
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Bronco skydives and parachutes from a stationary helicopter. Various stages of fall are shown in positions a through f as illustrated below. Using Newton's 2nd law, a = F(net)/m = W - R , where a is acceleration, W is weight and R is air Resistance. Find Bronco's acceleration at each positions athrough f (Type in on Google form answers a-f, show supporting calculations on your notes). Bronco's mass is 100 kg so his weight W is a constant 1000 N. Air resistance R varies with speed and cross-sectional area as show.
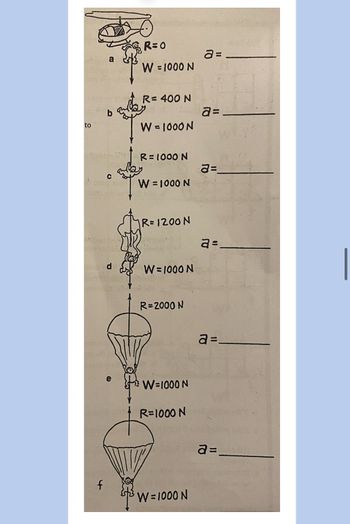
Transcribed Image Text:to
a
b
R=0
W = 1000 N
R= 400 N
W = 1000N
a=_
a=
R=1000 N
a=
C
W = 1000 N
R=1200 N
a=
d
W = 1000 N
e
R=2000 N
a=
W=1000 N
R=1000 N
a=
f
W=1000 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given the diagram apply Newton’s 2nd Law to the object (in other words, sum the forces and set equal to ma^-->).arrow_forwardhorizontal line (the + position axis). Assume that friction is so small that it can be neglected. Describe in words the graph of the force applied to the object that would cause the motion described to continue. Note that the positive direction is toward the right. Question 8: The object moves toward the right with a constant velocity.arrow_forwardInstructions given above Please solve Q1 and Q2 as soon as possible make it ASAP in 1 hour pleasearrow_forward
- Lesson: Newton's Law of Motions (including 1st, 2nd, and 3rd law of motion) note: please solve the problem using the GRESA method (indicate the given, required, equation, solution, and answer). thank you! objectives: Solve the following problem about Newton's Law of motions (including 1st, 2nd, and 3rd law of motion). Problem:The rocket sled showed below (see attached pic) decelerates at a rate of 106 m/s2. What force is necessary to produce this deceleration? Assume that the rockets are off. The mass of the system is 2.10 x 103 kg.arrow_forwardPlease see the image provided for context and solve the following problem: Solve for and use the magnitude of the force of friction on Debbie and the tension in the rope to solve the problem. The bruin is hungrier than Sarita anticipated, and she decided she needs to pull harder, accelerating Debbie up the rocky slope. Sarita's rope can only manage a tension of 950N. What is the maximum acceleration Sarita can accomplish with this rope?arrow_forwardA cart can move along a horizontal line (the + position axis). It moves with the velocity shown below. Time (s) Question 7A: Describe in words the acceleration-tim graph of the cart's motion. Question 7B: Assuming that friction is so small that it can be neglected, describe in words the force-time graph to keep the cart moving with this velocity and acceleration. Question 7C: Explain both of your graphs. Velocityarrow_forward
- A gymnast is practicing on a long, straight balance beam. Starting in the middle of thebeam (at a position of 1 m), the gymnast walks in the negative direction at 3 m/s for1.5 s, pauses for 2 s, and jogs in the opposite direction at 4 m/s for 2 s. Graph thegymnast’s motion on the three graphs below. You must show your reasoning for eachthe graph to receive full credit.arrow_forwardUse Newton's Second law to write equations of motion for each of the two masses. Make sure you use the coordinate system given in the figure in the introduction. Use notation so that's it's clear which object you're examining, for example call ag the acceleration of the glider and an the acceleration of the hanging weight. The acceleration of the glider and the hanging mass are related since they are connected by a string. The relevant relationship is aGz = -ahy - The reason for the minus sign is that when the glider accelerations in the +x direction, the hanging mass accelerates in the -y direction. Using this fact, and combining the two equations you wrote in the previous part, solve for the acceleration of the glider in terms of the masses m, , mG , and other known constants. TIE Tiaigti alltitialtɔ uuWIIwaiu, lauding liit giluti lu +x Surface is frictionless Pulley is massless and frictionlessarrow_forwardShow and explain the complete solution with the formulas. Label the symbols used accordingly.arrow_forward
- A box weighing 500 N hangs from two cables, as shown in the figure below. Find the tension in each cable. Carry your intermediate computations to at least 4 decimal places. Round your final answers to the nearest tenth. Note that the ALEKS graphing calculator can be used to make computations easier. Platform 45° 59° Tension in left cable: ||N ? Tension in right cable: N 500 Narrow_forwardPlease show formula's used and do step for step, please don't cut out any algebraarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON