
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
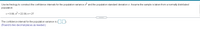
Transcribed Image Text:Use technology to construct the confidence intervals for the population variance o and the population standard deviation o. Assume the sample is taken from a normally distributed
population.
c= 0.99, s? = 22.09, n= 27
The confidence interval for the population variance is
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 5/12arrow_forwardplease solve for the followingarrow_forwardY 8.1.15 Question Help For the provided sample mean, sample size, and population standard deviation, complete parts (a) through (c) below. Assume that x is normally distributed. x = 38, n = 16, o = 8 %3D a. Find a 95% confidence interval for the population mean. The 95% confidence interval is from 34.08 to 41.92. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) b. Identify and interpret the margin of error. The margin of error is 3.92. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Interpret the margin of error. Choose the correct answer below. O A. We can be 95% confident that any possible value of the variable is within the margin of error of the sample mean, 38. B. We can be 95% confident that any possible sample mean is within the margin of error of 38. We can be 95% confident that any possible value of the variable is within the margin of error of the population mean, µ. D. We can be 95% confident that the population mean, µ, is within the margin of error of the sample mean, 38. c. Express the…arrow_forward
- Use technology to construct the confidence intervals for the population variance o² and the population standard deviation a. Assume the sample is taken from a normally distributed population. c=0.99, s= 33, n= 16 The confidence interval for the population variance is ( ). (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The confidence interval for the population standard deviation is ( ). (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardQ1. Using 625 trading days of data, you estimated the daily log return follows a normal distribution with a mean of 5 bps and and a stdev of 125 bps. Q1b. what is the 90, 95, and 99% confidence interval for your mean return estimate?arrow_forwardes A sample of 12 fossil skeletons of an extinct species of bird has been collected. The mean length of the skulls in this sample is 5.29 cm and the standard deviation of the sample is 0.21 cm. Assuming that such measurements are normally distributed, find a 90% confidence interval for the population mean length of the skulls of this species of bird. You may want to use one of these: qt (p-0.10, df-11, lower. tail-FALSE)=1.36343 qt(p-0.05, df-11, lower.tail-FALSE) =1.795885 qnorm(0.10, mean-0, sd-1, lower.tail-FALSE)=1.281552 qnorm(0.05, mean-0, sd-1, lower.tail=FALSE)=1.644854 O (4.945, 5.635) O (4.913, 5.667) O (5.021, 5.559) O (5.181, 5.399)arrow_forward
- # E DII C A previous study gave (0.11, 0.23) as a confidence interval for p. Find the minimum sample size required to ensure that your estimate (p) will be within 0.01 of p with 99% confidence. IMPORTANT: Use a critical value that you found with your calculator (not from a table), and round it to 3 places after the decimal point before you plug it into a formula and perform your calculations. Do not round-off any other intermediate results. n = F3 Submit Question $ 4 R F F4 V % 5 T J G F5 6 B Y H F6 & 7 X U N F7 - * PrtScn 8 F8 M K Home 9 F9 O End L F10 P Pg Altarrow_forward(1 point) A random sample of 70 observations produced a mean of a 39.5 from a population with a normal distribution and a standard deviation o = 2.14. (a) Find a 95% confidence interval for u (b) Find a 99% confidence interval for (c) Find a 90% confidence interval forarrow_forwardn1=16 x‾1=124 s1=35 n2=12 x‾2=86 s2=31 Use this data to find the 98% confidence interval for the true difference between the population means. Assume that the population variances are not equal and that the two populations are normally distributed. Copy Data Step 2 of 3 : Find the margin of error to be used in constructing the confidence interval. Round your answer to six decimal places. Step 3 of 3 : Please also find the high and low endpoints and round to four decimal points.arrow_forward
- solve for the image belowarrow_forwardInterstate Speeds It has been reported that the standard deviation of the speeds of drivers on Interstate 75 near Findlay, Ohio, is 8 miles per hour for all vehicles. A driver feels from experience that this is very low. A survey is conducted, and for 29 drivers the standard deviation is 9.1 miles per hour. At =α0.05, is the driver correct? Assume the variable is normally distributed. (a)State the hypotheses and identify the claim with the correct hypothesis.arrow_forwardUse the data to calculate the sample variance, s. (Round your answer to five decimal places.) n = 7: 1.6, 3.5, 1.6, 2.1, 3.1, 2.9, 3.0 %3D Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population variance, of. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) to Test Ho: = 0.8 versus H: of + 0.8 using a = 0.05. State the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) x2 State the rejection region. (If the test is one-tailed, enter NONE for the unused region. Round your answers to two decimal places.) x2 > x² State the conclusion. H, is rejected. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8. H, is rejected. There is insufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8. H, is not rejected. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8. O Ho is not rejected. There is insufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman