
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
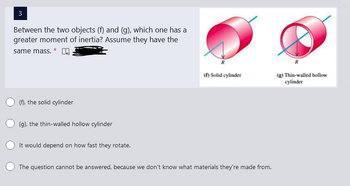
Transcribed Image Text:3
Between the two objects (f) and (g), which one has a
greater moment of inertia? Assume they have the
same mass. *
(f), the solid cylinder
(g), the thin-walled hollow cylinder
It would depend on how fast they rotate.
(f) Solid cylinder
The question cannot be answered, because we don't know what materials they're made from.
R
(g) Thin-walled hollow
cylinder
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 6 kg point mass is at coordinates (9 m, 4 m), a 7 kg mass is at (-6,2) and a 7kg mass is at (x,y) of (9,-2). Find the moment of inertia about the x axis. Ix = kg-m2arrow_forwardThe object shown below is centered on the origin, and has a width of 20 cm in the x direction, 3 cm in the y direction, and 5 cm in the z direction. Around which axis does it have the lowest moment of inertia l?arrow_forwardof Sides a and b has a mass M. Four point-like balls, each of rnass m = each corner of the plate as indicated in the figure. What is the moment of inertia of this object if the axis of M are glued to rotation is through the end of one sidt, like a door, as indicated in the figure by the blue fine? (A) Isoor=M (a² + b²) (B) Isoor= M(a² + b) (C) Idoor M(a² + b*) (D) Isoor = }M(a²+8) (F) Isoor = Ma² %3D (G) Isoor Ma? %3D (H) Idor Ma² A rectangular plate with four umall point-like balls glued to each corner. The blue line represents the axis of rotationarrow_forward
- Three masses, each m = 12 kg, are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle. Calculate the moment of inertia of the system about an axis running through one of the point masses perpendicular to the plane of the triangle. The length of one side of the triangle is 0.94 marrow_forwardThe moment of inertia of the lower leg and foot about an axis through the knee joint is 0.23 kgm^2. What is the moment of inertia of the leg and foot about the knee joint if a 0.82 kg shoe is worn on the foot? Assume that the shoe's mass is all concentrated in one point 40 cm from the knee. (please report to two decimal places)arrow_forwardCalculate the moment of inertia (in kg-m2) of a skater given the following information. (a) The 64.0 kg skater is approximated as a cylinder that has a 0.140 m radius. kg-m? (b) The skater with arms extended is approximately a cylinder that is 58.0 kg, has a 0.140 m radius, and has two 0.950 m long arms which are 3.00 kg each and extend straight out from the cylinder like rods rotated about their ends. kg-m2arrow_forward
- Calculate the moment of inertia of a skater given the following information. (a) The 92.0-kg skater is approximated as a cylinder that has a 0.120-m radius. kg · m2(b) The skater with arms extended is approximately a cylinder that is 86.0 kg, has a 0.120-m radius, and has two 0.850-m-long arms which are 3.00 kg each and extend straight out from the cylinder like rods rotated about their ends.arrow_forwardCalculate the moment of inertia (in kg·m2) of a skater given the following information. (a)The 88.0 kg skater is approximated as a cylinder that has a 0.130 m radius. ____kg·m2 (b)The skater with arms extended is approximately a cylinder that is 82.0 kg, has a 0.130 m radius, and has two 0.750 m long arms which are 3.00 kg each and extend straight out from the cylinder like rods rotated about their ends. _____kg·m2arrow_forwardFind the moment of inertia about y-axis if each mass is equal to 1 kg (in kg×m2)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON