
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
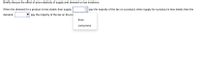
Transcribed Image Text:Briefly discuss the effect of price elasticity of supply and demand on tax incidence.
When the demand for a product is less elastic than supply.
pay the majority of the tax on a product; when supply for a product is less elastic than the
demand,
pay the majority of the tax on the pre
firms
consumers
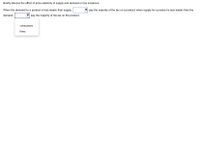
Transcribed Image Text:Briefly discuss the effect of price elasticity of supply and demand on tax incidence.
When the demand for a product is less elastic than supply,
pay the majority of the tax on a product; when supply for a product is less elastic than the
demand,
pay the majority of the tax on the product.
consumers
firms
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose the market for cigarette is competitive. An economist estimates the price elasticity of demand and supply for cigarette are -0.6 and 0.8 respectively. a. Suppose the government imposes a per-unit tax on the cigarette sellers. Who, buyers or sellers, would share a heavier tax burden? Explain your answers without calculation. b. Suppose the government imposes a per-unit tax of $40 on the cigarette sellers. By how much would buyers and sellers of cigarettes share the tax burden respectively? Show your calculation. c. Suppose many small sellers, such as newsstands, complain the heavy tax burden borne by them. Would it be better to these small sellers if the government decides to impose a $20 per-unit tax on both the buyers and the sellers of cigarette? Explain.arrow_forwardQuestion 36 For Questions 36-46, please refer to the following graph. The vertical distance between points A and B represents a per-unit tax in the market. tPrice 12 11 10 t. Supply H. G 4 3- 2- 1- Demand 0s 1 13 2 2s 3 33 4 45 s Deantit Without the tax, the equilibrium price in this market is $ , and the equilibrium quantity is units.arrow_forwardGovernment levied a tax on good A. The less elastic the demand is, the greater or the smaller the tax burden consumers bear? Also, is the after-tax equilibrium quantity the greater or smaller? Consumers’ tax burden: After-tax equilibrium quantity:arrow_forward
- Would consumer or producer carry the burden of tax if good is elastic? Show on a grapharrow_forwardif the demand curve is very inelastic and the supply curve is very elastic in the market then sellers will bear a greater burdeb of tax inposed on the market even if the tax imposed on buyers.True or falsearrow_forwardThe following graph shows the weekly market for handbags in some hypothetical economy. Suppose the government levies a tax of $23.20 per bag. The tax places a wedge between the price buyers pay and the price sellers receive. PRICE (Dollars per bag) 100 90 00 R 70 8 50 40 R20 10 0 10 Tax Wedge Supply Demand 20 30 40 50 00 70 QUANTITY (Bags of handbags) 00 00 100 C Darrow_forward
- The following graph shows the market for the long-distance bus rides. In the absence of taxes, the equilibrium price of a ride is $5 and the equilibrium quantity is 10 million rides. Suppose that regulator levies an excise tax on bus service providers. The amount of excise tax equals $2 per ride. How many rides will be demanded after the introduction of the excise tax? 7 million 10 million 8 million 9 millionarrow_forwardDoyle and Samphantharak (2008) find that when a 5% gas tax is implemented, prices consumers pay for gas increase by about 4%. What role does demand elasticity play in determining the size of this price change? That is, under what demand elasticity cases would the price change be closer to 5%, or closer to 0%? Illustrate and explain using supply-and-demand graph(s)..arrow_forwardWhat is an indirect tax give two examples in economicsarrow_forward
- The graph shows the market for basketballs in which sellers are taxed $6 a ball. Draw a shape that shows the excess burden of the tax on basketballs. The excess burden of the tax on basketballs is $ million. The supply of basketballs is more pays most of the tax. A. elastic; seller OB. elastic; buyer OC. inelastic; buyer O D. elastic; seller than the demand for basketballs, and thearrow_forwardThe table shows the market for chocolate bars Quantity demanded Quantity supplied (thousands per day) Price (dollars per chocolate bar) 1.10 1.20 1.30 1.40 1.50 50 5 40 10 30 15 20 20 10 25 A tax of $0.30 per chocolate bar is imposed on sellers What is the new price of a chocolate bar? Who pays the tax? The new price of a chocolate bar following the tax is $ The tax is A. paid totally by the buyer B. paid totally by the seller C. split between the buyer and the sellerarrow_forwardHelparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education