
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Rank the following compounds in the order of increasing reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
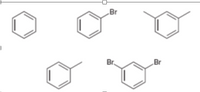
Transcribed Image Text:This image contains several structural formulas of organic compounds, specifically aromatic compounds (benzene derivatives). Below is a detailed transcription and description of each chemical structure from left to right and top to bottom:
1. The first structure is benzene, represented as a hexagon with alternating double bonds inside.
2. The second structure includes a benzene ring with one bromine (Br) atom attached to the ring. This is known as bromobenzene.
3. The third structure is a benzene ring with two methyl groups (CH₃) attached to it, positioned on the first and third carbon atoms of the ring, respectively. This compound is known as m-xylene (meta-xylene).
4. The fourth structure is similar to benzene but with this benzene ring having a single hydrogen atom substituted. This is a phenyl group.
5. The fifth structure is a benzene ring with two bromine (Br) atoms attached to it at the first and fourth positions. This compound is known as p-dibromobenzene (para-dibromobenzene).
These structures highlight simple derivatives of benzene, showcasing common functional groups and substituent patterns such as halogens and methyl groups. Each compound represents fundamental aspects of organic chemistry and can be used to explain concepts such as isomerism, electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, and the reactivity of aromatic compounds.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How would you introduce the following in an aromatic ring?i) –CH2-CH2-CH3 ii) -NH2 iii) –COOH iv) –OH v) –COC6H5arrow_forwardIbufenac, a para-disubstituted arene with the structureHO2CCH2C6H4CH2CH(CH3)2 , is a much more potent analgesic thanaspirin, but it was never sold commercially because it caused livertoxicity in some clinical trials. Devise a synthesis of ibufenac frombenzene and organic halides having fewer than five carbons.arrow_forwardName and Draw the structures of all possible chemical (Electrophilic aromatic substitution) reactions of the compound namely; Halogenation (Chlorination or Bromination) Nitration Sulphonation Friedal Craft Alkylation Friedal Craft Acylationarrow_forward
- Write the reagents for the following aromatic electrophilic substitutionsarrow_forwardWhich compound is more reactive in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction?arrow_forwardHighlight each of the positions on the benzene ring that you expect will be most likely to react by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Am I correct?arrow_forward
- Which position will an electophile (E*) most likely add in an Electophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) reaction? C Aarrow_forwardDraw both resonance structures of the anion formed by the reaction of the most acidic C-H bond of the compounds below with base.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is incorrect? Chlorobenzene undergoes EAS reactions faster that methoxybenzene Meta substitution means 1,3-arranged product is formed on benzene An aromatic compounded loses its aromaticity in the first step of EAS Benzene rings require strong electrophiles in order to undergo EAS reactionsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY