
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
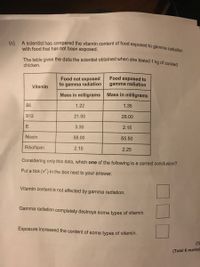
Transcribed Image Text:The table gives the data the scientist obtained when she tested 1 kg of cooked
A scientist has compared the vitamin content of food exposed to gamma radiation
(c)
with food that has not been exposed.
chicken.
Food not exposed
to gamma radiation
Food exposed to
gamma radiation
Vitamin
Mass in milligrams
Mass in milligrams
B6
1.22
1.35
B12
21.00
28.00
E
3.30
2.15
Niacin
58.00
55.50
Riboflavin
2.10
2.25
Considering only this data, which one of the following is a correct conclusion?
Put a tick (v) in the box next to your answer.
Vitamin content is not affected by gamma radiation.
Gamma radiation completely destroys some types of vitamin.
Exposure increased the content of some types of vitamin.
(1)
(Total 6 marks)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You suspect that a patient’s arm is broken. What type of radiation might help you find out?arrow_forwardA tumor is exposed to a beam of protons containing 2.6 × 1010 protons. If 25% of the beam energy is absorbed in a tumor of mass 1.25 kg, what is the dose equivalent in the tumor? Each proton has an energy of 52 MeV, and the RBE of this type of radiation is 32. a) 0.043 Sv b) 1.38 Sv c) 4.3 Sv d) 13.8 Sv e) 37 Svarrow_forwardCalculate the effective radiation dosage (in Sieverts) for a 81-kg person who is exposed to 1.9 x 109 particles of alpha radiation. Assume that 79% of the radiation is absorbed, each alpha particle has an energy of 6.2 x 10-13 J, and that the RBE of the alpha particles is 15. Note that RBE is sometimes called the quality factor, abbreviated as Q.arrow_forward
- A 75 kg patient swallows a 33 μCi beta emitter whose half-life is 5.0 days and whose RBE is 1.6. The beta particles are emitted with an average energy of 0.35 MeV, 90% of which is absorbed by the body. You are a health care worker needing to find the patient's dose equivalent after one week. These series of steps will help you find that dose equivalent. In all questions, assume the radioactive nuclei are distributed throughout the patient's body and are not being excreted. Part A How many radioactive nuclei did the patient swallow? Express your answer using three significant figures. ▸ View Available Hint(s) No= ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit ?arrow_forwardQUESTION 38 Rank the following procedures from lowest effective radiation dose to highest. The first choice should have little to no radiation and the last choice should have the highest radiaiton exposure. MRI of the brain extremity x-ray (ex. hand) full spine x-ray (cervical, thoracic, AND lumbar series) PET/CT fusion of the abdomen and pelvisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON