
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Both of the following organic ions exist but one is MUCH more stable (A or B). Choose the correct claim(s), evidence(s), and reasoning(s).
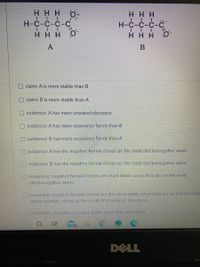
Transcribed Image Text:### Comparing Stability of Molecular Structures
#### Molecular Structures
- **Structure A:**
- Visual Representation: Consists of a carbon chain accompanied by hydrogen atoms and a negatively charged oxygen atom.
- **Structure B:**
- Visual Representation: Similar carbon chain with hydrogen atoms and a negatively charged oxygen atom distributed differently compared to Structure A.
#### Claims and Evidence
- **Claim Options:**
- Claim: A is more stable than B.
- Claim: B is more stable than A.
- **Evidence Options:**
- Evidence: A has more unpaired electrons.
- Evidence: A has more resonance forms than B.
- Evidence: B has more resonance forms than A.
- Evidence: A has the negative formal charge on the most electronegative atom.
- Evidence: B has the negative formal charge on the most electronegative atom.
#### Reasoning
- **Reasoning Options:**
- Reasoning: Negative formal charges are most stable when they are on the most electronegative atom.
- Reasoning: Negative formal charges are the most stable when they are spread out (delocalized) across multiple atoms as the result of resonance structures.
- Reasoning: Electrons are most stable when they are paired.
### Explanation
The images depict two different molecular structures labeled A and B. Each structure includes carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms, with the negatively charged oxygen atoms being crucial to the stability argument. The task is to assess which structure is more stable based on given claims, evidence about resonance forms, formal charges, and stability reasoning principles.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
In A negative charge on oxygen atom.
In B negative charge on the carbon atom.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- a) Draw the ring-flip isomer of the molecule from question (b) Show which of the two is favored in the equilibrium between them, and explain why, showing all possible forms of strain in each of the isomers. (c) What is the stereochemical relationship between the two isomers? (d) Draw another stereoisomer of the molecule and show all the strains it contains.(strains is the most important one in this questuon!!!)arrow_forwardThe structure shown below is has a very high pKa because the conjugate base is very unstable. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows to show the deprotonation step. Then, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. H Select to Add Arrows CH3CH2CH2CH2Li H Select to Edit Arrows H H LIⒸarrow_forwardOn the molecules on the back page, circle and label all of the functional groups that you see (identified in the table above). Please note the following tips that may help you on this assignment: If a molecule contains –COOH, or a C double bonded to an O and single-bonded to an –OH, the functional group you circle is only the carboxyl, not a carboxyl, carbonyl, and hydroxyl separately). Phosphate groups are tricky – any P surrounded by 4 O’s is a phosphate – adjacent phosphates may share an O, and sometimes the O is in the form of OH. There is often shorthand that is used in drawing these structures – if you see a jagged line or ring structure, assume that carbon is at each corner. There may be ionized forms of the functional groups above (such as NH2 or NH3+) – these are the same functional groups. The order of the atoms in the functional group may be switched, depending on which side of the molecule it is on. For example, “—NH3” and “H3N—“ are the same thing.arrow_forward
- A=B When a curved arrow starts from an bond and points to an adjacent atom, the n bond breaks and the o bond remains. This will typically generate two charges. A-B=C Note in the second mechanism shown, if the first curved arrow started from atom C, then atom B would violate the octet rule. A second a bond would need to delocalize. Read the curved arrow in the mechanism shown and draw the product. Be sure to draw lone pairs. Select Draw Rings More Erase C Harrow_forwardPlease answer all part of the question...thank youarrow_forward[References] Draw structures for the alkene (or alkenes) that gives the following reaction product. Br CH3CH₂CHCCHCH3 II Br CH3 Br₂ • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • Submit more than one structure only if the structures are constitutional isomers. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the ● Separate structures with + signs from the drop-down menu. e- ChemDoodle {}arrow_forward
- answer with explanation please!!arrow_forwardNeed help solving this, please show your work with the answer!arrow_forwardOn the molecules on the back page, circle and label all of the functional groups that you see (identified in the table above). Please note the following tips that may help you on this assignment: If a molecule contains –COOH, or a C double bonded to an O and single-bonded to an –OH, the functional group you circle is only the carboxyl, not a carboxyl, carbonyl, and hydroxyl separately). Phosphate groups are tricky – any P surrounded by 4 O’s is a phosphate – adjacent phosphates may share an O, and sometimes the O is in the form of OH. There is often shorthand that is used in drawing these structures – if you see a jagged line or ring structure, assume that carbon is at each corner. There may be ionized forms of the functional groups above (such as NH2 or NH3+) – these are the same functional groups. The order of the atoms in the functional group may be switched, depending on which side of the molecule it is on. For example, “—NH3” and “H3N—“ are the same thing.arrow_forward
- Four isomers A-D with the formula C5H12O exhibit different reactivity patterns as indicated below. Isomer A reacts with PCC and CrO3 to provide identical products. Isomer B reacts with PCC and CrO3 to provide different products. Isomers C and D do not react with either PCC or CrO3. Isomers A, B, and C readily react with NaH but D does not show any reactivity with NaH. The 1H NMR splitting patterns for these isomers are as follows. Isomer A: δ 0.91 (d, 3H), 0.90 (d, 3H), 1.18 (d, 3H), 1.92 (dqq, 1H), 3.38 (dq, 1H), 3.58 (bs, 1H). Isomer B: δ 1.25 (s, 9H), 3.45 (s, 2H), 3.65 (bs, 1H). Isomer C: δ 0.90 (t, 3H), 1.44 (q, 2H), 1.24 (s, 6H), 3.65 (bs, 1H). Isomer D: δ 1.10 (t, 3H), 1.13 (d, 6H), 3.19 (septet, 1H), 3.50 (q, 2H). Based on all of this information, provide the structures of A-D. (Note: If there is a chiral center on any of these molecules, assume the stereochemistry as “R”. dqq=doublet of a quartet of a quartet, bs=broad singlet)arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution.....arrow_forwardDraw both resonance structures of the anion formed by the reaction of the most acidic C-H bond of the compound below with base. • Include all valence lone pairs in your answer. . For structures having different hydrogens of comparable acidity, assume that the reaction occurs at the less-substituted carbon. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate resonance structures using the symbol from the drop-down menu. 0- O Bi % 5 T G ▾ 99-85 A 6 SCH₂CH3 ChemDoodleⓇ Cengage Learning Cengage Technical Support Y H F6 On [F & 7 O U J F7 * 8 PrtScn | K Home 9 83°F Sunny O L A End 0 F10 P IN Previous Next> C 4x PgUp F11 J Save and Exit 9:38 AM 7/18/2022 PgDn + = F12 80arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY