
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
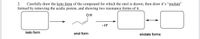
Transcribed Image Text:**Exercise 2: Drawing Keto, Enol, and Enolate Forms**
**Instructions:**
Carefully draw the keto form of the compound for which the enol is drawn; then draw its enolate form by removing the acidic proton, and show two resonance forms of it.
**Diagram Details:**
1. **Keto Form:**
- On the left side of the diagram, there is an empty rectangular box labeled "keto form."
2. **Enol Form:**
- In the middle, there is a structure displaying the enol form of the compound.
- The skeletal structure consists of a double bond between two carbon atoms.
- Attached to one of the doubly-bonded carbons, there is an OH group (hydroxyl group).
- The diagram shows an 'arrow' pointing from the keto form to the enol form.
3. **Enolate Forms:**
- To the right of the enol form, there is an instruction "- H⁺" (indicating the removal of an acidic proton).
- Subsequently, there are two empty rectangular boxes placed horizontally side by side with a bi-directional arrow between them, signifying resonance forms.
- These boxes are labeled "enolate forms."
**Diagram Summary:**
- From left to right: **Keto form** → **Enol form** → **Enolate forms (two resonance forms)**.
Please use the empty boxes to draw the respective structures as per the instructions. Some guidance on the structures:
- **Keto Form:** A carbonyl group (C=O) within the compound.
- **Enolate Form:** Resulting from deprotonation of the enol form, showing resonance between two structures:
1. A carbon-hydrogen double bond (C=C) with a negatively charged oxygen (O⁻).
2. A carbon-hydrogen single bond (C-N) with a negative charge on the carbon (C⁻) adjacent to a double-bond carbon-oxygen (C=O).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the malonic ester synthesis to prepare each carboxylic acid.arrow_forwardDraw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction. The four-membered ring in the starting material and product is called a β-lactam. This functional group confers biological activity on penicillin and many related antibiotics, as is discussed in Chapter 22. (Hint: The mechanism begins with β elimination and involves only two steps.)arrow_forwardIdentify the keto form of each enol tautomer. A. HO. H. B. OH C. HO A1 D. В1 C1 D1 C2 Resetarrow_forward
- Identify the enol form of each keto toutomer. A. OH B. C. D1 C. B1 B. HOT HO. D. D. A1 C1arrow_forward7. When the following ketone is treated with sodium hydroxide, two different enolates can form. a. Draw the two enolates, including an arrow pushing mechanism for their formation and any relevant resonance structures. NaOH b. Which enolate is favored when using sodium hydroxide as the base? Explain. c. Predict the product of the reaction and include an arrow-pushing mechanism. 1. NaOH 2. Brarrow_forwardmixed Claisen condensation of methyl benzoate with methyl propanoate 1 gives * 3-ethyl-2-methyl-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate O ethyl-2-methyl-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate O Methyl-2-methyl-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate 3-Methyl-2-methyl-3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoate Micheal reaction of 2-methyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione with methylvinylketone 1 2-methyl-2-(3-oxobutyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedion 4-methyl-2-(3-oxobutyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedion 3-methyl-2-(3-oxobutyl)-1,3-cyclohexanedionarrow_forward
- 1. You have an alkyl halide and the product has a thiol group without an alkyl, what is the reagant? 2. What is the reaction of disodium sulfide and Na2S, what is its product? 3. You have a thiol compound that reacts with sodium hydroxide, what do you get? 4. You have an oxyrane reacting with sulfuirc acid and methanol, what do you get? 5. Have an alkene reacting with Br, what do you get?arrow_forwardDraw the keto and enol form of the following compounds and identify the number of acidic hydrogen. a) 1,2-dihydronapthalen-2-one b) 2-Methyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl acetatearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY