
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
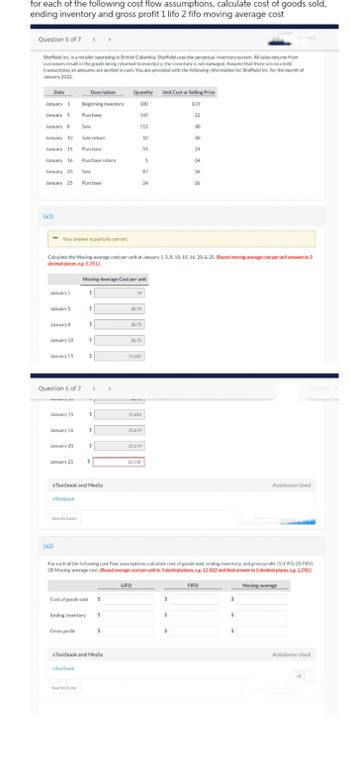
Transcribed Image Text:for each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate cost of goods sold,
ending inventory and gross profit 1 lifo 2 fifo moving average cost
Question 6 of 7
Sheffield Inc. is a retailer operating in British Columbia. Sheffield uses the perpetual inventory system. All sales returns from
customers result in the goods being returned to inventory; the inventory is not damaged. Assume that there are no credit
transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Sheffield Inc. for the month of
January 2022.
Date
January 1 Beginning inventory
January 5
Purchase
January 8
January 10
January 15
January 16
January 20
January 25
(a1)
January 1
- Your answer is partially correct.
January 5
January 8
January 10
January 15
Question 6 of 7
ya
January 15
January 16
January 20
January 25
eTextbook
Save for Later
(a2)
Calculate the Moving-average cost per unit at January 1, 5, 8, 10, 15, 16, 20, & 25. (Round moving-average cost per unit answers to 3
decimal places, eg. 5.251)
Description
Sale
Sale return
Purchase
Purchase return
Sale
Purchase
Gross profit
Cost of goods sold
Ending inventory
eTextbook
Save for Later
$
$
$
Moving-Average Cost per unit
$
eTextbook and Media
$
<
7
$
$
$
$
$
$
eTextbook and Media
$
Quantity Unit Cost or Selling Price
100
$19
22
>
140
113
19
20.75
20.75
20.75
21.681
21.681
21.619
LIFO
21.619
10
22.118
55
5
87
24
For each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate cost of goods sold, ending inventory, and gross profit. (1) LIFO. (2) FIFO
(3) Moving-average cost. (Round average-cost per unit to 3 decimal places, eg. 12.502 and final answer to O decimal places, eg. 1.250)
$
30
$
30
$
24
24
36
26
FIFO
$
$
Assistance Used
$
Moving-average
Assistance Used
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Question Content Area Three identical units of merchandise were purchased during July, as follows: Date Product Basic H Units Cost July 3 Purchase 1 $20 10 Purchase 1 23 24 Purchase 1 26 Total 3 $69 Average cost per unit $23 Assume one unit sells on July 28 for $34. Determine the gross profit, cost of goods sold, and ending inventory on July 31 using the (a) first-in, first-out, (b) last-in, first-out, and (c) weighted average cost flow methods. Line Item Description Gross Profit Cost of Goods Sold Ending Inventory a. First-in, first-out $fill in the blank 1 $fill in the blank 2 $fill in the blank 3 b. Last-in, first-out $fill in the blank 4 $fill in the blank 5 $fill in the blank 6 c. Weighted average $fill in the blank 7 $fill in the blank 8 $fill in the blank 9arrow_forwardW Using the specific identification method: Units purchased 15 Echo Show's 360 45 Echo Show's 360 60 Echo Show's 360 a. Calculate the cost of ending inventory. Date June 1 July 1 August 1 Ending inventory b. Calculate the cost of goods sold. Cost of goods sold Cost per unit $ 275 250 240arrow_forwardces Date March 1 March 5 March 9 March 18 March 25 March 29 Problem 6-1A (Algo) Part 3 Perpetual FIFO Perpetual LIFO Date March 1 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. March 5 Weighted Average Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using LIFO. Total March 5 Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Sales Purchase Purchase Sales Totals 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification. For specific identification, units sold include 60 units from beginning inventory, 190 units from the March 5 purchase, 40 units from the March 18 purchase, and 80 units from the March 25 purchase. March 9 Total March 9 March 18 Total March 18 Units Acquired at Cost 90 units @ $50.80 per unit 220 units @ $55.80 per unit Goods Purchased # of units 80 units @ $60.80 per unit 140 units @ $62.80 per unit Specific Id 530 units Cost per # of units unit sold Perpetual LIFO: Cost of Goods Sold Cost per…arrow_forward
- find cost of goods sold ending inventory and gross margin using FIFO and weighted average Kindly answer in text with all workingsarrow_forwardJanuary 1 January 12 January 24 January 28 Balance: 30 units @ 40 units @ 3 units @ 50 units @ $35 per unit $36 per unit $36 per unit $50 per unit Purchases: Purchase Return: Sales: The company uses the last in first out (LIFO) method of accounting for inventory. All purc and sales are done on account. Record all required entries related to inventory movemer order of occurrence using the period method (NOT THE PERPETUAL). Action/Date Periodic Method Beginning 1/1 Purchase 1/12 Return 1/24 Sales 1/28 Adjustment 1/31arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forward
- Ay 3. item Beta. Units. Cost The following three identical units of items PX2T are purchased during April April 2 Purchase 1 $104 April 15 Purchase 1 108 April 20. Purchase. 1. 112 Total. 3. $324 Average cost per unit. $108. ($324 ~ 3 units) Assume that one unit is sold on April 27 for $152. Determine the gross profit for April and ending inventory on April 30 using the (a) first -in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c)weighted average cost method a. First-in, first-out (FIFO). Gross Profit. Ending Inventory b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) c. Weighted average carrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardConcept Videos i es Required information UNIT 30s $45 May 1 April 5 April 10 April 15 April 201 April 22 # Knowledge Check 01 Assume that we use a perpetual inventory system and that five identical units are purchased at the following four dates and costs: 3 $ 10 $ 12 0:00-0:54 $14 $16 - $17 Cost of the ending inventory $ One unit is sold on April 25. The company uses the weighted average inventory costing method. Identify the cost of the ending inventory on the balance sheet. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places. 4 % 5 H 6 Inarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education