
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Brit-Brick is a company that produces bricks and cement in the UK. Their largest consumer is ConstrUK, a UK construction company. The manager of Brit-Brick has asked the research department to find out how sensitive ConstrUK’s demand for bricks is. The research department has estimated that ConstrUK’s preferences over bricks (x) and cement (y) can be described by the utility function
please see the picture attached,
and b=7
The
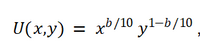
Transcribed Image Text:U(x,y) = xb/10 y1-b/10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a consumer with the utility function U (x1, x2 ) = 10x12/3x21/3 −50. Suppose the prices of x1 and x2 are 10 and 2 respectively and the consumer has an income of 150. How would the optimal bundle change if the utility function was log- linear: 2lnx1 +lnx2?arrow_forwardYou go to the store in search of laundry detergent, to discover that they offer two varieties: Myst and Breez. Your preferences between Myst and Breez can be represented by the following utility function: U(M. B) = 16M + 32B Myst costs 4$ unit. Breez costs 10$ per unit for the first 5 units, but all units after 5 only costs $6. Find your Engel Curve for Breez.arrow_forwardFrom the demand function Qdx = 12 – 2Px (Px is given in dollar), derive:(a) the individual’s demand schedule and demand curve, and(b) what is the maximum quantity this individual will ever demand of commodity X per time period?arrow_forward
- Q3: Are the following utility functions quasi-linear, quasi-concave, quasi-convex, homogenous of degree 0, homogenous of degree 1? Show your working: 1) U(x,y) = min(x,y) 2) U(x,y) = (x" + yajaarrow_forwardPlease I need help for part E and F. I have the intuition in mind but I am not too sure about it. I thought about reversing the inverse demand function given so it now looks like Q = 30 - P. Since Bertrand is concerned about prices, then we can solve for p1 and p2 using the reversed of the inverse demand function (P = 30 - Q). From here, we use the same familiar procedure to solve for the equilibrium price which I think will be the same. Please help explain if my understanding is correct and provide further explanation for me. Thanks for the help.arrow_forwardAlonso has preferences for sport cars (C) and paella (P) given by the utility function U(C, P) = 4CP. The prices for C and P are, respectively, pc and pp. In what follows, do not worry if the results are not integers.arrow_forward
- Consider the following demand function: U(X,Y) = X5Y5 Find the solution of the maximization problem.arrow_forwardAn agent's utility function is u(x1, X2, X3, X4) = 2min{x1,x2} + 3max{x3,x4}. Find the demand functions for each good.arrow_forwardSuppose that you want to derive and draw the demand function for Mr. Seong (also known as Player 456). Mr. Seong likes to eat Dalgona Candy (D) and drink Soju (S). Suppose Mr. Seong's preferences can be expressed as U(D,S) = (D)º.² · (S)0.8. Suppose further the price of a Dalgona Candy is 2 (pº = 2) and the price of Soju is 4 (ps = 4). Mr. Seong has a budget of 100 to spend on the two goods. A. Use the substitution method to find Mr. Seong's optimal choice of Dalgona Candy and Soju. B. Use any method to find Mr. Seong's optimal choice of Dalgona Candy and Soju if the price of Soju was 5 (instead of 4). Feel free to use the Cobb-Douglas short-cut method if you want. C. Use your answers to A and B to derive the demand for Soju in the two diagrams below. That is, draw the change in the top diagram and then use your result to derive the demand curve in the bottom diagram. Several hints have been drawn in the diagram below. D 50 10 ps 5 4 20 20 25 S FYI: The Cobb-Douglas short-cut can be…arrow_forward
- Xander has a utility function u(x,y) = xy and an income of M. Assume that the price of x is $4 and the price y is $2. If Xander's income rises from M = 104 to M = 152, what the resulting increase in demand for good x? increases by 6 units increases by 9 units increases by 11 units increases by 14.5 unitsarrow_forwardSuppose that an individual has a Utility function represented by a CES function. The utility function of the individual is given as: U(x,y) = x1/2 + y1/2 c. Is the demand more elastic or inelastic than a Cobb-Douglas Utility function? Use the Slutsky matrix to illustrate.arrow_forwardElsie sells homemade lemonade. If she prices a glass of lemonade at $3, she sells 12 glasses a day. If she gives a $0.50 discount (per glass), she can sell 3 more glasses per day. Write a linear demand equation q = mp + b, where p is the price per glass, and q is the number of glasses she can sell per day. Suppose that it costs her 20 cents a glass to make lemonade. There is no fixed cost. Write down the revenue function, cost function, and profit function as functions of p. How much should she charge per glass to maximize her profit? What is the maximum profit?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education