
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
do not give solution in image format
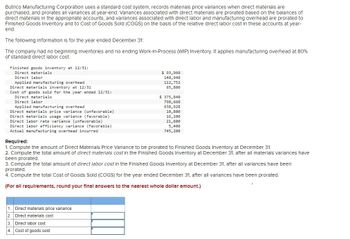
Transcribed Image Text:Butrico Manufacturing Corporation uses a standard cost system, records materials price variances when direct materials are
purchased, and prorates all variances at year-end. Variances associated with direct materials are prorated based on the balances of
direct materials in the appropriate accounts, and variances associated with direct labor and manufacturing overhead are prorated to
Finished Goods Inventory and to Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) on the basis of the relative direct labor cost in these accounts at year-
end.
The following information is for the year ended December 31:
The company had no beginning inventories and no ending Work-in-Process (WIP) Inventory. It applies manufacturing overhead at 80%
of standard direct labor cost.
Finished goods inventory at 12/31:
Direct materials.
Direct labor
Applied manufacturing overhead
Direct materials inventory at 12/31
Cost of goods sold for the year ended 12/31:
Direct materials
Direct labor
Applied manufacturing overhead
Direct materials price variance (unfavorable)
Direct materials usage variance (favorable)
Direct labor rate variance (unfavorable)
Direct labor efficiency variance (favorable)
Actual manufacturing overhead incurred
1. Direct materials price variance
2. Direct materials cost
$93,960
140,940
112,752
65,800
Required:
1. Compute the amount of Direct Materials Price Variance to be prorated to Finished Goods Inventory at December 31.
2. Compute the total amount of direct materials cost in the Finished Goods Inventory at December 31, after all materials variances have
been prorated.
3. Compute the total amount of direct labor cost in the Finished Goods Inventory at December 31, after all variances have been
prorated.
4. Compute the total Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for the year ended December 31, after all variances have been prorated.
(For all requirements, round your final answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
3. Direct labor cost
4. Cost of goods sold
$ 375,840
798,660
638,928
10,800
16,200
21,600
5,400
745,200
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education