
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Identify the organic
The reactant is a(n)
a. two hemiacetals
b. disaccharide
c. ester
d. ether
e. alcohol pyranoses
The product is a(n)
a. beta 1-6 disaccharide
b. beta 1-4 disaccharide
c. alpha 1-6 disaccharide
d. beta 1-2 disaccharide
e. alpha 1-2 disaccharide
f. alcohol pyranoses
g. alpha 1-4 disaccharide
h. two hemiacetals
The reaction type is:
a. hydrolysis
b. mutarotation
c. reduction (hydrogenation)
d. hemiacetal formation
e. acetal formation
f. oxidation (benedict's)
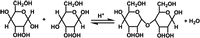
Transcribed Image Text:CH2OH
ÇH2OH
CH2OH
CH2OH
O OH
Но
H
Q OH
H*
Но
+
+ H20
H
H
OH
Но
H
ОНОН
ОНОН
ОНОН
ОНОН
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. In the blanks below, create at least 3 disaccharides by showing which monosaccharides bond:arrow_forwardWhich statements are correct regarding the formation of maltose?A. Hydrolysis reaction between alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucoseB. Condensation reaction between alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucoseC. Condensation reaction between beta-galactose and beta-glucoseD. Hydrolysis of starch into a di-saccharide product a). A and B b). C and D c). B and D d). B and C e). B, C and Darrow_forwardAnswer the following questionsarrow_forward
- Please answer all subparts pertaining to question 5arrow_forwardThe structure has what type of glycosidic linkage? a. b (1®4) b. b (1®6) c. a (1®4) d. a (1®6)arrow_forwardChoose the letter for the statement that is NOT TRUE. If all are true, then circle E. A. Sugars are stored in closed-chain (cyclical) forms to prevent premature breakdown. B. Carbohydrates tend to have a carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone) and multiple alcohols. C. An example of disaccharides is amylose and cellulose D. Amylose can be broken down by our body, but Cellulose cannot. E. All of the above are true. O B O D O A O Earrow_forward
- 1. Consider the following molecules. Clearly circle the glycosidic bond on each structure. In the Spae provided clearly describe the type of glycosidic bond illustrated. HO-CH2 O. H. H. OH HO. HO-CH2 OH H. H. H. OH H. OH Но H. H. H. OH OH HOH2Ç HO OH OH CH2OH HI エー エエーarrow_forward1. Draw the structure of a glucose molecule in hemiacetal (closed ring) form. Be sure to have the -OH groups in the correct orientation. What is the difference between alpha-D- glucose and beta-D-glucose? Indicate with chemical structures. α-D-Glucose B-D-Glucose 2. Why is glucose called a reducing sugar? Draw a chemical structure that clarifies your answer.arrow_forward7. Draw structure for the following compounds. D- fructose C. L-Mannose a - lactose g. B-D- ribose . نه نه ن a. e. i. Small section of amylopectin b. B-D- Galactose d. ß- maltose f. D-2-deoxyribose h. Small section of amylose j. Sucrosearrow_forward
- 12 CH2OH 1 H H 10 OH H H OH 9 6 H OH CH2 O. H H 4K OH OH 1 H H 12 OH isomaltose OH 3 a. Determine any acetal and hemiacetal in isomaltose. Carbon 7 is the acetal carbon. Carbon 1 is the hemiacetal carbon. b. Determine the numbering of each monosaccharide ring. The lower monosaccharide is numbered 5,4,3,2,1 v. The upper monosaccharide is numbered 7,8,9,10,11 c. Classify the glycosidic linkage as a or ß, and determine its location. The glycosidic linkage is B The linkage is 6 → 7. V d. Is the hemiacetal drawn as an a or ß anomer? The hemiacetal is a 00arrow_forwardThe following trisaccharide derivative is important to human health.The A ring is?arrow_forwardCompare the following monosaccharides and choose the best description. a. same sugar b. enantiomers c. diastereomers d. different sugarsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY