
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
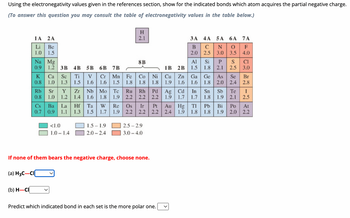
Transcribed Image Text:Using the electronegativity values given in the references section, show for the indicated bonds which atom acquires the partial negative charge.
(To answer this question you may consult the table of electronegativity values in the table below.)
(a) H3C-CI
1A 2A
Li Be
1.0 1.5
(b) H-CI
Na Mg
0.9 1.2 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B
K Ca Sc Ti
0.8
1.0 1.3 1.5
Rb Sr Y Zr
0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4
V
1.6
<1.0
1.0-1.4
Nb Mo
1.6
1.8
Cr Mn Fe Co
1.6 1.5
1.8
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os
H
2.1
8B
1.5-1.9
2.0-2.4
8122=2
Tc Ru
1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2
Ir
If none of them bears the negative charge, choose none.
Ni
1.8
Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te
1.9 1.7 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.1
2.5-2.9
3.0-4.0
3A 4A 5A 6A 7A
B
C
N O F
2.0
2.5
3.0 3.5
4.0
Al
1B 2B 1.5
Cu Zn
1.9 1.6
Predict which indicated bond in each set is the more polar one.
Si P
1.8 2.1
S
2.5
Ga Ge As Se
1.6
1.8 2.0 2.4
0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 1.9 1.8 1.8 1.9 2.0 2.2
CI
3.0
Br
2.8
I
2.5
Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A)review the section on Bond Polarity and Partial Ionic Character and the figure that has an ionic character on the Y-axis and delta EN on the X axis (see page 393). Review the graph and Critique the following statement: HF is a covalent molecule and LiI is an ionic compound. Provide as much detail and explanation as possible!arrow_forwardConsider an ionic compound, MX, composed of generic metal M and generic, gaseous halogen X. The enthalpy of formation of MX is Δ?∘f=−565. The enthalpy of sublimation of M is ΔHsub=115 kJ/mol. The ionization energy of M is IE=461 kJ/mol. The electron affinity of X is ΔHEA=−323 kJ/mol. The bond energy of X_2 is BE=205 kJ/mol. Determine the lattice energy of MX.arrow_forwardUsing the electronegativity values given in the references section, show for the indicated bonds which atom acquires the partial negative charge. (To answer this question you may consult the table of electronegativity values in the table below.) H 2.1 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A Li Be B с N 0 F 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Na Mg 8B Al Si P CI S 1.8 2.1 2.5 0.9 1.2 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 1B 2B 1.5 3.0 K Ge As Se Br Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni 1.0 1.3 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.5 1.8 1.8 1.8 Cu Zn Ga 1.9 .6 1.6 0.8 1.8 2.4 2.8 Rb Sr Y Zr 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 Nb Mo Te Ru Rh Pd 1.6 1.8 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 Ag Cd In Sn 1.9 1.7 Sb 1.7 1.8 1.9 2.1 Te I 2.5 TI Pb Bi Po Cs Ba La Hf 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.4 1.9 At 2.2 1.8 1.8 1.9 2.0 1.5-1.9 2.5-2.9 <1.0 1.0-1.4 2.0-2.4 3.0-4.0 If none of them bears the negative charge, choose none. (a) H3C-PH₂ (b) CH3P(H)-H Predict which indicated bond in each set is the more polar one. 8arrow_forward
- Consider the generic Lewis dot symbol for an element. Which element could this symbol represent? N O C Na F Ne B Ca X.arrow_forward3) For each of the compounds MgO, Br2 and HBr:(a) What are the two atoms that formed each molecule?(b) What is their electronegativity difference between the atoms in each molecule?(c) What type of bond is formed in each molecule?(d) Are the electrons shared or transferred between the atoms in each molecule?arrow_forward(a) The 03 molecule has a central oxygen atom bonded to two outer oxygen atoms that are another. In the box below, draw the Lewis electron-dot diagram of the 03 molecule. Include all valid resonance structures. 0 - 0 = 0 (b) Based on the diagram you drew in part (a), what is the shape of the ozone molecule? and trigonal Bent Ozone decomposes according to the reaction represented below. 2 03(g) → 3 0₂(8) (c) The bond enthalpy of the oxygen-oxygen bond in O₂ is 498 kJ/mol. Based on the enthalpy of the reaction represented above, what is the average bond enthalpy, in kJ/mol, of an oxygen-oxygen bond in 03 ? Ozone can oxidize HSO3(aq), as represented by the equation below. [0] 1.0 x 10-5. <-> 00: HSO3(aq) + O3(aq) → HSO4 (aq) + O₂(8) A solution is prepared in which the initial concentration of HSO₂ (aq) (6.4 × 10+ M) is much larger than that of O3(aq) (1.0 × 10-5 M). The concentration of O3(aq) is monitored as the reaction proceeds, and the data are plotted in the graph below. 8.0 x…arrow_forward
- Write the empirical formula of at least four binary ionic compounds that could be formed from the following ions: Mg²+, Al³+, I, 0²- 0,0,... Xarrow_forwardExplain in terms of the distribution of charge, why H2O is considered a nonpolar compound.arrow_forwardArrange the single covalent bonds within each set in order of INCREASING polarity. If: • most polar is b • medium polarity is c • least polar is a this leads to the following input: acb (To answer this question you may consult the table of electronegativity values in the table below.) 1A 2A Li Be 1.0 1.5 Na Mg 0.9 1.2 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B K 0.8 1.0 1.3 Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.5 1.8 Rb 0.8 Sr 1.0 Y 1.2 <1.0 1.0-1.4 1. a) C-H b) P-H c) Br-H Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os 0.7 0.9 1.1 1.3 1.5 1.7 1.9 2.2 2. a) P-H b) O-H c) N-H Zr 1.4 1.6 1.8 1.9 2.2 H 2.1 1.5-1.9 2.0-2.4 8B Nb Mo Te Ru Rh 8222=2 Co Ni 1.8 1.8 2.5-2.9 3.0-4.0 Pd 2.2 Pt 2.2 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A B C N 0 F 2.5 2.0 3.0 3.5 4.0 Al 1.5 1B Cu 1.9 1.6 1.6 2B Zn Ga Ge 1.8 Au Hg 2.4 Si P S CI 1.8 2.1 2.5 3.0 Ag Cd In Sn 1.9 1.7 1.7 1.8 TI Pb 1.9 1.8 1.8 As Se Br 2.0 2.4 2.8 Sb Te I 1.9 2.1 2.5 Bi Po At 1.9 2.0 2.2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY