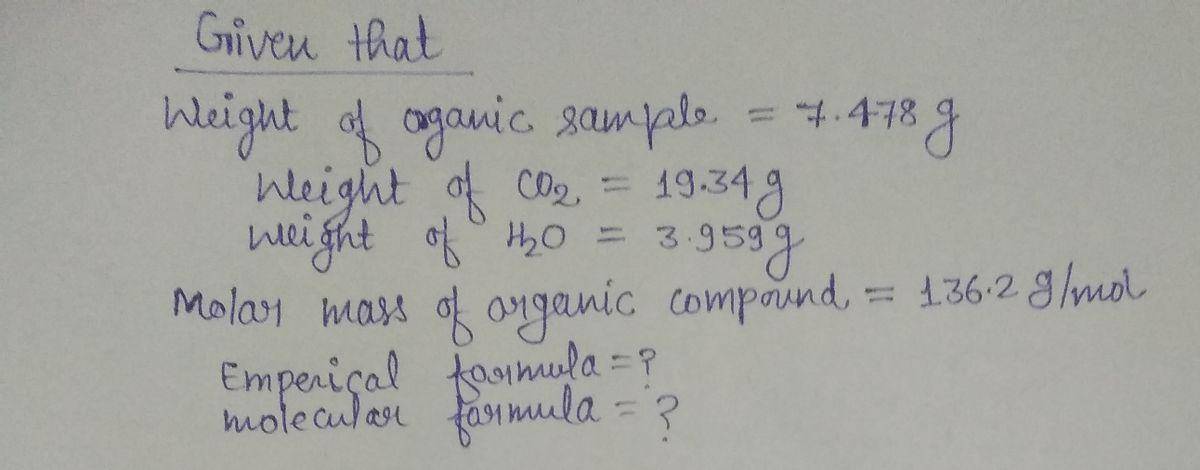
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the product of the reaction? HO. a. heat .OH ob. Ос o d. oe. 8 "" 4 HO. H of.arrow_forwardBased on the following reaction: 3 CO + Fe2O3 2 Fe + 3 CO2 What is the mole ratio of carbon monoxide to iron(III) oxide that react? A. 3:2 B. 1:2 C. 3:3 D. 1:3 E. 3:1arrow_forwardZOOM + 1. Calculate the molar mass of the following compounds. a. magnesium phosphate b. sodium sulfide c. dinitrogen tetroxide 2. Determine the molar mass of these ceramic materials. а. HfN b. ThO2 с. ВаTiO; 3. A chemist needs exactly 2 moles of NAOH to make a solution. What mass of NaOH must be used? 4. What mass of ozone (O3) gives 4.5 moles of the substance?5 5. Calculate the mass in the grams of each the following. a. 2.5 mol of aluminum b. 1.25×10-3 mol of iron c. 0.015 mol of calcium d. 653 mol of neon 6. Calculate the mass in grams of 13.5 mol of a. vinyl chloride, C,H3CI, the starting material for a plastic b. capsaicin, C13H27NO3, the substance that makes red chili peppers "hot" c. stearic acid, C13H36O2, used in soaps 7. How many moles are present in the given quantities of explosives? a. 358.1 g trinitrotoluene (TNT), C,H;N;O6 b. 82.6 g nitromethane, CH3NO2 c. 1.68 kg RDX, C;H,N,O6 8. How many H atoms are present in 7.52 g of propane, C3H3? 9. How many O atoms are present…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY