
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
HI I have some problems here. I would like to know the answer to the 3 questions and how you managed to obtain them.
To understand Cartesian representations of vectors and how they can be determined from direction and magnitude; to learn how to represent vectors expressed as a product of the component magnitude and the unit direction vectors i, j, and k; and to learn how to represent a vector component as a function of the angle between the vector and the coordinate axis.
As shown, a pole is subjected to three forces: F, P, and T. The force F expressed in Cartesian vector form is F=[8 i+9 j+6 k] N. Force P has magnitude 8.31 N and acts in the direction given by these direction angles: α=104∘, β=15.7∘, and γ=83.1∘ to the x, y, and z axes, respectively. Force T lies within the yz plane, its direction is given by the 3-4-5 triangle shown, and its magnitude is 16 N.
1) What is the magnitude of F?
2) Determine the components of P in the i, j, and k directions.
3)What are the Cartesian components of force T? (iN, jN, kN)
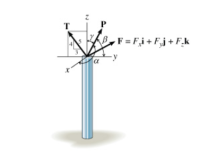
Transcribed Image Text:BF = F,i+ Fj+ F.k
a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please assist with this practice question 9. I don't know where to begin with this. Give details on how to do. Thank you.arrow_forwardMany aspects of a gymnast's motion can be modeled by representing the gymnast by four segments consisting of arms, torso (including the head), thighs, and lower legs, as in the figure below. Thigh O Arm Leg 60° 60° Torso a b In the figure, (b) shows arrows of lengths r, locating the center of gravity of each segment. Use the data below and the cg coordinate system shown in figure (b) to locate the center of gravity of the gymnast shown in figure (a). Masses for the arms, thighs, and legs include both appendages. (Enter your answers in m, to at least three significant figures.) Segment Mass (kg) Length (m) (m) Arms 6.89 0.548 0.242 Torso 33.6 0.613 0.337 Thighs 14.1 0.376 0.145 Legs 7.50 0.350 0.227 HINT m %D m y cg E Earrow_forwardSee image that is attached. Thank you.arrow_forward
- Problem 3: Note: Make sure to draw all diagrams. All Units must be included. Determine the magnitude and coordinate direction angles of the resultant force and sketch this vector on the coordinate system. 3-250 N Problem 2 60 60 45 F-350 Narrow_forwardIn a design, a line is constructed by connecting PO(2,2,2) and P1(6,6,11), and point P2(2,3,13) is defined. If point P2 is rotated about the axis POP1 anti clockwise by 60 degrees. Find the coordinate of the point P2 at the new location and verify your result by using SolidWorks. X Xp Z Z₂ 0 P P₂ Y₁ 5 P₁arrow_forwardI am struggling coming up with the equation to solve this.arrow_forward
- 2.1arrow_forwardThe traffic light shown below is supported by a system of cables. Points A and B are in a vertical plane which is parallel to the x-z plane. Point C is in the y-z plane. B Z X The traffic light has a mass of 75 kg The distances are: a = 4m, b = 6 m, c = 9 m, h = 6 m To answer the next set of questions you will determine the following: a. Position vectors for OA, OB, OC b. Unit vectors for OA, OB, OC c. Overall equilibrium equation d. Equilibrium equations in each of the x, y and z directions e. The tensions in the cables OA, OB and OC The traffic light has a mass of 75 kg. The distances are: a = 4 m, b = 6 m, c = 9 m, h = 6 m. Determine the position vector for OA. The position vector FOA can be written in the form: TOA = TOAzi+TOAİ+TOA-k You will have to input each of these three components separately below. Given: • The x component of the position vector,IOA = 4 m. • They component of the position vector,TOA = -9 m. 1. What is the z component of the position vector,TOA? Please report…arrow_forwardFind the missing coordinate of P, using the fact that P lies on the unit circle in the given quadrant. Coordinates Quadrant P( II -lenarrow_forward
- (a) Suppose you know the coordinates of two points A and B. How do you determine the scalar components of the position vector of point B relative to point A? (b) During the construction of a bridge, a bracket shown in Figure 1 was used to temporarily hold two cables FA and Fg = 600 N. After a while, you noticed that the bracket is shaking and slowly being pulled out of the wall by the cables. Given that e = 20°, find the resultant force and its direction counter clockwise from the positive y axis. FA 700 N 30 A Figure 1arrow_forwardNeed some assistance with this. l = 1.95 mm. w= 1.89 mm. h= 5.82 m. Coordinates for Point A is A(2,2,2)m Coordinates for Point D is D(2.25,2.5,0)m Force F acts along EA, (Magnitude is 55N) Force P acTS along AD 1. What is force F in Cartesian Vector form. (Fx, Fy, Fz) 2. If we are calculating the moment that Force F creates about point B, WHAT vectors will be used ? 3. If we are calculating the moment that Force P creates about point B , WHAT vectors will be used ? 4. What is BC as position vector rBC. ( rBCx, rBCy, rBCz ) 5. What is BC as unit vector uBC. (uBCx, uBCy, uBCz ) 6. What is the moment that F creates around B ? (MB) 7. What is the magnitude of the moment that F creates around axis BC. ( |MBC| )arrow_forwardI need help with parts a,b,c. All three figures are in the corners that align with each problem :)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY