
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
11
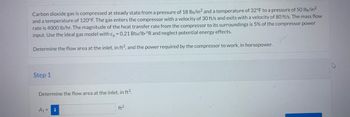
Transcribed Image Text:Carbon dioxide gas is compressed at steady state from a pressure of 18 lb/in² and a temperature of 32°F to a pressure of 50 lb/in²
and a temperature of 120°F. The gas enters the compressor with a velocity of 30 ft/s and exits with a velocity of 80 ft/s. The mass flow
rate is 4000 lb/hr. The magnitude of the heat transfer rate from the compressor to its surroundings is 5% of the compressor power
input. Use the ideal gas model with cp = 0.21 Btu/lb-ºR and neglect potential energy effects.
Determine the flow area at the inlet, in ft2, and the power required by the compressor to work, in horsepower.
Step 1
Determine the flow area at the inlet, in ft².
A₁ = i
ft²
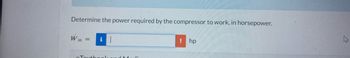
Transcribed Image Text:Determine the power required by the compressor to work, in horsepower.
Win
=
i
Textbook-M
! hp
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 55 kmol per hour of air is compressed from P1 = 1 bar to P2 = 6.1 bar in a steady flow compressor. Delivered mechanical power is 98.9 kW. Temperatures and velocities are: T1 = 301K T2 = 520 K, u1 = 10.8 m/s and u2 = 3.8 m/s. Estimate the rate of heat transfer from the compressor in kW, 3 decimal values. Assume that Cp = 7/2R and that enthalpy is independent of pressure.arrow_forwardSteam enters the nozzle operating a steady state pressure of 2.5 MPa and a temperature of 300 °C ( H1 = 3008.8 kJ/kg) and leaves at a pressure of 1.7 MPa with a velocity of 470 m/s. The rate of flow of steam through the nozzle is 1360 kg/hr. Neglecting the inlet velocity of the steam and considering the flow in the nozzle is adiabatic, find:a. the exit enthalpy in kJ/kg, ( H2)b. the nozzle exit area ( in cm) if V exit is 0.132 m^3 /kgc. the systemarrow_forwardThe volumetric flow rate of an ideal gas in a pipe is 3.51lt/sec. If the temperature of the gas is T=300°K and the pressure is 1bar, determine the mass flow rate of the gas in the pipe. The specific gas constant is R=287J/(kg.°K). Present your answer in grams per second (gram/s).arrow_forward
- I am getting lost in this practice problem for thermodynamics - thank you! Air at 100 kPa and 280K is compressed steadily to 600 kPa and 400K in an air compressor. The mass flow rate of air through the compressor is 0.02 kg/s and the compressor a heat loss of 16 kJ/kg from the compressor occurs. Assuming steady state steady flow conditions and ideal gas behavior (with constant specific heats, Cp=1.009 kJ/kgK, R=0.287 kJ/kgK, determine: a) The necessary power in put to the compressor(kW).b) The volumetric flow rate of air at the exit of the compressor (m3/s).arrow_forwardAir at 15 degree Celsius and 95 kpa enters the diffuser of a jet engine and steadily with a velocity of 250 m/s. The inlet area of the diffuser is 0.5 m^2. The air leaves the diffuser with a velocity that is very small compared with the inlet velocity. Find the mass flow of air, temperature of air leaving diffuser, power and rate of heat transfer within diffuser.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide gas is compressed at steady state from a pressure of 20 Ibf/in? and a temperature of 32°F to a pressure of 50 Ibf/in? and a temperature of 120°F. The gas enters the compressor with a velocity of 30 ft/s and exits with a velocity of 80 ft/s. The mass flow rate is 2500 Ib/hr. The magnitude of the heat transfer rate from the compressor to its surroundings is 5% of the compressor power input. Use the ideal gas model with cp = 0.21 Btu/lb.°R and neglect potential energy effects. Determine the flow area at the inlet, in ft2, and the power required by the compressor to work, in horsepower.arrow_forward
- 4. In a steady flow apparatus,135kJ of work is done by each kg of fluid. The specific volume of the fluid, pressure and speed at the inlet are 0.37 m3/kg, 600 kpa, and 16 m/s. The inlet is 32 m above the floor, and the discharge pipe is at floor level. The discharge conditions are 0.62 m3/kg,-100 kpa, and 270 m/s. The total heat loss between the inlet and discharge is 9kJ/kg of fluid. In flowing through this apparatus, does the specific internal energy increase or decrease, and by how much? Draw a figure or FBD that will support the problem. Explain each step by step formula.arrow_forwardIn turbochargers a turbine is directly connected to a compressor. The power harvested by the turbine is used to power the compressor. In the figure below a turbine runs on steam and powers a compressor on air. Air can be considered a perfect gas with k = 1.34, R = = 300K and a mass flow 0.28 kJ/kgk = 1bar, T₁ = and Cp 1.02 kJ/kgK. The air enters the compressor at p₁ rate of mdot = 5.9 kg/s and exits at p2 = 5.2 bars. The steam enters the isentropic turbine at P3 = 2 MPa, T3 = 320°C and exits at p4 = 100 kPa. State 2 Isentropic Compressor State 1 Air-perfect gas T₁ = 300K P₁ = 1 bar W Answer: tubine = ? State 4 Isentropic Turbine State 3 Steam T3=320°C P3= 2MPa What is the enthalpy at state 2? Please enter your answer in kJ/kgarrow_forwardNINEVEH UNIVERSITY THERMODYNAMICS Nozzles and Diffusers Ex,) Air at 10°C and 80 Kpa (abs) enters the diffuser of a jet engine steadily with a velocity of 200 m/s. The inlet area of the diffuser is 0.4 m2. The air leaves the diffuser with a velocity that is very small compared with the inlet velocity. Determine the mass flow rate of the air and the temperature of the air leaving the diffuser.arrow_forward
- In turbochargers a turbine is directly connected to a compressor. The power harvested by the turbine is used to power the compressor. In the figure below a turbine runs on steam and powers a compressor on air. Air can be considered a perfect gas with k = 1.34, R = 0.28 kJ/kgk and cp = 1.02 kJ/kgK. The air enters the compressor at p₁ = 1bar, T₁ 300K and a mass flow rate of mdot = 5.9 kg/s and exits at p2 = 5.2 bars. The steam enters the isentropic turbine at P3 = 2 MPa, T3 = 320°C and exits at p4 = 100 kPa. 9 State 2 Isentropic Compressor State 1 Air - perfect gas T₁=300K P₁ = 1 bar W Answer: tubine =? State 4 Isentropic Turbine State 3 Steam T3=320°C P3= 2MPa What is the quality of steam leaving the turbine?arrow_forwardSteam enters a well-insulated turbine at 500 bar and 600oC with a velocity of 100 m/s. The stream exits the turbine at 5 bar and 225oC with a velocity of 200 m/s. The turbine produces 32.5 MW of power. Calculate the steam mass flow rate (kg/s) through the turbine and the diameter (m) of the exit line assuming it is a cylindrical pipe.arrow_forwarda. Air at 8 bar 100°C flows in a duct of 15 cm diameter at rate of 150 kg/min. It is throttled by upto 4 bar pressure. Determine the velocity of air after throttling and also show that enthalpy constant before and after throttling. b, Ans. 37.8 m/s 1. Determine the power required by a compressor designed to compress atmospheric through inlet area of 90 cm? with velocity of 50 m/s and leaves with velocity of 120 m/s from exit area of 5 cm?. Consider heat losses to environment to be 10% of power input to compressor. Ans. 50.4 kw C' Determine the power available from a steam turbine with following details; Steam flow rate = 1 kg/s Velocity at inlet and exit = 100 m/s and 150 m/s Enthalpy at inlet and exit = 2900 kJ/kg, 1600 k]/kg Change in potential energy may be assumed negligible. Ans. 1293.75 kw d. Determine the heat transfer in emptying of a rigid tank of 1 m² volume containing air at 3 bar and 27°C initially. Air is allowed to escape slowly by opening a valve until the pressure in…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY