Question
thumb_up100%
Please no hand writing solution
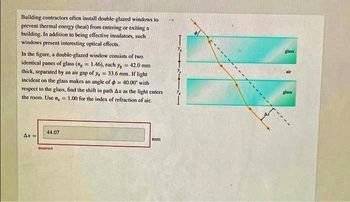
Transcribed Image Text:Building contractors often install double-glazed windows to
prevent thermal energy (heat) from entering or exiting a
building. In addition to being effective insulators, such
windows present interesting optical effects.
In the figure, a double-glazed window consists of two
identical panes of glass (n = 1.46), each y = 42.0 mm
thick, separated by an air gap of y, = 33.6 mm. If light
incident on the glass makes an angle of = 40.00' with
respect to the glass, find the shift in path Ax as the light enters
the room. Use n,= 1.00 for the index of refraction of air.
Ax=
44.07
Incorrect
mm
1x1
glass
glass
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios