Question
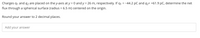
Transcribed Image Text:Charges \( q_1 \) and \( q_2 \) are placed on the y-axis at \( y = 0 \) and \( y = 26 \, \text{m} \), respectively. If \( q_1 = -44.2 \, \text{pC} \) and \( q_2 = +61.9 \, \text{pC} \), determine the net flux through a spherical surface (radius = 6.5 m) centered on the origin.
Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Add your answer:
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Concept
Using Gauss law of electrostatics
The net flux through a closed surface is given by
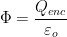
Where Qenc = Charge enclosed by the closed surface, 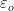 = Permittivity of free space = 8.854 × 10- 12 C2m- 2 N- 1
= Permittivity of free space = 8.854 × 10- 12 C2m- 2 N- 1
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two concentric imaginary spherical surfaces of radius R and 2R respectively surround a positive point charge Q located at the center of the surfaces. Which of the following assumptions is TRUE if you compare the electric flux $1 through the surface of radius R to the electric flux $2 through the surface of radius 2R? a. 42 = 1/4 01 b. 02 = 1/2 01 c. φ2 = $1 d. 42 = 201arrow_forwardanswer please varrow_forwardA hollow sphere of radius .05m contains a negative charge sitting right at its center. (The sphere itself is not charged.) The electric field everywhere on the surface of the sphere has the magnitude 3.0*10^-4 N/C. Draw the sphere and show the electric field vectors on your drawing. What is the total electric flux through the surface of the sphere?arrow_forward
- Charges q, and 92 are placed on the y-axis at y = 0 and y = 25.1 m, respectively. If q, = -46.8 pC and q2= +64 pC, determine the net flux through a spherical surface (radius = 9.5 m) centered on the origin. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardA charge q = +3.05 ?C is located at the center of a regular tetrahedron (a four-sided surface) as in figure below. (a) Find the magnitude of the total electric flux through the tetrahedron. Answer in N · m2/C (b) Find the magnitude of the electric flux through one face of the tetrahedron. Answer in N · m2/Carrow_forwardThe figure below shows a uniform electric field of magnitude E = 470 N/C making an angle of ? = 61.0° with a flat surface of area A = 3.10 m2. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through this surface (in N · m2/C)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios