Question
Need help finding the roational interia and

Transcribed Image Text:Calculation Section
For the calculations described below, write
your answers to three significant figures,
except for percent discrepancy. Always use
un-rounded numbers to do all calculations.
Attach a sheet showing your cal cul ations,
and attach your DataStudio graphs, and turn
them in when Lab AM is due.
Transcribed Image Text:Calculations - Part II - Rotational
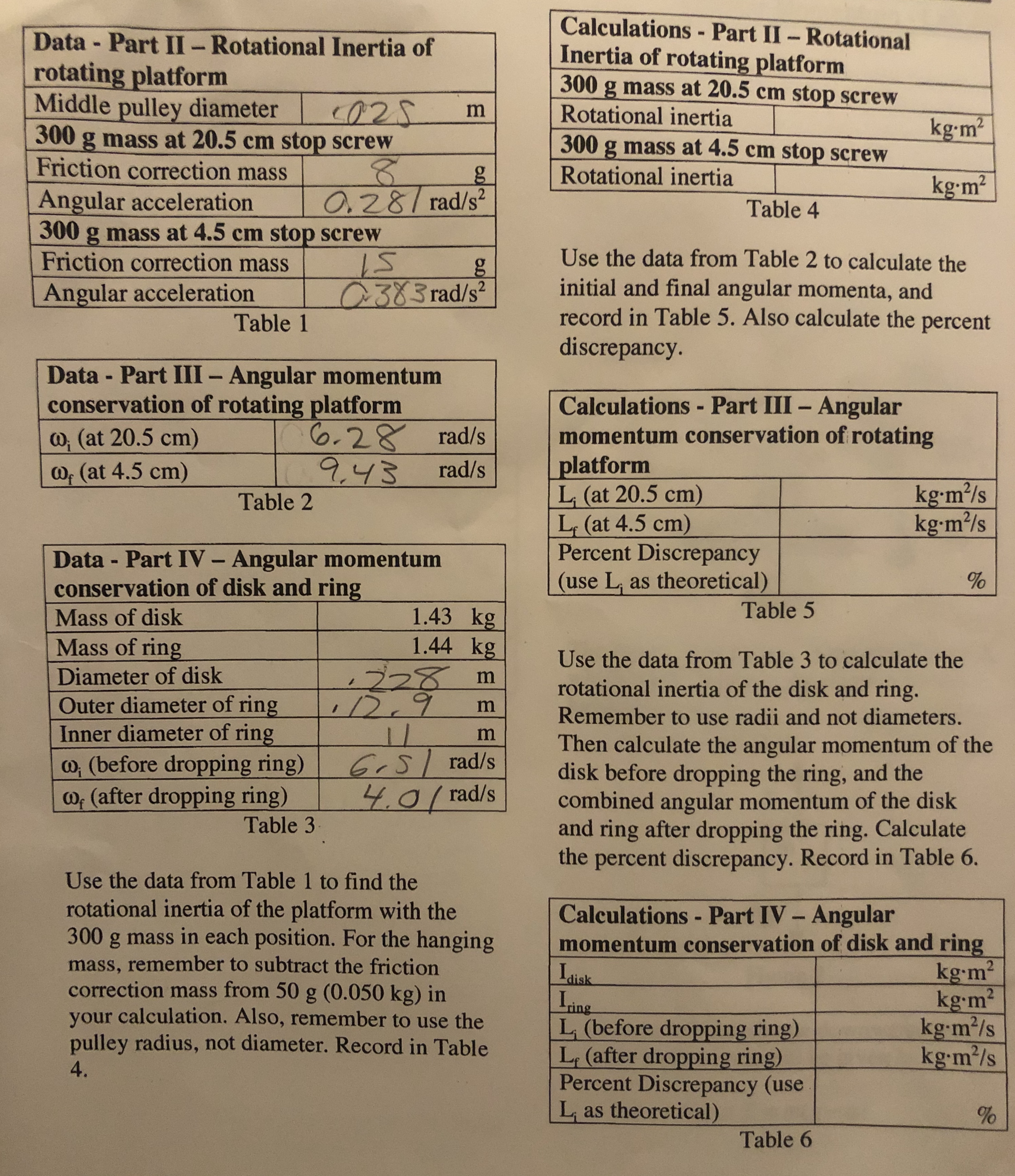
Data - Part II-Rotational Inertia of
rotating platform
Middle pulley diameter
300
Inertia of rotating platform
300 g mass at 20.5 cm stop screw
O2 m
Rotational inertia
kg-m2
g mass at 20.5 cm stop screw
Friction correction mass
300 g mass at 4.5 cm stop screw
Rotational inertia
kg-m2
O.z8/rad/s2
Angular acceleration
Table 4
300 g mass at 4.5 cm stop screw
Friction correction mass
Use the data from Table 2 to calculate the
g
initial and final angular momenta, and
record in Table 5. Also calculate the percent
discrepancy.
Angular acceleration
Table 1
C383 rad/s2
Data - Part III - Angular momentum
conservation of rotating platform
Calculations- Part III- Angular
momentum conservation of rotating
platform
L (at 20.5 cm)
L (at 4.5 cm)
Percent Discrepancy
(use L, as theoretical)
O.28 rad/s
943
o (at 20.5 cm)
rad/s
Dp (at 4.5 cm)
kg-m/s
kg-m2/s
Table 2
Data - Part IV - Angular momentum
conservation of disk and ring
Table 5
1.43 kg
1.44 kg
Mass of disk
Mass of ring
Use the data from Table 3 to calculate the
228
/29
11
GSrad/s
0rad/s
Diameter of disk
m
rotational inertia of the disk and ring.
Remember to use radii and not diameters.
Outer diameter of ring
Inner diameter of ring
m
m
Then calculate the angular momentum of the
disk before dropping the ring, and the
combined angular momentum of the disk
and ring after dropping the ring. Calculate
the percent discrepancy. Record in Table 6.
o (before dropping ring)
o (after dropping ring)
Table 3
Use the data from Table 1 to find the
rotational inertia of the platform with the
300 g mass in each position. For the hanging
mass, remember to subtract the friction
correction mass from 50 g (0.050 kg) in
your calculation. Also, remember to use the
pulley radius, not diameter. Record in Table
4.
Calculations - Part IV- Angular
momentum conservation of disk and ring
Ldisk
Iing
L (before dropping ring)
L (after dropping ring)
Percent Discrepancy (use
Las theoretical)
kg-m2
kg-m2
kg-m2/s
kg-m2/s
%
Table 6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Next, imagine that a bullet impacts the block that you see and embeds itself. Let's say that you know the speed of the bullet just before it hits and also the mass of the bullet. Explain, with words and equations, how you would determine the angle theta. eed to know i L-h L Center of Pendulum catcharrow_forwardNeed help don't understand how to solve.arrow_forwarda shower if JU equivalent situation, a rolle FIGURE 8.14 Shows a roller-coaster car gu radius r. Why doesn't the car fall off at the top of the circle eircle is not uniform circular motion; the car slows down as it goes up one and speeds up as it comes back down the other. But at the very top tom points, only the car's direction is changing, not its speed, so at those points the acceleration is purely centripetal. Thus there must be a net force toward the center The aus poats toward abe center and very bot- motion, so the water trajectory toward yo of the circle. 8-8 CHAPTER 8 Dynamics II: Motion in a Plane 15. It's been proposed that future space stations create "artificial gravity" by rotating around an axis. a. How would this work? Explain. b. Would the artificial gravity be equally effective throughout the space station? If not, where in space station would the residents want to live and work?arrow_forward
- Please solve be integrating, draw out all free body diagrams, and show any formulas used, thanks!arrow_forwardExpress the torque of F, on ab, with respect of the axis ef, in terms of F, and Ly. Express the torque of F, on ed, with respect of the axis ef, in terms of F and L2. What is the total torque on the current loop with respect of axis ef, in terms of F, and L2? Calculate the numerical value of the total torque in Nm. Express the torque of F, on ab, with respect of the axis ed, in terms of F, and Lz.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios