
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
please help quickly
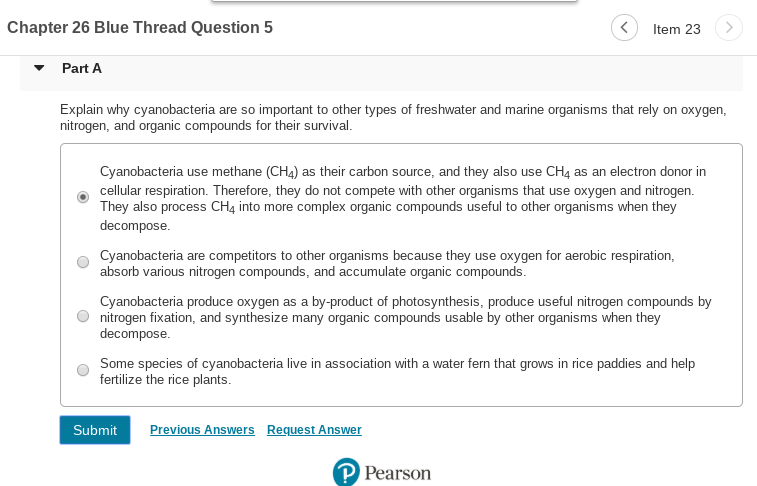
Transcribed Image Text:Chapter 26 Blue Thread Question 5
Item 23
Part A
Explain why cyanobacteria are so important to other types of freshwater and marine organisms that rely on oxygen,
nitrogen, and organic compounds for their survival.
Cyanobacteria use methane (CH4) as their carbon source, and they also use CH4 as an electron donor in
cellular respiration. Therefore, they do not compete with other organisms that use oxygen and nitrogen.
They also process CH4 into more complex organic compounds useful to other organisms when they
decompose.
Cyanobacteria are competitors to other organisms because they use oxygen for aerobic respiration,
absorb various nitrogen compounds, and accumulate organic compounds.
Cyanobacteria produce oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis, produce useful nitrogen compounds by
nitrogen fixation, and synthesize many organic compounds usable by other organisms when they
decompose.
Some species of cyanobacteria live in association with a water fern that grows in rice paddies and help
fertilize the rice plants.
Previous Answers
Request Answer
Submit
P Pearson
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mary O'Keefe calls the Inner City Health Care office in a panic. Gwen Carr, CMA (AAMA), answers the telephone. Mary: "Oh my God, help me. I need Dr. King." Gwen: "This is Ellen Armstrong, Who is this calling? What is the situation?" Mary: "It's my haby, oh God, get Dr. King." Gwen: "Dr. King is unavailable, but we can help you. Now, tell me your name." Mary: "It's Mary O'Keefe. Help me, I think my baby is dead." Gwen: "Are you at home?" Mary: "Yes" Gwen: "Ok. Try to calm down. Speak slowly and tell me what's happened." Mary: "My son Chris pried the plug off an outlet and he's electrocuted himself!" Mary cries. "He's just lying there. I'm so scared, if I touch him, will I electrocute myself? Oh my God, my baby, my baby. What should I do?" Gwen, who has been writing down the details on a piece of paper, motions to Joe Guerrero, another CMA (AAMA) in the office, and hands him her notes. Joe immediately accesses the O'Keefe address from the patient database and uses…arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardB- A C E- F- H- Karrow_forward
- Which letter represents the destination for molecules that get reabsorbed? A .B -Darrow_forwardExplain the physiological and pathophysiological changes that occur with ascent to altitude. I need to write 750 word on this question. can you please help me. Thank youarrow_forwardi was thinking about Aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education