
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
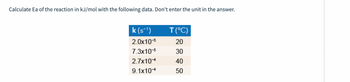
Transcribed Image Text:Calculate Ea of the reaction in kJ/mol with the following data. Don't enter the unit in the answer.
k (s™¹)
2.0x10-5
7.3x10-5
2.7x10-4
9.1x10-4
T(°C)
20
30
40
50
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- O Macmillan Learning Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction at 25 °C. C3H₂(g) + 5O₂(g) → 3 CO₂ (g) + 4H₂O(g) 2 AH values can be found in this table of thermodynamic values. AH rxn = kJ/molarrow_forward10arrow_forward__P4(s) + __Cl2(g) --> __PCl5(g) H°rxn = –1500 kJ In a reaction mixture of 0.22 g(P4) and 1.45 g(Cl2): If 0.12 LSTP(PCl5) was isolated, the percent reaction yield is _______% The most heat this reaction mixture can form is _______ kJarrow_forward
- true of falsearrow_forwardThe thermite reaction, Fe2O3(s) + 2 Al(s) ---->2 Fe(s) +Al2O3(s), ΔH° = -851.5 kJ/mol, is one of the most exothermicreactions known. Because the heat released issufficient to melt the iron product, the reaction is used toweld metal under the ocean. How much heat is released permole of Al2O3 produced? How does this amount of thermalenergy compare with the energy released when 2 mol ofprotons and 2 mol of neutrons combine to form 1 mol ofalpha particles?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: 2 NH,(9) - N,(9)+3H,(9) AH = 160. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. O endothermic. This reaction is... alo O exothermic. Suppose 46.5 g of NH, react. O Yes, absorbed. O Yes, released. Will any heat be released or absorbed? O No. If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward-1. How much heat is released (in kJ) from 253 g of silver when it cools from 85 °C to 26 °C? The heat capacity of silver is 0.235 Jg C-¹. Hint: "heat released" means you should get a negative change in heat. But enter a positive number for this question.arrow_forwardThe reaction 4AI (s) + 302 (g)→ 2 Al203 (s) AH° = -3351 kJ is and therefore heat is by the reaction. thermoneutral, neither released nor absorbed O endothermic, absorbed exothermic, released exothermic, absorbed endothermic, releasedarrow_forward
- A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: 2 HgO(s) → 2 Hg(1)+O,(g) AH=182. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. endothermic. This reaction is... x10 exothermic. Yes, absorbed. Suppose 56.6g of HgO react. Yes, released. Will any heat be released or absorbed? No. If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. kJ Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardConsider the reaction 2H2+O2⟶2H2O Δ?rxn=−484 kJ Which answer best describes the transfer of heat that occurs when 1.70 mol H21.70 mol H2 reacts? A.) 823 kJ absorbed B.) 484 kJ released C.) 484 kJ absorbed D.) 823 kJ released E.) 411 kJ absorbed F.) 411 kJ releasedarrow_forwardCalculate ΔΗ°rxn for the combustion of carbon monoxide, producing CO2 in KJ. 2CO(g)+O2(g)-->2CO2(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY