
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A box is tethered to a frictionless ramp by a horizontal string as shown in the picture. The box is at rest. Is the normal force exerted by the ramp on the box greater than, less than, or equal to the weight of the box? Show a free body diagram and/or explain your reasoning.

Transcribed Image Text:HINT: Make your free body diagram and notice that if the string is horizontal then the Weight and
the Tension force must be acting at 90 degrees from each other. Then do a separate diagram with
a graphical vector addition, noticing that if the system is in equilibrium the sum of all the force the
vectors must add up to zero, i.e. after adding all of the vectors the end of the last one must meet
the beginning of the first one. If you have your graphical vector addition right, you should have
formed a right angle triangle with all your vectors, with the right angle of the triangle at the
connection of the Weight and the Tension force vectors. Can the Normal force vector be shorter
or of the same length than the Weight vector?
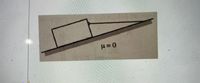
Transcribed Image Text:u=0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You don't need to make a free body diagramarrow_forwardIn , the man has a mass of 65 kg and the crate has a mass of 110 kg. The coefficient of static friction between his shoes and the ground is μs = 0.4 and between the crate and the ground is μc = 0.3. A) Determine if the man is able to move the crate using the rope-and-pulley system shown. B) Prove your answer to part A by calculating the static frictional force F�between the man's shoes and the ground required to move the crate and the maximum static frictional force Fmax which can be developed. Express your answers in newtons to three significant figures separated by a com_ma.arrow_forwardBlock 1 (9 kg) is located on the surface of a table. A hand pushes horizontally to the right on block 1 with a normal force of 108 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface equals 0.8.On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component.FORCES on BLOCK 1Weight force on block 1 by Earth W1E = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by Surface N1S = i + j N Normal force on block 1 by Hand N1H = i + j N Frictional force on block 1 by Surface f1S = i + j N What is the acceleration a of block 1?a = i + j m/s2arrow_forward
- Consider the system in the picture below: a cart of mass M with a static friction coefficient u is connected through a massless string to a hanging mass m. M is a capital letter, m is lower case. Write them as such, or vour equations will be confusing, M We want to find the maximum value of the hanging mass m such that the system is in equilibrium. 1. Free body diagram (FBD): Draw a FBD for each: the Cart and the hanging mass. Clearly show all the forces. 2. Clearly write the equilibrium equations for the cart in the horizontal and vertical direction. 3. Clearly write the equilibrium equation for the hanging mass. 4. Solve the system of the three equations above for the hanging mass m. Show your calculation to get credit. 5. What would happen if mass m exceeds this value? Explain.arrow_forwardCrate A hangs from a cable C and rests against the wall, so that the cable makes an angle with the wall. Draw a complete free-body diagram of crate A. Include labeledangle(s), in terms of ?, for any force(s) that are at an angle (not purely horizontal or vertical).arrow_forwardPlease draw the free diagram clear and also add any forcearrow_forward
- Consider a person serving a platter of hot food to their family who is gathered around a table. When holding theplatter, the person can choose how to hold the platter in front of them and would like compare the differences between position 1 and position 2 as shown below. In position 1, the shoulder is at 0 degrees while the elbow is at 90 degrees and in position 2, the arm is flexed as shown. a.) Consider the elbow joint and draw free body diagrams for each of the positions shown, including gravitational forces (consider the weight of the combined forearm and hand), elbow flexor forces, and the joint contact force. b.) Use the information provided below to solve for the magnitude of the elbow flexor force (in Newtons) for positions 1 and 2, the magnitude of the joint contact force (in Newtons), and the angle that the joint contact force makes with respect to the horizontal axis. • The platter of food weighs 7 lbs; the person weighs 175 lbs, and the person is 5’8” tall. • θ = 130…arrow_forwardFind I and J values and please answer all parts of this question 3. Block 1 (10 kg) is setting on the floor of an elevator. The elevator is moving upward with an increasing speed and the magnitude of the acceleration is 2 m/s2. On a sheet of paper, draw the free body diagram for block 1 using the two-subscript notation from class. After completing the free body diagram, enter below each force and its x & y-components. (use g = 10 m/2) Remember that the x-component is the "i" component and the y-component is the "j" component. -NET force on Block 1 (round to nearest integer) Fnet1 = ——- i + ——- j N The DIRECTION of the net force on block 1 is in the same direction as its acceleration. If the elevator is moving upward with an increasing speed, then the direction of the block's acceleration is up (positive y-value). The MAGNITUDE of the net force on block 1 equals its mass times acceleration, which are both given in the problem. -FORCES on BLOCK 1 Weight force on block 1…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON