
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
w/ Free body diagram
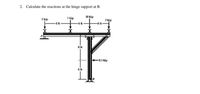
Transcribed Image Text:2. Calculate the reactions at the hinge support at B.
Skip
7 kip
10 kip
2 kip
-8f
-as kip
6 ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- shear force and bending moment on skateboard: write : introductionarrow_forwardWhile cutting a piece of paper, a person exerts the two indicated forces on a paper cutter. Reduce the two forces to an equivalent force-couple system at corner O and then specify the coordinates of the point P in the x-y plane through which the resultant of the two forces passes. The cutting surface is 28" x 28". 30 lb 13" A 4" 5 lb 1"arrow_forward■ Consider ■ h 457 × 152 × 52 UKB = 449.8 mm; b = 152.4 mm tw = 7.6 mm; t₁ = 10.9 mm r = 10.2 mm; d = 407.6 mm ■ h = 449.8 203.8 ■ What is the cross-sectional area, A? ■ What is the second moment of area, Iy? What is the elastic modulus, Wel,y? ■ What are the contributions of the flanges and the web? ■ What is the plastic modulus, Wply? ■ What are the contributions of the flanges and the web? ■ What is the shape factor of this section? b = 219.45 tw = 7.6 152.4 tf = 10.9 h₁ = 428arrow_forward
- Explain Kinematic and Static Indeterminacy for beams, frames and trusses.arrow_forwardFor the 2d coordinate system below, complete the following: a) Break up the force vector into Fx and Fy components; show these components on the figure. Add a superscript to each component to indicate whether they are acting in the positive (+) or negative (-) direction b) Draw a position vector from the origin (0) to the tail (point a) of the force vector c) Break up the position vector into rx and ry components; show these components on the figure Add a superscript to each component to indicate whether they are acting in the positive (+) or negative (-) direction d) Calculate the "moment" of force F about the origin by multiplying F times its perpendicular distance from the origin (ry), and add the product of Fy times its perpendicular distance from the origin (rx). Assume that a counterclockwise rotation about the origin is a "positive" moment. Think of rx as a string connected to the origin. If you pull the string in the direction of d, will that cause a clockwise (-) or…arrow_forwardProblem 4: The two bars can deform elastically. They are pinned at point B. The length of AB is 400 mm, length of BC is 250 mm, areas of cross- section of AB and BC are both equal to 35 square millimeters, and modulus of elasticity for material of the bars is the same, and equal to 250 GPa. Angle between AB and the horizontal is 30 degrees. Showing proper coordinate system (positive and negative directions), a. Consider the first figure below. A vertically downward force Facts at pin B. If the horizontal component of the displacement of B is 0.25 mm, determine the magnitude of the force applied, the vertical component of the displacement of B, and the net displacement of point B due to the elongation of bars AB and BC. Show all work and figures clearly. B F b. Now, consider the second figures, where there is a leftward force of magnitude F = 2500 N acting at pin B. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the deflection of point B, as well as the net deflection of point B. F…arrow_forward
- Draw the figure in a half-meter cross-section paper, and provide a scale. -The solution will be place in the activity template. -Fold the cross-section (Engineering fold style)arrow_forwardThe subject is Statics of Rigid Bodiesarrow_forwardLearning Goal: To replace force-couple systems with an equivalent force by specifying the magnitude and direction of the equivalent force and the location where the force needs to be applied. Certain force-couple systems can be replaced by a single force. The requirement is that the lines of action of the resultant force, FR, and the resultant couple moment, (MR)o, are perpendicular to each other. This is equivalent to saying the following types of force systems can be simplified to a single force: Figure F₂ X F₁ 3 ft A B 2 ft < 2 of 3 Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning