
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Calculate the value of K, for the equation
C(s) + CO, (g) = 2CO(g)
2 CO(g)
Kp = ?
given that at a certain temperature
C(s) + 2 H,O(g) = C0,(g) + 2 H,(g)
Kp1 = 3.29
H, (g) + CO, (g) =H,0(g)+CO(g)
Kp2 = 0.763
Kp
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
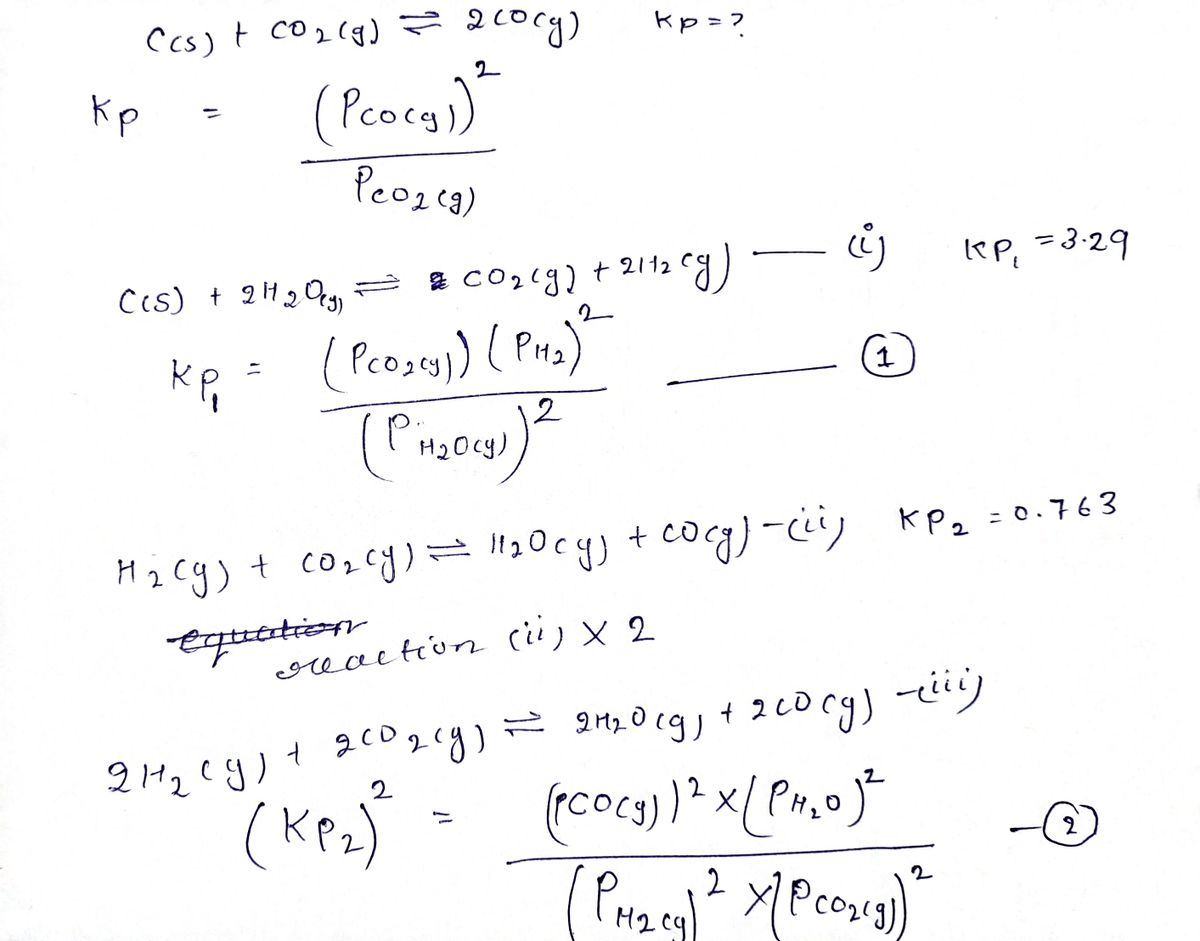
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Cl3] ² [Hz] ² [A] [AC] Consider the chemical equation and equilibrium constant for the synthesis of ammonia at 25 °C: N₂ (g) + 3 H₂ (g) = 2 NH3 (g) K = 5.6 x 105 Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25 °C: NH3 (g) 1/2 N₂ (g) + 3/2 H₂ (g) K' = ? Kc = [NH3 ]² [₂] [H₂]] Kc- [~₂] ¹/2 [H NH3arrow_forwardIf Kp is the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 A (g) + B (g) ⇌ 4 C (g). What is equilibrium constant (in terms of Kp) for the reaction 2 C (g) ⇌ A (g) + ½ B (g)?arrow_forwardA (g) =B (g) Kp1 = 4.35 x 10-3 %3D C (g) + D (g) = 3 B (g) Kp2 = 4.95 x 104 Using the above information, calculate the value of K, for the below reaction: C (g) + D (g) = 3 A (g)arrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 HF (g) H2 (g) + F2 (g) is 0.120 at a particular temperature. What is the equiliarium constant for the equation ½ H2 (g) + ½ F2 (g) = HF (g)?arrow_forwardFor which of these reactions will there be no effect on the relative amounts of the substances present at equilibrium when the pressure of the system is increased at constant temperature? O 2 sO, (g) + 0,(g) = 2 SO, (g) + heat heat + CO, (g) + NO(g) =CO(g) + NO, (g) heat + 2 Cl, (g) + 2 H,O(g) = 4 HCI(g) + 0, (g) N, (g) + 3 H, (g) = 2 NH, (g) + heatarrow_forwardFor the reaction below, the thermodynamic equilibrium constant is K= 1.92x103 at 35 °C. NHẠCO2NH2(s) → 2 NH3(g) + CO2(g) Suppose that 0.0046 moles of NHẠCO2NH2, 0.0092 moles of NH3, and 0.0046 moles of CO2 are added to a 3.00 L container at 35 °C. (a) What are Q and A,G for the initial reaction mixture? Your answers must be accurate to 3 significant figures. Q = Number A,G= Number kJ mol-1 (b) Is the spontaneous reaction to the left or to the right? Click for Listarrow_forward
- Consider the endothermic decomposition reaction of chlorine monofluoride at 1031.0 K. 2 CIF(g) - Ch(g) + F2(g) The equilibrium constant at 1031.0 Kis K= 2.52x106.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant for the chemical equation N2(g)+3H2(g)↽−−⇀2NH3(g) N 2 ( g ) + 3 H 2 ( g ) ↽ − − ⇀ 2 NH3(g) is Kp = 0.249 at 253 ∘C. 253 ∘ C. Calculate the value of Kc for the reaction at 253 ∘Carrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant for the chemical equation N,(g) + 3 H, (g) 2 NH,(g) is K, 0.356 at 197 °C. Calculate the value of the K, for the reaction at 197 °C. K.arrow_forward
- Be sure to answer all parts. The following reactions have the indicated equilibrium constants at a particular temperature: N2(g) + O2(g) = 2NO(g) K = 4.3 x 10-25 2NO(g) + O2(g) == 2NO,(g) K= 6.4 × 10' Determine the value of the equilibrium constant for the following equation at the same temperature: N2(g) + 202(g) = 2NO2(g) K. - x 10 (Enter your answer in scientific notation.)arrow_forwardThe reaction HCO₂H(g) CO(g) + H₂O(g) has Kp = 1.6 × 106 at 400 °C. What is the value of Kc for this reaction at this temperature? Kc = Harrow_forwardUsing any data you can find in the ALEKS Data resource, calculate the equilibrium constant K at 25.0 °C for the following reaction. N,(g) + 3 H, (g) 2 NH, (g) Round your answer to 2 significant digits. = [ ロ x10 %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY