
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337093347
Author: Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
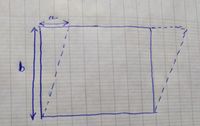
A material having a shear modulus G, is deformed under a pure shear stress as shown in the following figure. Calculate the applied shear stress. Given: a = 1 mm, b = 200 mm and G = 25 GPa.
Consider a linear elastic behavior
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) Solve part (a) of the preceding problem if the pressure is 8.5 psi, the diameter is 10 in., the wall thickness is 0,05 in., the modulus of elasticity is 200 psi, and Poisson's ratio is 0.48. (b) If the strain must be limited to 1.01, find the maximum acceptable inflation pressurearrow_forwardA spherical steel pressure vessel (diameter 500 mm, thickness 10 mm) is coated with brittle lacquer that cracks when the strain reaches 150 X 10~ (see figure). (a) What internal pressure p will cause the lacquer to develop cracks? (Assume E = 205 GPa and v = 0.30.) (b) If the strain is measured at 125 x 10-6, what is the internal pressure at that point?arrow_forwardSolve the preceding problem if the cube is granite (E = 80 GPa, v = 0.25) with dimensions E = 89 mm and compressive strains E = 690 X l0-6 and = = 255 X 10-6. For part (c) of Problem 7.6-5. find the maximum value of cr when the change in volume must be limited to 0.11%. For part. find the required value of when the strain energy must be 33 J.arrow_forward
- A circular cylindrical steel tank (see figure) contains a volatile fuel under pressure, A strain gage at point A records the longitudinal strain in the tank and transmits this information to a control room. The ultimate shear stress in the wall of the tank is 98 MPa, and a factor of safety of 2,8 is required. (a) At what value of the strain should the operators take action to reduce the pressure in the tank? (Data for the steel are modulus of elasticity E = 210 GPa and Poisson's ratio v = 0.30.) (b) What is the associated strain in the radial directionarrow_forwardA standard brick (dimensions 8 in. × 4 in. × 2.5 in ) is compressed lengthwise by a force P. as shown in the figure, If the ultimate shear stress for brick is 1200 psi and the ultimate compressive stress is 3600 psi. what force Pmax is required to break the brick?arrow_forwardA copper wire having a diameter ofd = 4 mm is bent into a circle and held with the ends just touching (see figure), If the maximum permissible strain in the copper is = 0.0024, what is the shortest length L of wire that can be used? If L = 5.5 m, what is the maximum acceptable diameter of the wire if the maximum normal strain must remain below yield? Assume E = 120 GPa and(7K= 300 MPa.arrow_forward
- A steel wire- and an aluminum allay wire have equal lengths, and support equal loads P (see figure). The moduli of elasticity for the steel and aluminum alloy are Ea= 30,000 ksi and Ea= 11,000 ksi, respectively. (a) IF the wires have the same diameters, what is the ratio of the elongation of the aluminum alloy wire to the elongation of the steel wire? (b) If the wires stretch the same amount, what is the ratio of the diameter of the aluminum alloy wire to the diameter of the steel wire? (c) If the wires have the same diameters and same load P, what is the ratio of the initial length of the aluminum alloy wire to that of the steel wire if the aluminum alloy wire stretches 1.5 limes that of the steel wire? (d) If the wires have the same diameters, same initial length, and same load P. what is the material of the upper wire if it elongates 1.7 times that of the steel wire?arrow_forwardThree prismatic bars, two of material A and one of material B. transmit a tensile load P (see figure). The two outer bars (material A) are identical. The cross-sectional area of the middle bar (material B) is 50% larger than the cross-sectional area of one of the outer bars. Also, the modulus of elasticity of material A is twice that of material B. (a) What fraction of the load P is transmitted by the middle bar? (b) What is the ratio of the stress in the middle bar to the stress in the outer bars? (c) What is the ratio of the strain in the middle bar to the strain in the outer bars?arrow_forwardA brass wire of diameter d = 2.42 mm is stretched tightly between rigid supports so that the tensile force is T = 98 N (see figure). The coefficient of thermal expansion for the wire is 19.5 × 10-6/°C. and the modulus of elasticity is E = 110 GPa. (a) What is the maximum permissible temperature drop AT if the allowable shear stress in the wire is 60 MPa? (b) At what temperature change does the wire go slack?arrow_forward
- A sliding collar of weight W = 150 lb falls From a height h = 2.0 in. onto a flange at the bottom of a slender vertical rod (see figure). The rod has a length L = 4.0 ft, cross-sectional area A = 0.75 in2, and modulus of elasticity E = 30 X 106 psi. Calculate the following quantities: (a) the maximum downward displacement of the flange, (b) the maximum tensile stress in the rod, and (c) the impact factor.arrow_forwardDuring a tension lest of a mild-steel specimen (see figure), the extensometer shows an elongation of 0.00120 in. with a gage length of 2 in. Assume that the steel is stressed below the proportional limit and that the modulus of elasticity E = 30 × 10 psi. (a) What is the maximum normal stress (j^, in the specimen? (b) What is the maximum shear stress tmax? (c) Draw a stress element oriented at an angle of 45° to the axis of the bar, and show all stresses acting on the faces of this element.arrow_forwardAn aluminum bar subjected to tensile Forces P has a length L = 150 in. and cross-sectional area A = 2.0 in2 The stress-strain behavior of the aluminum may be represented approximately by the bilinear stress-strain diagram shown in the figure. Calculate the elongation S of the bar for each of the following axial loads: p = 8 kips, 16 kips. 24 kips, 32 kips, and 40 kips. From these results, plot a diagram of load P versus elongation S (load-displacement diagram).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning