
Phlebotomy Essentials
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781451194524
Author: Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)
Publisher: JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Questions are attached
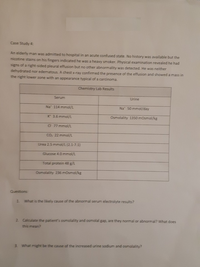
Transcribed Image Text:Case Study 4:
An elderly man was admitted to hospital in an acute confused state. No history was available but the
nicotine stains on his fingers indicated he was a heavy smoker. Physical examination revealed he had
signs of a right-sided pleural effusion but no other abnormality was detected. He was neither
dehydrated nor edematous. A chest x-ray confirmed the presence of the effusion and showed a mass in
the right lower zone with an appearance typical of a carcinoma.
Chemistry Lab Results
Serum
Urine
Na" 114 mmol/L
Na 50 mmol/day
K" 3.6 mmol/L
Osmolality 1350 mOsmol/kg
O 77 mmol/L
Co, 22 mmol/L
Urea 2.5 mmol/L (2.1-7.1)
Glucose 4.0 mmol/L
Total protein 48 g/L
Osmolality 236 mOsmol/kg
Questions:
1. What is the likely cause of the abnormal serum electrolyte results?
2. Calculate the patient's osmolality and osmolal gap, are they normal or abnormal? What does
this mean?
3. What might be the cause of the increased urine sodium and osmolality?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Pleural effusion
It is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production and decreased absorption.
Causes:
- Congestive heart failure
- Cancer
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism.
Management
- Thoracentesis.
- Tube thoracostomy (chest tube).
- Pleural drain.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, nursing and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The membranes that surround and protect the brain and spinal cord are the ______ (plural form).arrow_forwardWhich is reductional division.arrow_forwardQuestion 21 A DRG is based on the following except a patient's: A Secondary diagnosis B) Principal procedure Principal diagnosis D. Discharge diagnosisarrow_forward
- The intracellular fluid compartment includes all water and electrolytes enclosed by _______________.arrow_forwardQuestion 44 Uncertainty of measurement is calculated to give the scientist wiggle-room in their results. O True O Falsearrow_forwardNormal Anatomy – Cystic fibrosis with bullet points great detailsarrow_forward
- Keratin and fibrinogen are examples of _____________ proteins.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Homeostasis is hazardous to complex organisms. O True O False Warrow_forwardCharacteristics (Manifestations) of-9 life through which we cannot understand the life of living organisms and see it True Errorarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning

Phlebotomy Essentials
Nursing
ISBN:9781451194524
Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)
Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.

Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...
Nursing
ISBN:9780323414425
Author:Robert J Hubert BS
Publisher:Saunders

Fundamentals Of Nursing
Nursing
ISBN:9781496362179
Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.
Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,

Fundamentals of Nursing, 9e
Nursing
ISBN:9780323327404
Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNE
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...
Nursing
ISBN:9780323414142
Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.
Publisher:Saunders

Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...
Nursing
ISBN:9781337406291
Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy Corey
Publisher:Cengage Learning