
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Answer for the number 6 question, Thank you. No need for long explanation.
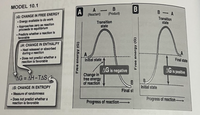
Transcribed Image Text:MODEL 10.1
A
(Reactant)
-
B- A
AG: CHANGE IN FREE ENERGY
Energy available to do work
Approaches zero as reaction
proceeds to equillibrium
• Predicts whether a reaction is
favorable
(Product)
Transition
state
Transition
state
AH: CHANGE IN ENTHALPY
• Heat released or absorbed
during a reaction
• Does not predict whether a
reaction is favorable
A
Initial state
Final state
AG is negative
AG is positive
Change in
free energy
of reaction
AG = AH-TAS
%3D
AS: CHANGE IN ENTROPY
Initial state
Final st
Measure of randomness
• Does not predict whether a
reaction is favorable
Progress of reaction-
Progress of reaction–
B
(5) KBJoue 00
Free energy (G)

Transcribed Image Text:Name:
Date:
Year/Section:
Score:
ACTIVITY 10.1
Refer to Model 10. 1 and answer the question that follows
1. What is free energy? What is its symbol?
2. For an exergonic reaction, what is the value of AG?
3. For an endergonic, what is the value of AG?
4. What are the factors that affect AG?
5. What is energy coupling? In a coupling reaction, what must be the
overall value of AG?
6. What does the cell do with the energy produced from exergonic
reactions?
7. What molecule does the cell use as an energy carrier? Draw its
structure.
8. Why is it that this energy carrier is considered to be high energy
containing phosphate?
9. Bond of this energy carrier of cells is broken through what?
212 Copyright 2019. All Rights Reserved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The two major types of cell-surface receptors that bind tohormone molecules are G-protein linked receptors and_____________________.arrow_forwardB. Question A 75-year-old man was found unconscious in his bathroom after falling and hitting his head. He survived for several hours but died later in the hospital. An autopsy was performed to determine the exact cause of death. Evidence indicated that the man had suffered two strokes, both due to blocked blood vessels. One had occurred a few weeks earlier; the other had occurred very recently and may have led to the fall. Autopsy findings also indicated that, when the man hit his head, some damage to his brain occurred as well. Based on what you know about inflammation and the cellular structure of the brain, describe what the pathologist found in each of the damaged areas of the brain. C. Question Predict the effect of a decrease in the extracellular concentration of Ca2+ on the resting membrane potential.arrow_forwardANSWER BRIEFLY BUT COMPLETE. ANSWERS MUST BE ORIGINAL AND NOT JUST COPIED ON THE INTERNET. I WILL UPVOTE IF YOU FOLLOW MY INSTRUCTIONS. THANK YOUarrow_forward
- Help me please. I'm cryingarrow_forwardQuestion 34 Answers A - E A 55-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician with a 2-day history of oozing, foul-smelling wound on her foot. Physical examination shows a 4-cm, necrotizing wound on the heel with purplish black discoloration of the skin around the wound, and crepitant bullae producing thin, serous fluid. A Gram stain of tissue biopsy from the site shows gram-positive rods. Which of the following toxins is produced by the most likely causal organism? A Alpha toxin B Endotoxin C Exfoliative toxin D FLAG QUESTION E Exotoxin A Panton Valentine toxin 000 Oarrow_forwardQuestion 20 The client with inflammatory bowel disease has the following blood test results. Identify the correct interpretation: Patient Normal Range CRP (C-Reactive Protein) 10 ≤5.0 mg/L Hgb (hemoglobin): 104 (130 - 180 g/L (Male); (115 - 165 g/L (Female)) HCT (hematocrit): 0.35 (0.400 - 0.540 L/L (Male)) (0.370 - 0.470 L/L (Female)) Platelets: 350 (150 - 400 x 109/L) Question 20 options: Inflammation Hypoalbuminemia Infection Dehydrationarrow_forward
- I need help please.arrow_forwardTopic: Fred Davis is a 52 - year old overweight male who is complaining of tiredness and blurred vision. He says that for the last two weeks, he's been very hungry and very thirsty, but despite eating more, he has lost 8 pounds. He also mentions that he has been urinating more frequently. When asked, he mentions that his paternal grandfather suffered from heart disease and diabetes. Blood tests show blood glucose of 190 mg / dL. Question: Symptoms (what is the patient complaining of / experiencing)arrow_forwardEither answer 18 or 19&20 both but please answer asaparrow_forward
- answer choices in grey are for selected boxarrow_forwardQuestion 19 Write one or two sentences describing the Physics behind Heart attacks.arrow_forwardPart I – SymptomsCallie was 26 years old when she opened a bakery called “Callie’s Cupcakes” in downtown San Francisco with herf ancé, Jeremy. Despite the competitive market, her business was booming; everyone loved the clever recipes and thetrendy atmosphere. Between running their fast-growing business and planning for their wedding, Callie hadn’t beenable to keep to her usual eight hours of sleep a night. Although she had always lived a very healthy lifestyle, exercisingdaily and eating healthy, she just hadn’t been feeling herself lately. She was tired all the time, had dif culty breathing,felt stressed, coughed up sputum, consistently ran a low-grade fever, and had lost weight as her appetite decreased.None of these symptoms alone had been particularly alarming so she had put of seeing her physician for a few weeks.Questions1. What are Callie’s symptoms? List all that were mentioned.2. Based on the symptoms presented, what are three possible respiratory infectious diseases Callie…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON