
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Could you help me with the first few steps on solving this using
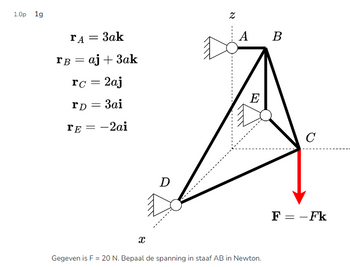
Transcribed Image Text:1.0p 1g
rA = 3ak
rB = aj + 3ak
rc = 2aj
rD= 3ai
TE = -2ai
X
D
N
A
E
Gegeven is F = 20 N. Bepaal de spanning in staaf AB in Newton.
B
C
F = -Fk
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the general solution. a. y' 5y = 3ex - 2x + 1 - b. y" +4y' + 4y = e¯*cos(x) c. (D² + I)y = cos(wt), w² # 1arrow_forwardnovig size modestib Beri N 1-12 12- 60° 37. A block-and-tackle pulley hoist is suspended in a warehouse ay by ropes of lengths 2 m and 3 m. The hoist weighs 350 N. The ropes, fastened at different heights, make angles of 50° and th 38° with the horizontal. Find the tension in each rope and the magnitude of each tension. 50° brd 60° 2 m 38° 3 m 501001 hon sit 44. 45 4arrow_forwardWhat would be the resultant force Fof the triangular distributed load and its location d measured from point A. 90 lb/ft 3 ft 5 ft 2 ft > Select one: O a. F= 225 Ib and d= 3.67 ft O b. F= 300 Ib and d=2.5 ft O C.F= 450 ib and d=3.67 ft O d. F= 300 Ib and d= 1.67 ftarrow_forward
- S00 Ib In the fig. shown, compute the ff: (16-18) the resultant using cosine law (force polygon) 60 R = 35 (19-20) the angle of the R measured 500 lb cW from the x- axis.arrow_forwardRequired information 3 Consider the given vectors. Given: A = (4i – 3j + 2k ) lb and B = (-141 - 2 + 5k) i in. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. y es Determine the angle between vectors and The angle between vectors A and B is .. K Prev 4. of 8 Next > 个8arrow_forwardThe answer is already given. I just need the solution. Also, please make the solution neat and readable. Thank you. Answer: R= 193 lb, A= 74 lbarrow_forward
- touchO 0"| 63% ( 23:50 MENG250 - Practice Assi... Not saved yet Page Break *2-60. Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction angles of the resultant force acting on the bracket. F1 = 450 N 45° 30° 60° F2 = 600 N Oarrow_forwardTwo cables support an unknown weight. If the tension in cable BC is 100 lbs, thenwhat is the unknown weight? Don’t forget to draw a FBD. (Im new to this and need some help)arrow_forwardHelp!!! Answer all the parts correctly! Pleasearrow_forward
- QUESTION 2 Question 2 A cross-section of a beam is shown in Figure Q2. If the shear force in this section is V = 125 KN, determine the value and the location of the maximum shear stress in the section. In Figure Q2, a = 30 mm and the origin of the coordinate system is at centroid of the cross section. 7 y= Z= A a AY S= 20 4a mm; mm; O Figure Q2 Answer The vertical coordinate (y-coordinate; the y-axis serves as the axis of symmetry of the cross- section.) and horizontal coordinate (z-coordinate) of the location where the maximum shear stress occurs in the section are ← a The vertical distance from the location where the maximum shear stress occurs in the section to the bottom side (AB cross section can be calculated as Distance = mm (units: mm) 3a Second moment of area The second moment of area employed in the equation to calculate maximum shear stress can be calculated as I₂ = a (units: mm²) Shear stress The second moment of area employed in the equation to calculate maximum shear…arrow_forwardNeed only a handwritten solution only (not a typed one).arrow_forwardSolve step by step dont use chatgpt DETERMINE THE DIAGRAM OF THE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS 0 995 2m Z 11 3m W₁ = 1 ton m 21 w₂= 2 tun m 12.5marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L