
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
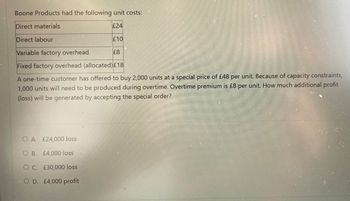
Transcribed Image Text:Boone Products had the following unit costs:
Direct materials
£24
Direct labour
Variable factory overhead
£8
Fixed factory overhead (allocated) £18
A one-time customer has offered to buy 2,000 units at a special price of £48 per unit. Because of capacity constraints,
1,000 units will need to be produced during overtime. Overtime premium is £8 per unit. How much additional profit
(loss) will be generated by accepting the special order?
O A. £24,000 loss
OB. £4,000 loss
O C. £30,000 loss
O. D. £4,000 profit.
£10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Miller Company produces speakers for home stereo units. The speakers are sold to retail stores for £30. Variable costs per unit are: Direct materials £9.00; Direct labour 4.50; Distribution 1.50 and Variable Factory overhead 3.00. Fixed costs per month are: Factory overhead £120,000 and Selling and admin. 60,000. The variable distribution costs are for transportation to the retail stores. The current production and sales volume is 20,000 per year. Capacity is 25,000 units per year. An Atlanta wholesaler has proposed to place a special one-time order for 7,000 units at a special price of £25.20 per unit. The wholesaler would pay all distribution costs, but there would be additional fixed selling and administrative costs of £6,000. In addition, assume that overtime production is not possible and that allother information remains the same as the original data. The effect on profits if the special order is accepted is Select one: a. cannot be determined b. £30,900 decrease c. £50,100…arrow_forwardConsider the following production and cost data for two products, H and C: Product H $120 10 minutes Product C $112 8 minutes Contribution margin per unit Machine minutes needed per unit A total of 60,000 machine minutes are available each period and there is unlimited demand for each product. What is the largest possible total contribution margin that can be realized each period? Multiple Choice O $780,000 $1,560,000 $840,000 $720,000arrow_forwardBluebell Ltd is a small company making gadgets. Two models are made: E_bell and D_bell. Both products require the same skilled labour which is limited. Information/data: E_bell D_bell Selling Price £150 £190 Variable Costs £110 £120 Direct labour hours per unit 4 6 Hours Direct labour hours available (per week) 900 Hours Maximum demand 100 140 Fixed overheads (per week) £4,000 a). If products can be sold up-to their max demand. What will be the maximum profit?arrow_forward
- A company is looking to launch a new product line, which requires new facilities to be used and at the moment has two planned products, called ‘Basic’ and ‘Super’. The cost per unit is planned as follows: Basic Super Direct materials £20 £24 Direct labour £14 £16 While using the absorption costing approach, the company uses machine hours as the basis to charge its production overheads. One unit of Basic will use 3 machine hours while one unit of Super will use 4 machine hours. The business sells these products at a price that gives a standard profit mark-up of 30% of full cost. For the coming year, the company expects to make and sell 8,000 units of Basic and 6,000 units of Super. If the company adopts the ABC approach, the details relating to the…arrow_forwardBluebell Ltd is a small company making gadgets. Two models are made: E_bell and D_bell. Both products require the same skilled labour which is limited. Information/data: E_bell D_bell Selling Price £150 £190 Variable Costs £110 £120 Direct labour hours per unit 4 6 Hours Direct labour hours available (per week) 900 Hours Maximum demand 100 140 Fixed overheads (per week) £4,000 If products can be sold up-to their max demand. Recommend the best production plan to maximise the use of the limited resource and maximise profit.arrow_forwardMenk Corporation has provided the following information: Cost per Unit Cost per Period Direct materials $ 6.80 Direct labor $ 3.80 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 2.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 20,200 Sales commissions $ 0.50 Variable administrative expense $ 0.40 Fixed selling and administrative expense $ 10,100 Required: a. If 5,220 units are sold, what is the variable cost per unit sold? Note: Round "Per unit" answer to 2 decimal places. b. If 5,220 units are sold, what is the total amount of variable costs related to the units sold? c. If 5,220 units are produced, what is the total amount of manufacturing overhead cost incurred? a. Variable cost per unit sold b. Total variable costs c. Total manufacturing overhead costarrow_forward
- SAMMI Manufacturing has two divisions. Division A makes a part with the following characteristics: Production capacity in units 15,000 units Selling price to outside customers .. Variable cost per unit........ £25 £18 £60,000 Total fixed costs Division B, of the same company, would like to purchase 5,000 units of the part each period from Division A. Division B is now purchasing these parts from an outside supplier at a price of £24 each. Suppose that Division A has ample idle capacity to handle all of Division B's needs without any increase in fixed costs and without cutting into sales to outside customers. If Division B continues to purchase parts from an outside supplier rather than from Division A, the company as a whole will be: a. b. C. d Better off by £15,000 each period. Worse off by £10,000 each period. Worse off by £30,000 each period. Worse off by £35,000 each period.arrow_forwardAlgee Ltd plans to manufacture kettles and the following information is applicable: Estimated sales for the year 20.15 Estimated costs for the year 20.15 Direct material 14 000 units at R80 each R24 per unit Direct labour Factory overheads (all fixed) Selling expenses Administrative expenses (all fixed) R4 per unit R48 000 per annum 30% of sales R78 000 per annum 3.1 Calculate the break-even quantity 3.2 Calculate the break-even value using the marginal income ratio. 3.3 Calculate the selling price per unit if the profit per unit is R4. 3.4 Calculate the new break-even quantity and value if selling price is increased by 10%. 3.5 Calculate the selling price if 14 000 units provide an operating profit of RO after an additional advertising expense of R54 000arrow_forwardFRANCORP sells two products. Products M N Selling price per unit $80 $60 Less variable expenses per unit $46 $40 Contribution margin per unit $34 $20 Current demand per week (units) 2,100 2,400 Processing time required on machine XYZ per unit 2 min. 1 min. Machine XYZ is a constrained resource and is being used at 100% capacity. Machine XYZ has a capacity of 3,000 minutes per week. Assuming FRANCORP wants to maximize its total contribution margin, how much of each product should it produce? a. 2400 units of N and 300 units of M b. 300 units of N and 2100 units of M c. 1200 units of N and 1050 units of M d. 2400 units of N and 0 units of Marrow_forward
- Please do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forwardZena Technology sells arc computer printers for $56 per unit. Unit product costs are: Direct materials $15 Direct labor 20 Manufaturing overhead 6 Total $41 A special order to purchase 16,000 arc printers has recently been received from another company and Zena has idle capacity to fill the order. Zena will incur an additional $3 per printer for additional labor costs due to a slight modification the buyer wants made to the original product. One-third of the manufacturing overhead costs is fixed and will be incurred no matter how many units are produced. When negotiating the price, what is the minimum selling price that Zena should accept for this special order? $fill in the blank 1 per unitarrow_forwardCompany XYZ makes face shields that sells for P30. During the period fixed costs representing payment for salaried employees are P150,000. Variable costs which mostly are materials costs P26 per unit. How many units should the company sell to earn P 80,000? 3,750 units 7,500 units 37,500 units 75,000 units Group of answer choices 1 2 3 4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education