
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
3. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the point P for the configuration below. The loops are 10 cm in diameter and 10 cm away from each other. The point P is exactly in the middle point between the two loops. The direction of the current in each loop is shown in the picture and its magnitude is equal to 1.3A
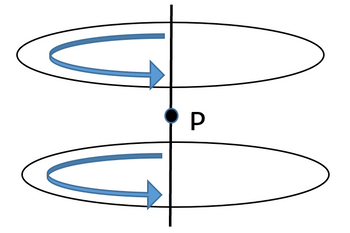
Transcribed Image Text:P
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. A wire is formed so as to make a circular loop connecting two long, straight sections as shown in Figure 6. If the radius of the loop is R = 20 cm and the wire carries a current I = 2.4 A, what are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the center of the loop? I If needed, you can use the magnetic field due to a straight wire, and and the magnetic field at the center of a loop derived from Ampere's law. (Hint: The two long sections form one long straight current- carrying wire.)arrow_forward1. Two straight parallel wires, running north/south are separated by 10 cm and carry currents of 3A in the same direction (north). a) Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at a point midway between the wires. b) Find the magnetic field 6 cm east of the "easternmost" wire. c) Calculate the force of one wire on the other. Is it attractive or repulsive?arrow_forwardDescribe how the magnetic domains in an unmagnetized iron rod will respond to the presence of a strong external magnetic field. a. The domains will split into monopoles. b. The domains will tend to align with the external field. c. The domains will tend to orient themselves perpendicular to the external field. d. The domains will tend to align so as to cancel out the external field.arrow_forward
- 3. DETAILS MY NOTES You are working during the summer at a company that builds theme parks. The company is designing an electromagnetic propulsion system for a new roller coaster. A model of a substructure of the device appears in the figure below. The rod is of length d = 1.00 m and mass m = 0.700 kg. The rod carries a current I = 100 A in the direction shown and rolls along the rails of length L = 15.0 m without slipping. The entire system of rod and rails is immersed in a uniform downward-directed magnetic field with magnitude 8 = 1.90 T. The electromagnetic force on the rod is parallel to the rails, causing the rod to roll to the right in the figure. When a full-scale device is produced, this rod will represent the axle of wheels on which the car and i on the grounds of the company. By projecting the rod from the rails in a horizontal direction from a height h = 1.80 m, the projection speed can be determined from how far from the ends of the rails the rod hits the ground. Your…arrow_forward9. The figure below shows two crossed wires that are carrying currents (1, = 66.0 A and l, = 50.0 A ). What is the magnitude of the total magnetic field at point (P) where a = 16.5 cm and b = 6.80 cm? barrow_forwardThe diagram below shows two concentric, conducting, circular loops with currents traveling in opposite directions. If the current in the outer loop is I2 = 90.0 μA, what must be the magnitude of the current in the inner loop so that the total magnetic field at the center, C, of both loops is zero? a. 60.0 μA b. 45.0 μA c. 90.0 μA d. 75.0 μA e. 105 μAarrow_forward
- An electron is introduced into a uniform magnetic field, Bx = 50.0 μTesla directed at right angles to the electron’s velocity vy = 5 x105 m/s. The electron subsequently moves in a circular path. What is the radius of the circular path? Select one: a. 2.84 cm b. 5.68 cm c. 56.8 cm d. 2.84 marrow_forwardThe diagram below shows two, thin, infinitely-long, parallel conducting wires that are separated by a perpendicular distance of 2.0 cm. What is the coordinate on the y-axis where the total magnetic field is zero? a. y = 4.8 cm b. y = 5.6 cm c. y = 4.4 cm d. y = 6.6 cm e. y = 5.2 cmarrow_forward1. A DC power line for a light-rail system carries 950 A at an angle of 33° to the Earth’s 5.00 × 10-5 T magnetic field. What is the magnitude of the force (in N) on a 125 m section of this line? 2. Consider a 150 turn square loop of wire 15.5 cm on a side that carries a 56 A current in a 1.6 T field. What is the maximum torque on the loop of wire in N⋅m? What is the magnitude of the torque in N⋅m when the angle between the field and the normal to the plane of the loop θ is 14°? 3. Consider two two long, straight, parallel, current-carrying wires, separated by a distance d = 4.5 cm, as shown in the figure. The left wire is directed out of the page with current I1, and the right wire is directed into the page with current I2. The point P is a distance d from both wires, so the wires and the point form an equilateral triangle. If both wires are carrying a current of 3.5 A, what is the magnitude of the magnetic field, in teslas, at point P? If the current from the left wire is 3.5 A…arrow_forward
- 1. A wire runs from north to south a. A compass needle placed above the wire points with its north pole toward the east. In what direction is the current flowing? b. If a compass is placed underneath the wire, in which direction will its needle point? 2. What will be the direction of the magnetic field if the current is due upward? 3. How does the magnitude of the current passing through the conductor affect the magnetic field?arrow_forward3. Current head-on to point P: Consider the case where the current is heading straight toward the point where we want the magnetic field. What is the magnetic field at the point P shown? Hint: consider a small piece ds and think about what the Biot-Savart law tells you. Holds x f 4πr2 Think about the angle between ds and î. dB 7 D Parrow_forward18. Two very long conductors (both oriented in the same plane) are shown in the sketch below. The same magnitude of conventional current in each is represented by the red arrows. The black dot is at a position (in the same plane) equidistant between the conductors. Determine the direction of the magnetic field at the position of the black dot. A. There is no magnetic field at this position. B. The magnetic field is oriented out of the page. C. The magnetic field is oriented into the page. D. The magnetic field is oriented to the left. E. The magnetic field is oriented to the right.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON